Popular Posts
What Is Token Burning? A Complete Guide
Token burning has become a prominent strategy within the cryptocurrency and blockchain ecosystem. As digital assets continue to evolve, understanding what token burning entails, why it is used, and its potential effects on markets is essential for investors, developers, and enthusiasts alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of token burning, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, risks, recent trends, and regulatory considerations.
Understanding Token Burning in Cryptocurrency
Token burning refers to the process of permanently removing a certain number of tokens from circulation. This is typically achieved by sending tokens to an address that cannot be accessed or spent—often called a "burn address"—effectively making them inaccessible forever. Unlike traditional financial transactions where assets change hands between parties, token burning reduces the total supply available in the market.
The primary motivation behind this practice is to create scarcity. By decreasing the overall supply of a particular cryptocurrency or digital asset, token burns aim to increase demand for remaining tokens—potentially leading to higher prices. It’s comparable in concept to stock buybacks in traditional finance but tailored for decentralized digital economies.
How Does Token Burning Work?
Token burns are usually executed through smart contracts—self-executing code stored on blockchain networks—that automate the destruction process based on predefined conditions. For example:
- Scheduled Burns: Tokens are burned at regular intervals (monthly or quarterly).
- Event-Based Burns: Triggered by specific events such as reaching certain milestones or profit levels.
- Transaction-Based Burns: A percentage of transaction fees collected may be automatically burned.
This automation ensures transparency and trustworthiness since all burn transactions are recorded publicly on blockchain ledgers.
Why Do Projects Burn Tokens?
The main reasons projects implement token burns include:
- Increasing Token Value: By reducing circulating supply, projects hope that remaining tokens will appreciate over time due to increased scarcity.
- Rewarding Holders: Regular burns can incentivize users to hold onto their tokens rather than sell immediately.
- Market Confidence: Demonstrating commitment through periodic burns can signal project confidence and stability.
Additionally, some projects use token burning as part of their broader economic model—for instance, deflationary strategies designed explicitly around reducing supply over time.
Impact on Market Dynamics
Token burning can influence market behavior significantly:
- When large quantities are burned unexpectedly or periodically announced (like Binance's quarterly BNB burn), it often leads traders and investors to anticipate price increases due to reduced supply.
However — while many see it as beneficial — there are risks involved:
- Market Volatility: Sudden reductions in available tokens can cause sharp price swings if traders react strongly.
- Manipulation Concerns: Some critics argue that frequent or large-scale burns could be used manipulatively if not transparently managed.
- Speculative Behavior: Investors might focus more on short-term gains related to burn announcements rather than long-term project fundamentals.
Recent Trends in Token Burning
Over recent years—particularly 2022 and 2023—the adoption of token burning has accelerated among major cryptocurrencies like Binance Coin (BNB) and Solana (SOL). These high-profile moves aim not only at increasing value but also at demonstrating active management strategies that appeal both ethically and economically.
In 2022 especially marked a period where regulators began clarifying guidelines regarding such practices; although not directly regulated themselves—as they involve voluntary actions—they still attract scrutiny under broader anti-money laundering (AML) laws when associated with financial transactions involving fiat conversions or exchanges.
Smart contract innovations have also played an important role here; automated processes make it easier for projects worldwide—from DeFi platforms to NFT ecosystems—to incorporate transparent burn mechanisms into their operations seamlessly.
Risks Associated With Token Burning
Despite its advantages—and growing popularity—token burning carries inherent risks:
Market Volatility: As noted earlier; sudden reductions may lead traders into speculative frenzy causing unpredictable price swings.
Perception Challenges: If investors perceive burns as superficial marketing tactics rather than genuine value-enhancing measures—they might lose confidence altogether.
Regulatory Scrutiny: As authorities scrutinize crypto activities more closely—including practices like coin burns—it’s possible new regulations could impose restrictions or require disclosures that impact how these strategies are implemented legally.
Furthermore—and crucially—it’s important for participants within these ecosystems always consider whether such measures align with long-term project sustainability versus short-term hype cycles.
Notable Examples of Token Burn Strategies
Some prominent examples illustrate how different projects utilize this approach effectively:
Binance Coin (BNB): In 2023 alone—a significant portion of BNB was burned when Binance announced removing approximately one billion coins from circulation during quarterly updates aimed at reducing total supply strategically tied with platform revenues.
Solana (SOL): Solana employs periodic burn events intended partly for stabilizing prices amid volatile trading environments while fostering investor confidence through transparent procedures outlined via smart contracts.
The Future Outlook for Token Burning
As blockchain technology advances—with improvements in smart contract security—and regulatory frameworks become clearer—the practice of token burning is likely poised for further growth but will need careful management regarding transparency and compliance standards.
Investors should remain vigilant about understanding each project's specific approach toward implementing these mechanisms since not all burns have equal impact nor serve equally well-defined economic purposes.
By grasping what token burning entails—from its operational mechanics through strategic motivations—you gain insight into one facet shaping modern cryptocurrency markets today. Whether viewed as an innovative tool fostering scarcity-driven appreciation—or scrutinized under regulatory lenses—the practice continues evolving alongside technological progressions within decentralized finance ecosystems.
Keywords:
cryptocurrency , blockchain , deflationary strategy , smart contracts , market volatility , investor sentiment , crypto regulation


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 12:59
What is token burning?
What Is Token Burning? A Complete Guide
Token burning has become a prominent strategy within the cryptocurrency and blockchain ecosystem. As digital assets continue to evolve, understanding what token burning entails, why it is used, and its potential effects on markets is essential for investors, developers, and enthusiasts alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of token burning, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, risks, recent trends, and regulatory considerations.
Understanding Token Burning in Cryptocurrency
Token burning refers to the process of permanently removing a certain number of tokens from circulation. This is typically achieved by sending tokens to an address that cannot be accessed or spent—often called a "burn address"—effectively making them inaccessible forever. Unlike traditional financial transactions where assets change hands between parties, token burning reduces the total supply available in the market.
The primary motivation behind this practice is to create scarcity. By decreasing the overall supply of a particular cryptocurrency or digital asset, token burns aim to increase demand for remaining tokens—potentially leading to higher prices. It’s comparable in concept to stock buybacks in traditional finance but tailored for decentralized digital economies.
How Does Token Burning Work?
Token burns are usually executed through smart contracts—self-executing code stored on blockchain networks—that automate the destruction process based on predefined conditions. For example:
- Scheduled Burns: Tokens are burned at regular intervals (monthly or quarterly).
- Event-Based Burns: Triggered by specific events such as reaching certain milestones or profit levels.
- Transaction-Based Burns: A percentage of transaction fees collected may be automatically burned.
This automation ensures transparency and trustworthiness since all burn transactions are recorded publicly on blockchain ledgers.
Why Do Projects Burn Tokens?
The main reasons projects implement token burns include:
- Increasing Token Value: By reducing circulating supply, projects hope that remaining tokens will appreciate over time due to increased scarcity.
- Rewarding Holders: Regular burns can incentivize users to hold onto their tokens rather than sell immediately.
- Market Confidence: Demonstrating commitment through periodic burns can signal project confidence and stability.
Additionally, some projects use token burning as part of their broader economic model—for instance, deflationary strategies designed explicitly around reducing supply over time.
Impact on Market Dynamics
Token burning can influence market behavior significantly:
- When large quantities are burned unexpectedly or periodically announced (like Binance's quarterly BNB burn), it often leads traders and investors to anticipate price increases due to reduced supply.
However — while many see it as beneficial — there are risks involved:
- Market Volatility: Sudden reductions in available tokens can cause sharp price swings if traders react strongly.
- Manipulation Concerns: Some critics argue that frequent or large-scale burns could be used manipulatively if not transparently managed.
- Speculative Behavior: Investors might focus more on short-term gains related to burn announcements rather than long-term project fundamentals.
Recent Trends in Token Burning
Over recent years—particularly 2022 and 2023—the adoption of token burning has accelerated among major cryptocurrencies like Binance Coin (BNB) and Solana (SOL). These high-profile moves aim not only at increasing value but also at demonstrating active management strategies that appeal both ethically and economically.
In 2022 especially marked a period where regulators began clarifying guidelines regarding such practices; although not directly regulated themselves—as they involve voluntary actions—they still attract scrutiny under broader anti-money laundering (AML) laws when associated with financial transactions involving fiat conversions or exchanges.
Smart contract innovations have also played an important role here; automated processes make it easier for projects worldwide—from DeFi platforms to NFT ecosystems—to incorporate transparent burn mechanisms into their operations seamlessly.
Risks Associated With Token Burning
Despite its advantages—and growing popularity—token burning carries inherent risks:
Market Volatility: As noted earlier; sudden reductions may lead traders into speculative frenzy causing unpredictable price swings.
Perception Challenges: If investors perceive burns as superficial marketing tactics rather than genuine value-enhancing measures—they might lose confidence altogether.
Regulatory Scrutiny: As authorities scrutinize crypto activities more closely—including practices like coin burns—it’s possible new regulations could impose restrictions or require disclosures that impact how these strategies are implemented legally.
Furthermore—and crucially—it’s important for participants within these ecosystems always consider whether such measures align with long-term project sustainability versus short-term hype cycles.
Notable Examples of Token Burn Strategies
Some prominent examples illustrate how different projects utilize this approach effectively:
Binance Coin (BNB): In 2023 alone—a significant portion of BNB was burned when Binance announced removing approximately one billion coins from circulation during quarterly updates aimed at reducing total supply strategically tied with platform revenues.
Solana (SOL): Solana employs periodic burn events intended partly for stabilizing prices amid volatile trading environments while fostering investor confidence through transparent procedures outlined via smart contracts.
The Future Outlook for Token Burning
As blockchain technology advances—with improvements in smart contract security—and regulatory frameworks become clearer—the practice of token burning is likely poised for further growth but will need careful management regarding transparency and compliance standards.
Investors should remain vigilant about understanding each project's specific approach toward implementing these mechanisms since not all burns have equal impact nor serve equally well-defined economic purposes.
By grasping what token burning entails—from its operational mechanics through strategic motivations—you gain insight into one facet shaping modern cryptocurrency markets today. Whether viewed as an innovative tool fostering scarcity-driven appreciation—or scrutinized under regulatory lenses—the practice continues evolving alongside technological progressions within decentralized finance ecosystems.
Keywords:
cryptocurrency , blockchain , deflationary strategy , smart contracts , market volatility , investor sentiment , crypto regulation
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Transaction Nonce? A Complete Guide
Understanding transaction nonces is essential for anyone involved in blockchain technology or cryptocurrency transactions. This guide provides a clear explanation of what nonces are, their purpose, how they work across different blockchain platforms, recent developments, and potential security implications.
What Is a Transaction Nonce?
A transaction nonce is a unique number assigned to each transaction initiated from an account within a blockchain network. Think of it as a counter that keeps track of the number of transactions sent from your wallet address. Its primary role is to ensure that each transaction remains distinct and prevents malicious actors from replaying old transactions.
In simple terms, every time you send cryptocurrency or interact with smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum or Bitcoin, your wallet increments the nonce value by one. This incremental process guarantees that each transaction has a unique identifier and helps maintain the chronological order of operations on the blockchain.
Why Are Nonces Important in Blockchain Transactions?
The core purpose of using nonces is to prevent replay attacks—an attack where an attacker intercepts valid data transmission and fraudulently repeats it to trick the system into executing duplicate transactions. Without proper nonce management, malicious actors could reuse old signed transactions to illicitly transfer funds multiple times.
By assigning sequential nonces to each transaction:
- Transaction Uniqueness: Ensures no two transactions share the same identifier.
- Order Preservation: Maintains correct sequence when multiple transactions are sent from one address.
- Security Enhancement: Protects against replay attacks by making intercepted data invalid once used.
This mechanism forms part of broader security protocols embedded within various blockchain protocols such as Ethereum's EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) and Bitcoin's UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model.
How Do Different Blockchains Use Nonces?
While the fundamental concept remains consistent across networks—serving as unique identifiers—the implementation details can vary:
Ethereum
In Ethereum's account-based model, each account maintains its own nonce counter. When creating a new transaction:
- The sender’s current nonce value must match the expected value stored in their account.
- After signing and broadcasting this transaction, their nonce increases by one.
This process ensures that all pending transactions are processed sequentially without duplication or reordering issues.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin employs an UTXO model where individual unspent outputs are referenced rather than maintaining per-account counters like in Ethereum. However, within Bitcoin’s Segregated Witness (SegWit) protocol and certain multi-signature setups:
- A sequence number acts similarly but serves more for relative locktime purposes rather than strict uniqueness.
Thus, while not called 'nonces' explicitly in Bitcoin’s core protocol for regular transfers, similar concepts exist within advanced scripting features for ensuring transactional integrity under specific conditions.
Other Protocols
Different blockchains may implement variations suited to their consensus mechanisms—Proof-of-Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), etc.—but generally adhere to principles ensuring transactional uniqueness and order through some form of counters or sequence numbers akin to nonces.
Recent Developments Related To Transaction Nonces
Blockchain technology continues evolving rapidly; recent updates have refined how nonces are managed:
Ethereum's EIP-1559 Implementation
In August 2021, Ethereum introduced EIP-1559—a significant upgrade aimed at improving fee estimation accuracy and network efficiency. While primarily focused on fee structure adjustments via base fees burning mechanism,
this update also impacted how nonces are handled indirectly by reducing network congestion caused by inefficient fee bidding strategies. As users experience fewer failed or stuck transactions due to improper nonce management during high traffic periods,
the overall reliability improves significantly.
Scalability Solutions & Research Efforts
As blockchains scale up with higher throughput demands—such as Layer 2 solutions like rollups—the management of nonces becomes more complex yet critical for maintaining security without sacrificing performance. Researchers explore cryptographic techniques such as zk-SNARKs/zk-STARKs,
which can help validate large batches of off-chain activities while preserving accurate on-chain state including correct nonce sequencing.
Smart Contract Security & Best Practices
Smart contracts often rely heavily on proper handling of nonces—for example,
to prevent double-spending vulnerabilities or reentrancy attacks where malicious code exploits incorrect state updates related to counters like nonces.
Risks Associated With Poor Nonce Management
Mismanaging or neglecting proper nonce handling can lead directly into serious security issues:
Replay Attacks – If an attacker captures valid signed transactions with outdated/non-incremented/non-updated nonces,they might resend them causing unintended repeated transfers unless safeguards exist.
Network Congestion & Delays – When multiple pending transactions share identical or conflicting nonce values,the network may become congested trying to resolve which should be processed first,leading potentially to delays or failed payments.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities – Incorrect implementation involving manual handling of counters inside smart contracts can open doors for exploits resulting in financial loss.
Best Practices For Managing Transaction Nonce
To ensure smooth operation within blockchain environments:
Always check your current account’s latestnonce before initiating new transfers– Most wallets automatically handle this but verify if manual control is needed during batch operations.
Avoid reusing old/non-incrementednoncesto prevent replay risks
– Use reliable tools that synchronize your local state with network status
- Be aware when dealingwith high-frequencytransactionsor interactingwith complex smart contracts requiring precisenonce sequencing
How To View Your Account’s Current Nonce?
Most cryptocurrency wallets provide straightforward ways:
In MetaMaskor MyEtherWallet,you can view pendingtransactionsand currentnoncevalues directly
Blockchain explorerslike Etherscanallow youto inputyour walletaddressand seeall associatedtransactionsalongwiththeirnoncesequence numbers
Regularly monitoring these values helps avoid accidental double-spendsor stucktransactions due tononce conflicts.
Understanding Transaction Nonce Is Key To Secure Blockchain Usage
Transaction nonceso play an indispensable role in safeguarding digital assets across various blockchain networks—from preventing replay attacksto maintaining orderly processingof numerous concurrent operations.By understanding how they functionand stay updatedon recent innovations,you enhance bothyour security postureand operational efficiencyin this rapidly evolving space.Having sound knowledge about managingnoncesequencing ensures smoother interactions whether you're sending cryptocurrencies,signing smartcontracts,and participatingin decentralized applications( dApps).


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 12:46
What is a transaction nonce?
What Is a Transaction Nonce? A Complete Guide
Understanding transaction nonces is essential for anyone involved in blockchain technology or cryptocurrency transactions. This guide provides a clear explanation of what nonces are, their purpose, how they work across different blockchain platforms, recent developments, and potential security implications.
What Is a Transaction Nonce?
A transaction nonce is a unique number assigned to each transaction initiated from an account within a blockchain network. Think of it as a counter that keeps track of the number of transactions sent from your wallet address. Its primary role is to ensure that each transaction remains distinct and prevents malicious actors from replaying old transactions.
In simple terms, every time you send cryptocurrency or interact with smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum or Bitcoin, your wallet increments the nonce value by one. This incremental process guarantees that each transaction has a unique identifier and helps maintain the chronological order of operations on the blockchain.
Why Are Nonces Important in Blockchain Transactions?
The core purpose of using nonces is to prevent replay attacks—an attack where an attacker intercepts valid data transmission and fraudulently repeats it to trick the system into executing duplicate transactions. Without proper nonce management, malicious actors could reuse old signed transactions to illicitly transfer funds multiple times.
By assigning sequential nonces to each transaction:
- Transaction Uniqueness: Ensures no two transactions share the same identifier.
- Order Preservation: Maintains correct sequence when multiple transactions are sent from one address.
- Security Enhancement: Protects against replay attacks by making intercepted data invalid once used.
This mechanism forms part of broader security protocols embedded within various blockchain protocols such as Ethereum's EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) and Bitcoin's UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model.
How Do Different Blockchains Use Nonces?
While the fundamental concept remains consistent across networks—serving as unique identifiers—the implementation details can vary:
Ethereum
In Ethereum's account-based model, each account maintains its own nonce counter. When creating a new transaction:
- The sender’s current nonce value must match the expected value stored in their account.
- After signing and broadcasting this transaction, their nonce increases by one.
This process ensures that all pending transactions are processed sequentially without duplication or reordering issues.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin employs an UTXO model where individual unspent outputs are referenced rather than maintaining per-account counters like in Ethereum. However, within Bitcoin’s Segregated Witness (SegWit) protocol and certain multi-signature setups:
- A sequence number acts similarly but serves more for relative locktime purposes rather than strict uniqueness.
Thus, while not called 'nonces' explicitly in Bitcoin’s core protocol for regular transfers, similar concepts exist within advanced scripting features for ensuring transactional integrity under specific conditions.
Other Protocols
Different blockchains may implement variations suited to their consensus mechanisms—Proof-of-Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), etc.—but generally adhere to principles ensuring transactional uniqueness and order through some form of counters or sequence numbers akin to nonces.
Recent Developments Related To Transaction Nonces
Blockchain technology continues evolving rapidly; recent updates have refined how nonces are managed:
Ethereum's EIP-1559 Implementation
In August 2021, Ethereum introduced EIP-1559—a significant upgrade aimed at improving fee estimation accuracy and network efficiency. While primarily focused on fee structure adjustments via base fees burning mechanism,
this update also impacted how nonces are handled indirectly by reducing network congestion caused by inefficient fee bidding strategies. As users experience fewer failed or stuck transactions due to improper nonce management during high traffic periods,
the overall reliability improves significantly.
Scalability Solutions & Research Efforts
As blockchains scale up with higher throughput demands—such as Layer 2 solutions like rollups—the management of nonces becomes more complex yet critical for maintaining security without sacrificing performance. Researchers explore cryptographic techniques such as zk-SNARKs/zk-STARKs,
which can help validate large batches of off-chain activities while preserving accurate on-chain state including correct nonce sequencing.
Smart Contract Security & Best Practices
Smart contracts often rely heavily on proper handling of nonces—for example,
to prevent double-spending vulnerabilities or reentrancy attacks where malicious code exploits incorrect state updates related to counters like nonces.
Risks Associated With Poor Nonce Management
Mismanaging or neglecting proper nonce handling can lead directly into serious security issues:
Replay Attacks – If an attacker captures valid signed transactions with outdated/non-incremented/non-updated nonces,they might resend them causing unintended repeated transfers unless safeguards exist.
Network Congestion & Delays – When multiple pending transactions share identical or conflicting nonce values,the network may become congested trying to resolve which should be processed first,leading potentially to delays or failed payments.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities – Incorrect implementation involving manual handling of counters inside smart contracts can open doors for exploits resulting in financial loss.
Best Practices For Managing Transaction Nonce
To ensure smooth operation within blockchain environments:
Always check your current account’s latestnonce before initiating new transfers– Most wallets automatically handle this but verify if manual control is needed during batch operations.
Avoid reusing old/non-incrementednoncesto prevent replay risks
– Use reliable tools that synchronize your local state with network status
- Be aware when dealingwith high-frequencytransactionsor interactingwith complex smart contracts requiring precisenonce sequencing
How To View Your Account’s Current Nonce?
Most cryptocurrency wallets provide straightforward ways:
In MetaMaskor MyEtherWallet,you can view pendingtransactionsand currentnoncevalues directly
Blockchain explorerslike Etherscanallow youto inputyour walletaddressand seeall associatedtransactionsalongwiththeirnoncesequence numbers
Regularly monitoring these values helps avoid accidental double-spendsor stucktransactions due tononce conflicts.
Understanding Transaction Nonce Is Key To Secure Blockchain Usage
Transaction nonceso play an indispensable role in safeguarding digital assets across various blockchain networks—from preventing replay attacksto maintaining orderly processingof numerous concurrent operations.By understanding how they functionand stay updatedon recent innovations,you enhance bothyour security postureand operational efficiencyin this rapidly evolving space.Having sound knowledge about managingnoncesequencing ensures smoother interactions whether you're sending cryptocurrencies,signing smartcontracts,and participatingin decentralized applications( dApps).
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Session Separators Work on TradingView?
Understanding how session separators function on TradingView is essential for traders aiming to refine their market analysis and improve trading strategies. These tools are designed to segment the trading day into distinct periods, allowing users to focus on specific times when market behavior tends to differ. By leveraging session separators, traders can identify patterns such as increased volatility or low liquidity phases, which are crucial for making informed decisions.
What Are Session Separators in TradingView?
Session separators are visual tools integrated into TradingView's charting platform that divide a trading day into predefined or custom time segments. They typically appear as vertical lines or shaded regions across the chart, marking the start and end of each session. These divisions help traders distinguish between different parts of the trading day—such as morning, mid-day, and afternoon sessions—and analyze how price action varies during these periods.
The primary goal of session separators is to facilitate a more granular analysis of market movements by isolating specific time frames. For example, a trader might notice that certain currency pairs exhibit high volatility during the London open but tend to stabilize later in the afternoon. Recognizing these patterns allows traders to tailor their strategies accordingly.
How Do Session Separators Function in Practice?
On TradingView, setting up session separators involves selecting or customizing time intervals that align with your trading hours or market activity patterns. Once configured, these separators visually segment your chart without altering underlying data—meaning they serve purely as analytical guides rather than affecting trade execution directly.
Traders can customize start and end times for each session based on their preferred markets (e.g., forex sessions like London or New York) or personal schedules. This flexibility ensures that analysis remains relevant regardless of whether you trade stocks during U.S hours or cryptocurrencies 24/7.
Moreover, session separators can be combined with other technical tools such as indicators (like RSI or MACD), alerts (to notify when price enters a particular session), and overlays (like volume profiles). This integration enhances strategic planning by enabling context-specific analysis—for instance, applying different indicator settings during high-volatility sessions versus quieter periods.
Customization Options for Session Separators
One key feature that makes TradingView’s session separator tool valuable is its customization capability:
- Start and End Times: Users can define exact times for each segment based on their target markets.
- Multiple Sessions: It’s possible to set up several sessions within a single day—for example, separating Asian markets from European ones.
- Color Coding: Different colors can be assigned to various sessions for quick visual identification.
- Recurring Settings: Traders often save templates so they don’t need reconfigure settings daily; this streamlines ongoing analysis efforts.
This level of customization ensures traders aren’t limited by default configurations but instead craft an environment tailored precisely to their analytical needs.
Benefits of Using Session Separators
Implementing session separators offers multiple advantages:
Enhanced Market Context Understanding: By observing how prices behave differently across sessions—such as spikes at opening bells—traders gain deeper insights into potential entry and exit points.
Strategy Optimization: Certain strategies perform better during specific periods; recognizing these windows helps optimize timing.
Risk Management Improvement: Knowing when volatile periods occur allows traders to adjust position sizes accordingly or tighten stop-loss levels.
Pattern Recognition: Repeatedly analyzing segmented data helps identify recurring behaviors tied specifically to certain times of day.
These benefits collectively contribute toward more disciplined decision-making grounded in temporal market dynamics rather than generic assumptions about price movements.
Integration With Other Tools & Strategies
TradingView’s platform supports seamless integration between session separators and other analytical features:
- Indicators & Overlays: Applying indicators like Bollinger Bands within specific sessions reveals if volatility expands at particular times.
- Alerts: Setting alerts based on time segments enables proactive responses—for example, notifying you when price reaches support levels during high-volume hours.
- Backtesting: Traders can backtest strategies within individual sessions separately from overall daily data — helping refine tactics suited explicitly for those periods.
- Multi-Timeframe Analysis: Combining shorter-term charts with longer-term views alongside segmented days provides comprehensive insights into trend strength versus short-term fluctuations tied closely with timing factors.
This synergy enhances strategic flexibility while maintaining focus on temporal nuances influencing asset prices.
Practical Tips for Using Session Separators Effectively
To maximize benefits from this feature:
Start by aligning your custom sessions with major market openings relevant to your traded assets (e.g., New York Open if you trade US stocks).
Use color coding consistently across charts so you quickly recognize active vs inactive periods at a glance.
Combine with volume profile tools within each segment; higher volume often correlates with increased movement opportunities.
Regularly review past performance metrics segmented by time frames—they reveal which parts of the day yield better results under current conditions.
By systematically incorporating these practices into your routine, you'll develop sharper awareness around intra-day dynamics critical for successful trading outcomes.
Why Are Session Separators Important For Traders?
In today’s fast-paced financial markets—which include stocks, forex pairs, cryptocurrencies—and evolving global economic conditions understanding intra-day variations becomes vital. The introduction of customizable session separators addresses this need directly by providing clarity over complex data sets through simple visual cues aligned precisely with user-defined timings.
Final Thoughts
Tradingview's implementation of customizable session separators empowers traders through enhanced visibility into daily market rhythms—a crucial aspect often overlooked in generic analyses focused solely on price charts alone. Whether you're seeking improved timing accuracy in entries/exits or aiming at refining strategy performance according to different active phases throughout the day—the ability now exists within an intuitive interface designed specifically around trader needs.
By integrating this tool thoughtfully alongside existing technical setups—including indicators and alert systems—you'll gain deeper insights rooted firmly in real-time behavioral patterns associated with distinct trading hours—ultimately leading toward more disciplined decision-making grounded in robust analytical frameworks tailored uniquely per asset class and personal strategy preferences.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-26 20:30
How do session separators work on TradingView?
How Do Session Separators Work on TradingView?
Understanding how session separators function on TradingView is essential for traders aiming to refine their market analysis and improve trading strategies. These tools are designed to segment the trading day into distinct periods, allowing users to focus on specific times when market behavior tends to differ. By leveraging session separators, traders can identify patterns such as increased volatility or low liquidity phases, which are crucial for making informed decisions.
What Are Session Separators in TradingView?
Session separators are visual tools integrated into TradingView's charting platform that divide a trading day into predefined or custom time segments. They typically appear as vertical lines or shaded regions across the chart, marking the start and end of each session. These divisions help traders distinguish between different parts of the trading day—such as morning, mid-day, and afternoon sessions—and analyze how price action varies during these periods.
The primary goal of session separators is to facilitate a more granular analysis of market movements by isolating specific time frames. For example, a trader might notice that certain currency pairs exhibit high volatility during the London open but tend to stabilize later in the afternoon. Recognizing these patterns allows traders to tailor their strategies accordingly.
How Do Session Separators Function in Practice?
On TradingView, setting up session separators involves selecting or customizing time intervals that align with your trading hours or market activity patterns. Once configured, these separators visually segment your chart without altering underlying data—meaning they serve purely as analytical guides rather than affecting trade execution directly.
Traders can customize start and end times for each session based on their preferred markets (e.g., forex sessions like London or New York) or personal schedules. This flexibility ensures that analysis remains relevant regardless of whether you trade stocks during U.S hours or cryptocurrencies 24/7.
Moreover, session separators can be combined with other technical tools such as indicators (like RSI or MACD), alerts (to notify when price enters a particular session), and overlays (like volume profiles). This integration enhances strategic planning by enabling context-specific analysis—for instance, applying different indicator settings during high-volatility sessions versus quieter periods.
Customization Options for Session Separators
One key feature that makes TradingView’s session separator tool valuable is its customization capability:
- Start and End Times: Users can define exact times for each segment based on their target markets.
- Multiple Sessions: It’s possible to set up several sessions within a single day—for example, separating Asian markets from European ones.
- Color Coding: Different colors can be assigned to various sessions for quick visual identification.
- Recurring Settings: Traders often save templates so they don’t need reconfigure settings daily; this streamlines ongoing analysis efforts.
This level of customization ensures traders aren’t limited by default configurations but instead craft an environment tailored precisely to their analytical needs.
Benefits of Using Session Separators
Implementing session separators offers multiple advantages:
Enhanced Market Context Understanding: By observing how prices behave differently across sessions—such as spikes at opening bells—traders gain deeper insights into potential entry and exit points.
Strategy Optimization: Certain strategies perform better during specific periods; recognizing these windows helps optimize timing.
Risk Management Improvement: Knowing when volatile periods occur allows traders to adjust position sizes accordingly or tighten stop-loss levels.
Pattern Recognition: Repeatedly analyzing segmented data helps identify recurring behaviors tied specifically to certain times of day.
These benefits collectively contribute toward more disciplined decision-making grounded in temporal market dynamics rather than generic assumptions about price movements.
Integration With Other Tools & Strategies
TradingView’s platform supports seamless integration between session separators and other analytical features:
- Indicators & Overlays: Applying indicators like Bollinger Bands within specific sessions reveals if volatility expands at particular times.
- Alerts: Setting alerts based on time segments enables proactive responses—for example, notifying you when price reaches support levels during high-volume hours.
- Backtesting: Traders can backtest strategies within individual sessions separately from overall daily data — helping refine tactics suited explicitly for those periods.
- Multi-Timeframe Analysis: Combining shorter-term charts with longer-term views alongside segmented days provides comprehensive insights into trend strength versus short-term fluctuations tied closely with timing factors.
This synergy enhances strategic flexibility while maintaining focus on temporal nuances influencing asset prices.
Practical Tips for Using Session Separators Effectively
To maximize benefits from this feature:
Start by aligning your custom sessions with major market openings relevant to your traded assets (e.g., New York Open if you trade US stocks).
Use color coding consistently across charts so you quickly recognize active vs inactive periods at a glance.
Combine with volume profile tools within each segment; higher volume often correlates with increased movement opportunities.
Regularly review past performance metrics segmented by time frames—they reveal which parts of the day yield better results under current conditions.
By systematically incorporating these practices into your routine, you'll develop sharper awareness around intra-day dynamics critical for successful trading outcomes.
Why Are Session Separators Important For Traders?
In today’s fast-paced financial markets—which include stocks, forex pairs, cryptocurrencies—and evolving global economic conditions understanding intra-day variations becomes vital. The introduction of customizable session separators addresses this need directly by providing clarity over complex data sets through simple visual cues aligned precisely with user-defined timings.
Final Thoughts
Tradingview's implementation of customizable session separators empowers traders through enhanced visibility into daily market rhythms—a crucial aspect often overlooked in generic analyses focused solely on price charts alone. Whether you're seeking improved timing accuracy in entries/exits or aiming at refining strategy performance according to different active phases throughout the day—the ability now exists within an intuitive interface designed specifically around trader needs.
By integrating this tool thoughtfully alongside existing technical setups—including indicators and alert systems—you'll gain deeper insights rooted firmly in real-time behavioral patterns associated with distinct trading hours—ultimately leading toward more disciplined decision-making grounded in robust analytical frameworks tailored uniquely per asset class and personal strategy preferences.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Data Analysis Methods Have Evolved with Computing Advances Since the 1980s
Understanding how data analysis has transformed over the decades reveals much about the rapid pace of technological innovation and its impact on industries, research, and everyday decision-making. From manual calculations to sophisticated AI-driven models, each era reflects a response to advancements in computing power, storage capacity, and algorithm development. This evolution not only enhances our ability to interpret complex datasets but also raises important considerations around ethics, privacy, and security.
The State of Data Analysis in the 1980s
During the 1980s, data analysis was largely a manual process that relied heavily on statistical techniques. At this time, tools like Lotus 1-2-3 and early versions of Microsoft Excel revolutionized basic data manipulation by providing accessible spreadsheet environments. These tools enabled analysts to perform simple calculations and generate basic charts but were limited in handling large datasets or complex analyses.
Data processing was often labor-intensive; statisticians manually coded formulas or used paper-based methods for more advanced computations. The focus was primarily on descriptive statistics—mean values, standard deviations—and simple inferential tests such as t-tests or chi-square analyses. Despite these limitations, this period laid foundational skills for future developments.
The Impact of Early Computing: 1990s-2000s
The advent of personal computers during the 1990s marked a significant turning point for data analysis practices. Software like SAS (Statistical Analysis System) and SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) gained popularity among researchers and businesses alike because they offered more robust statistical capabilities than earlier spreadsheets.
Simultaneously, database management systems such as Oracle Database and Microsoft SQL Server emerged as essential infrastructure components for storing vast amounts of structured data efficiently. These systems allowed organizations to retrieve information quickly from large datasets—a critical feature that supported growing business intelligence needs.
Data visualization also saw early innovations with tools like Tableau (founded in 2003) beginning to make complex data insights more accessible through graphical representations. Although these visualizations were less sophisticated than today’s interactive dashboards or real-time analytics platforms, they marked an important step toward making data insights understandable at a glance.
Rise of Big Data: Early 2000s-2010s
The explosion of digital information characterized this era—social media platforms, e-commerce transactions, sensor networks—all contributed to what is now called "big data." Handling such enormous volumes required new approaches beyond traditional relational databases.
Apache Hadoop emerged as an open-source framework capable of distributed storage and processing across clusters of commodity hardware. Its MapReduce programming model allowed analysts to process petabytes worth of unstructured or semi-structured data efficiently—a game-changer compared to previous methods reliant on centralized servers.
Alongside Hadoop’s rise came NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Cassandra designed specifically for flexible schema management suited for big datasets that did not fit neatly into tables. Cloud computing services from Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and others provided scalable infrastructure without heavy upfront investments—making advanced analytics accessible even for smaller organizations.
During this period too saw the integration of machine learning algorithms into mainstream workflows with languages like R becoming popular among statisticians while Python gained traction due to its simplicity combined with powerful libraries such as scikit-learn.
Recent Breakthroughs: Deep Learning & AI Integration
Since around 2010 onwards—and especially over recent years—the field has experienced exponential growth driven by breakthroughs in deep learning architectures like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs). These models excel at recognizing patterns within images, speech signals—or even text—leading to applications ranging from facial recognition systems to natural language processing tasks such as chatbots or sentiment analysis.
Artificial Intelligence has become deeply embedded within modern analytics ecosystems; predictive modeling now incorporates AI-driven algorithms capable not just of identifying trends but also adapting dynamically based on new incoming information—a process known as online learning or continuous training.
Platforms such as TensorFlow by Google or PyTorch by Facebook have democratized access to deep learning frameworks enabling researchers worldwide—including those outside traditional tech hubs—to innovate rapidly within their domains while cloud services facilitate scalable deployment at enterprise levels via APIs or managed services like AWS SageMaker or GCP AI Platform.
Furthermore, edge computing has gained prominence—processing real-time IoT sensor streams locally rather than transmitting all raw data back centrally—which reduces latency significantly crucial in applications requiring immediate responses such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation systems.
Emerging Trends Shaping Future Data Analysis
As we look ahead at ongoing developments:
Data Privacy & Ethics: Regulations like GDPR enforce stricter controls over personal information use; ethical AI practices are increasingly emphasized.
Cybersecurity: With rising reliance on cloud infrastructure comes heightened risk; securing sensitive datasets against cyber threats remains paramount.
Quantum Computing: Although still nascent commercially—for example IBM Quantum Experience—it promises revolutionary speedups in solving certain classes of problems related directly to optimization tasks common in machine learning.
These trends underscore both opportunities—for faster insights—and challenges—in ensuring responsible use amid growing complexity.
Summary: From Manual Calculations To Intelligent Systems
The journey from basic spreadsheets used during the 1980s through today's sophisticated AI-powered analytics illustrates how advances in computing technology have expanded our capacity—not just quantitatively but qualitatively—to analyze vast amounts of diverse data types effectively. Each technological leap has opened new possibilities—from automating routine statistical tests early on—to enabling predictive models that inform strategic decisions across industries today.
Key Takeaways:
- Early days involved manual calculations, limited by computational power.
- Introduction of specialized software improved efficiency during the late '80s/early '90s.
- Big Data technologies revolutionized handling massive unstructured datasets starting mid-2000s.
- Machine Learning & Deep Learning have transformed predictive capabilities since the last decade.
- Ongoing concerns include privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA) alongside emerging fields (quantum computing) promising further breakthroughs.
By understanding this evolution—from humble beginnings rooted in statistics towards intelligent automation—we can better appreciate current challenges while preparing ourselves for future innovations shaping how we analyze—and act upon—the world’s ever-growing sea of digital information.
This article aims at providing clarity about how technological progress influences analytical methodologies. For professionals seeking practical insights into implementing modern techniques responsibly—with attention paid toward ethical standards—it offers both historical context and forward-looking perspectives aligned with current industry trends.*


kai
2025-05-19 10:10
How have analysis methods evolved with computing advances since the 1980s?
How Data Analysis Methods Have Evolved with Computing Advances Since the 1980s
Understanding how data analysis has transformed over the decades reveals much about the rapid pace of technological innovation and its impact on industries, research, and everyday decision-making. From manual calculations to sophisticated AI-driven models, each era reflects a response to advancements in computing power, storage capacity, and algorithm development. This evolution not only enhances our ability to interpret complex datasets but also raises important considerations around ethics, privacy, and security.
The State of Data Analysis in the 1980s
During the 1980s, data analysis was largely a manual process that relied heavily on statistical techniques. At this time, tools like Lotus 1-2-3 and early versions of Microsoft Excel revolutionized basic data manipulation by providing accessible spreadsheet environments. These tools enabled analysts to perform simple calculations and generate basic charts but were limited in handling large datasets or complex analyses.
Data processing was often labor-intensive; statisticians manually coded formulas or used paper-based methods for more advanced computations. The focus was primarily on descriptive statistics—mean values, standard deviations—and simple inferential tests such as t-tests or chi-square analyses. Despite these limitations, this period laid foundational skills for future developments.
The Impact of Early Computing: 1990s-2000s
The advent of personal computers during the 1990s marked a significant turning point for data analysis practices. Software like SAS (Statistical Analysis System) and SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) gained popularity among researchers and businesses alike because they offered more robust statistical capabilities than earlier spreadsheets.
Simultaneously, database management systems such as Oracle Database and Microsoft SQL Server emerged as essential infrastructure components for storing vast amounts of structured data efficiently. These systems allowed organizations to retrieve information quickly from large datasets—a critical feature that supported growing business intelligence needs.
Data visualization also saw early innovations with tools like Tableau (founded in 2003) beginning to make complex data insights more accessible through graphical representations. Although these visualizations were less sophisticated than today’s interactive dashboards or real-time analytics platforms, they marked an important step toward making data insights understandable at a glance.
Rise of Big Data: Early 2000s-2010s
The explosion of digital information characterized this era—social media platforms, e-commerce transactions, sensor networks—all contributed to what is now called "big data." Handling such enormous volumes required new approaches beyond traditional relational databases.
Apache Hadoop emerged as an open-source framework capable of distributed storage and processing across clusters of commodity hardware. Its MapReduce programming model allowed analysts to process petabytes worth of unstructured or semi-structured data efficiently—a game-changer compared to previous methods reliant on centralized servers.
Alongside Hadoop’s rise came NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Cassandra designed specifically for flexible schema management suited for big datasets that did not fit neatly into tables. Cloud computing services from Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and others provided scalable infrastructure without heavy upfront investments—making advanced analytics accessible even for smaller organizations.
During this period too saw the integration of machine learning algorithms into mainstream workflows with languages like R becoming popular among statisticians while Python gained traction due to its simplicity combined with powerful libraries such as scikit-learn.
Recent Breakthroughs: Deep Learning & AI Integration
Since around 2010 onwards—and especially over recent years—the field has experienced exponential growth driven by breakthroughs in deep learning architectures like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs). These models excel at recognizing patterns within images, speech signals—or even text—leading to applications ranging from facial recognition systems to natural language processing tasks such as chatbots or sentiment analysis.
Artificial Intelligence has become deeply embedded within modern analytics ecosystems; predictive modeling now incorporates AI-driven algorithms capable not just of identifying trends but also adapting dynamically based on new incoming information—a process known as online learning or continuous training.
Platforms such as TensorFlow by Google or PyTorch by Facebook have democratized access to deep learning frameworks enabling researchers worldwide—including those outside traditional tech hubs—to innovate rapidly within their domains while cloud services facilitate scalable deployment at enterprise levels via APIs or managed services like AWS SageMaker or GCP AI Platform.
Furthermore, edge computing has gained prominence—processing real-time IoT sensor streams locally rather than transmitting all raw data back centrally—which reduces latency significantly crucial in applications requiring immediate responses such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation systems.
Emerging Trends Shaping Future Data Analysis
As we look ahead at ongoing developments:
Data Privacy & Ethics: Regulations like GDPR enforce stricter controls over personal information use; ethical AI practices are increasingly emphasized.
Cybersecurity: With rising reliance on cloud infrastructure comes heightened risk; securing sensitive datasets against cyber threats remains paramount.
Quantum Computing: Although still nascent commercially—for example IBM Quantum Experience—it promises revolutionary speedups in solving certain classes of problems related directly to optimization tasks common in machine learning.
These trends underscore both opportunities—for faster insights—and challenges—in ensuring responsible use amid growing complexity.
Summary: From Manual Calculations To Intelligent Systems
The journey from basic spreadsheets used during the 1980s through today's sophisticated AI-powered analytics illustrates how advances in computing technology have expanded our capacity—not just quantitatively but qualitatively—to analyze vast amounts of diverse data types effectively. Each technological leap has opened new possibilities—from automating routine statistical tests early on—to enabling predictive models that inform strategic decisions across industries today.
Key Takeaways:
- Early days involved manual calculations, limited by computational power.
- Introduction of specialized software improved efficiency during the late '80s/early '90s.
- Big Data technologies revolutionized handling massive unstructured datasets starting mid-2000s.
- Machine Learning & Deep Learning have transformed predictive capabilities since the last decade.
- Ongoing concerns include privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA) alongside emerging fields (quantum computing) promising further breakthroughs.
By understanding this evolution—from humble beginnings rooted in statistics towards intelligent automation—we can better appreciate current challenges while preparing ourselves for future innovations shaping how we analyze—and act upon—the world’s ever-growing sea of digital information.
This article aims at providing clarity about how technological progress influences analytical methodologies. For professionals seeking practical insights into implementing modern techniques responsibly—with attention paid toward ethical standards—it offers both historical context and forward-looking perspectives aligned with current industry trends.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Commodity Inventory Data Chart?
A commodity inventory data chart is a visual tool that displays the current stock levels and historical trends of various commodities. These charts are essential for understanding how much of a particular raw material, agricultural product, or metal is stored at any given time. They serve as vital indicators for businesses, investors, and policymakers to assess supply conditions and forecast future market movements.
Typically presented as line graphs, bar charts, or heat maps, these visualizations help users quickly interpret complex data sets. For example, a chart showing wheat inventories over several months can reveal seasonal patterns or sudden changes due to weather events or policy shifts. By providing real-time insights into stock levels across different storage locations—such as warehouses or silos—these charts enable more informed decision-making in supply chain management and investment strategies.
Why Are Commodity Inventory Data Charts Important?
Understanding the significance of commodity inventory data charts begins with recognizing their role in supply chain efficiency and market stability. These charts provide transparency about the availability of key resources that underpin industries like agriculture, manufacturing, energy production, and finance.
For companies involved in production processes, knowing current inventory levels helps prevent disruptions caused by shortages or excess stock. For investors and traders in commodity markets, these visuals offer clues about potential price movements; rising inventories might signal oversupply leading to price drops while declining stocks could indicate tightening supplies pushing prices higher.
Moreover, policymakers rely on this data to monitor national reserves and develop strategic stockpiles during crises such as food shortages or energy crises. Overall, accurate commodity inventory data charts support risk mitigation by offering timely insights into global supply-demand dynamics.
Types of Commodities Tracked Using Inventory Charts
Commodity inventory data charts encompass a broad spectrum of products across various sectors:
- Agricultural Products: Grains like wheat and corn; coffee beans; soybeans.
- Metals: Gold; copper; silver.
- Energy Resources: Crude oil; natural gas; coal.
- Raw Materials: Lumber; rubber.
Each type has unique factors influencing its storage levels—seasonality for crops or geopolitical issues affecting oil supplies—that are reflected visually through these charts. Tracking multiple commodities simultaneously can also reveal correlations—for instance: how crude oil inventories impact gasoline prices.
Sources of Commodity Inventory Data
Reliable data sources are crucial for constructing accurate commodity inventory graphs:
- Storage Facilities & Warehouses: Direct reports from companies managing physical stocks provide real-time figures.
- Market Exchanges & Reports: Major trading platforms like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) publish weekly reports on futures inventories which influence market perceptions.
- Government Agencies: Organizations such as USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) track agricultural stocks globally while agencies like EIA (Energy Information Administration) monitor energy reserves.
These sources ensure transparency but may differ slightly due to reporting delays or methodological differences. Combining multiple datasets enhances accuracy when analyzing trends over time.
Tools Used to Create & Analyze Commodity Inventory Charts
Creating insightful commodity inventory visuals involves leveraging specialized tools:
- Spreadsheet Software (Excel): Widely used for basic charting capabilities with manual updates.
- Data Visualization Platforms (Tableau / Power BI): Offer advanced features like interactive dashboards that facilitate deeper analysis.
- Inventory Management Software: Designed specifically for tracking physical stocks within organizations—integrating real-time sensor inputs via IoT devices enhances accuracy further.
The choice depends on user needs—from simple trend analysis to complex predictive modeling—and technological infrastructure available within organizations.
How Market Analysts Use These Charts
Market analysts interpret trends from commodity inventory data charts to predict future price movements:
- Identifying Surpluses: A sharp increase in inventories often indicates oversupply which can lead to falling prices unless demand rises correspondingly.
- Spotting Shortages: Declining stocks suggest tightening supplies possibly driving prices upward if demand remains steady.
- Recognizing Seasonal Patterns: Agricultural commodities often show predictable cycles aligned with planting/harvesting seasons captured visually through these graphs.
By combining this information with other economic indicators such as global trade flows or currency fluctuations—they craft comprehensive forecasts that guide trading strategies and policy decisions.
Recent Trends Shaping Commodity Inventory Analysis
Technological innovations have transformed how we collect and analyze this critical data:
- Digital Technologies & IoT Sensors – Real-time tracking via connected devices improves accuracy dramatically compared to traditional manual reporting methods.
- Blockchain Technology – Enhances transparency by securely recording transactions related to storage movements across global supply chains—aiding verification processes during audits or disputes.
- Impact of Global Events – The COVID-19 pandemic underscored vulnerabilities in international logistics networks leading firms worldwide toward maintaining higher buffer stocks amid uncertainties—a trend reflected clearly on recent inventory charts.
Furthermore, increased digital engagement has empowered individual investors through online platforms offering instant access to live warehouse reports alongside analytical tools—broadening participation beyond institutional players alone.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Commodity Inventories
Despite their usefulness, reliance on accurate inventory data comes with challenges:
Inaccurate Reporting: Delays or errors can mislead stakeholders about actual supply conditions resulting in poor decision-making either through unnecessary panic selling/buying—or missed opportunities altogether.*
Market Volatility: Sudden shifts indicated by abrupt changes in inventories may trigger rapid price swings affecting broader financial markets.*
Environmental Concerns: Excessive stockpiling might reflect inefficiencies contributing negatively toward sustainability goals—for example: overproduction leading land degradation.*
Regulatory Changes: Governments imposing new standards around environmental compliance could restrict storage practices impacting overall availability metrics displayed visually via these graphs.
How Understanding Commodity Inventory Data Shapes Business Strategy
For businesses operating within resource-dependent sectors—or those heavily invested in commodities—the ability to interpret these visualized datasets offers competitive advantages:
• Optimizing procurement schedules based on anticipated shortages• Adjusting production plans proactively• Managing risks associated with volatile markets• Aligning sustainability initiatives with actual resource usage patterns
Investors benefit similarly by making more informed decisions grounded not only on current prices but also underlying supply fundamentals depicted graphically through detailed dashboards.
Final Thoughts
Commodity inventory data charts serve as vital instruments bridging raw numbers into actionable insights across industries worldwide—from agriculture producers safeguarding harvests against spoilage risks—to traders seeking profitable entry points based on fluctuating supplies—and policymakers designing resilient strategic reserves plans amidst geopolitical tensions globally.. As technology continues advancing rapidly—with AI-driven analytics becoming commonplace—the capacity for precise forecasting will only improve further enhancing trustworthiness at every level from local farms up through international markets.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-19 08:24
What is Commodity Inventory Data Chart?
What Is a Commodity Inventory Data Chart?
A commodity inventory data chart is a visual tool that displays the current stock levels and historical trends of various commodities. These charts are essential for understanding how much of a particular raw material, agricultural product, or metal is stored at any given time. They serve as vital indicators for businesses, investors, and policymakers to assess supply conditions and forecast future market movements.
Typically presented as line graphs, bar charts, or heat maps, these visualizations help users quickly interpret complex data sets. For example, a chart showing wheat inventories over several months can reveal seasonal patterns or sudden changes due to weather events or policy shifts. By providing real-time insights into stock levels across different storage locations—such as warehouses or silos—these charts enable more informed decision-making in supply chain management and investment strategies.
Why Are Commodity Inventory Data Charts Important?
Understanding the significance of commodity inventory data charts begins with recognizing their role in supply chain efficiency and market stability. These charts provide transparency about the availability of key resources that underpin industries like agriculture, manufacturing, energy production, and finance.
For companies involved in production processes, knowing current inventory levels helps prevent disruptions caused by shortages or excess stock. For investors and traders in commodity markets, these visuals offer clues about potential price movements; rising inventories might signal oversupply leading to price drops while declining stocks could indicate tightening supplies pushing prices higher.
Moreover, policymakers rely on this data to monitor national reserves and develop strategic stockpiles during crises such as food shortages or energy crises. Overall, accurate commodity inventory data charts support risk mitigation by offering timely insights into global supply-demand dynamics.
Types of Commodities Tracked Using Inventory Charts
Commodity inventory data charts encompass a broad spectrum of products across various sectors:
- Agricultural Products: Grains like wheat and corn; coffee beans; soybeans.
- Metals: Gold; copper; silver.
- Energy Resources: Crude oil; natural gas; coal.
- Raw Materials: Lumber; rubber.
Each type has unique factors influencing its storage levels—seasonality for crops or geopolitical issues affecting oil supplies—that are reflected visually through these charts. Tracking multiple commodities simultaneously can also reveal correlations—for instance: how crude oil inventories impact gasoline prices.
Sources of Commodity Inventory Data
Reliable data sources are crucial for constructing accurate commodity inventory graphs:
- Storage Facilities & Warehouses: Direct reports from companies managing physical stocks provide real-time figures.
- Market Exchanges & Reports: Major trading platforms like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) publish weekly reports on futures inventories which influence market perceptions.
- Government Agencies: Organizations such as USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) track agricultural stocks globally while agencies like EIA (Energy Information Administration) monitor energy reserves.
These sources ensure transparency but may differ slightly due to reporting delays or methodological differences. Combining multiple datasets enhances accuracy when analyzing trends over time.
Tools Used to Create & Analyze Commodity Inventory Charts
Creating insightful commodity inventory visuals involves leveraging specialized tools:
- Spreadsheet Software (Excel): Widely used for basic charting capabilities with manual updates.
- Data Visualization Platforms (Tableau / Power BI): Offer advanced features like interactive dashboards that facilitate deeper analysis.
- Inventory Management Software: Designed specifically for tracking physical stocks within organizations—integrating real-time sensor inputs via IoT devices enhances accuracy further.
The choice depends on user needs—from simple trend analysis to complex predictive modeling—and technological infrastructure available within organizations.
How Market Analysts Use These Charts
Market analysts interpret trends from commodity inventory data charts to predict future price movements:
- Identifying Surpluses: A sharp increase in inventories often indicates oversupply which can lead to falling prices unless demand rises correspondingly.
- Spotting Shortages: Declining stocks suggest tightening supplies possibly driving prices upward if demand remains steady.
- Recognizing Seasonal Patterns: Agricultural commodities often show predictable cycles aligned with planting/harvesting seasons captured visually through these graphs.
By combining this information with other economic indicators such as global trade flows or currency fluctuations—they craft comprehensive forecasts that guide trading strategies and policy decisions.
Recent Trends Shaping Commodity Inventory Analysis
Technological innovations have transformed how we collect and analyze this critical data:
- Digital Technologies & IoT Sensors – Real-time tracking via connected devices improves accuracy dramatically compared to traditional manual reporting methods.
- Blockchain Technology – Enhances transparency by securely recording transactions related to storage movements across global supply chains—aiding verification processes during audits or disputes.
- Impact of Global Events – The COVID-19 pandemic underscored vulnerabilities in international logistics networks leading firms worldwide toward maintaining higher buffer stocks amid uncertainties—a trend reflected clearly on recent inventory charts.
Furthermore, increased digital engagement has empowered individual investors through online platforms offering instant access to live warehouse reports alongside analytical tools—broadening participation beyond institutional players alone.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Commodity Inventories
Despite their usefulness, reliance on accurate inventory data comes with challenges:
Inaccurate Reporting: Delays or errors can mislead stakeholders about actual supply conditions resulting in poor decision-making either through unnecessary panic selling/buying—or missed opportunities altogether.*
Market Volatility: Sudden shifts indicated by abrupt changes in inventories may trigger rapid price swings affecting broader financial markets.*
Environmental Concerns: Excessive stockpiling might reflect inefficiencies contributing negatively toward sustainability goals—for example: overproduction leading land degradation.*
Regulatory Changes: Governments imposing new standards around environmental compliance could restrict storage practices impacting overall availability metrics displayed visually via these graphs.
How Understanding Commodity Inventory Data Shapes Business Strategy
For businesses operating within resource-dependent sectors—or those heavily invested in commodities—the ability to interpret these visualized datasets offers competitive advantages:
• Optimizing procurement schedules based on anticipated shortages• Adjusting production plans proactively• Managing risks associated with volatile markets• Aligning sustainability initiatives with actual resource usage patterns
Investors benefit similarly by making more informed decisions grounded not only on current prices but also underlying supply fundamentals depicted graphically through detailed dashboards.
Final Thoughts
Commodity inventory data charts serve as vital instruments bridging raw numbers into actionable insights across industries worldwide—from agriculture producers safeguarding harvests against spoilage risks—to traders seeking profitable entry points based on fluctuating supplies—and policymakers designing resilient strategic reserves plans amidst geopolitical tensions globally.. As technology continues advancing rapidly—with AI-driven analytics becoming commonplace—the capacity for precise forecasting will only improve further enhancing trustworthiness at every level from local farms up through international markets.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Transfer of Cryptocurrency Between Wallets: A Complete Guide
Understanding Cryptocurrency Wallets and Their Functionality
Cryptocurrency wallets are essential tools that enable users to store, send, and receive digital assets securely. These wallets come in two primary forms: hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets are connected to the internet, making them suitable for frequent transactions but more vulnerable to cyber threats. Cold wallets, on the other hand, operate offline—such as hardware devices or paper wallets—and are ideal for long-term storage due to their enhanced security features.
Each wallet is identified by a unique address—a string of alphanumeric characters—that serves as the destination or source for transactions. When transferring funds between wallets, understanding how these addresses work is crucial because sending cryptocurrency to an incorrect address can result in permanent loss of funds.
Step-by-Step Process for Transferring Cryptocurrency
Transferring cryptocurrency involves several key steps designed to ensure accuracy and security:
Selecting Compatible Wallets
Before initiating a transfer, verify that both the sender’s and recipient’s wallets support the specific cryptocurrency you intend to transfer (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum). Compatibility issues can lead to failed transactions or lost funds.Generating Recipient Address
The sender must obtain the recipient's wallet address accurately. This can be done by copying it directly from the recipient’s wallet app or scanning a QR code if available. Double-checking this address minimizes errors.Entering Transfer Amount
Specify exactly how much cryptocurrency you want to send. Many platforms allow you to include transaction fees within this amount; higher fees often result in faster confirmation times on congested networks.Reviewing Transaction Details
Carefully review all details before confirming—recipient's address, amount, transaction fee—to prevent mistakes that could lead to loss of funds or delays.Confirming and Broadcasting Transaction
Once confirmed, your wallet will broadcast the transaction across the blockchain network where miners/nodes verify it before adding it permanently into blocks on the chain.
The entire process relies heavily on blockchain technology's transparency and decentralization principles—once confirmed by miners/nodes through consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake—the transfer becomes irreversible.
Recent Innovations Enhancing Cryptocurrency Transfers
Advancements in blockchain technology have significantly improved how transfers are executed:
- Blockchain Scalability Solutions: To handle increasing transaction volumes efficiently without congestion delays or high fees, solutions such as sharding (dividing data into smaller pieces) and layer 2 protocols like Lightning Network (for Bitcoin) have been developed[1]. These innovations enable faster processing times and lower costs.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: As cyber threats evolve rapidly, security measures have become more sophisticated—examples include multi-signature authentication processes requiring multiple approvals before executing transfers[2]. Partnerships like Bullet Blockchain with Sailo Technologies aim at safeguarding U.S.-based Bitcoin ATMs against hacking attempts.
- Regulatory Clarity: Governments worldwide are establishing clearer guidelines around AML (Anti-Money Laundering) & KYC (Know Your Customer), which help legitimize transfers while preventing illicit activities such as money laundering or fraud[3].
These developments not only streamline user experience but also bolster trustworthiness within crypto ecosystems—a critical factor for mainstream adoption.
Risks Associated with Transferring Cryptocurrency
While transferring cryptocurrencies offers numerous benefits—including speediness compared with traditional banking—it also carries inherent risks:
- Legal Disputes Over Digital Assets: Cases involving intellectual property rights over NFTs exemplify potential legal complications when ownership disputes arise post-transfer[4].
- Market Volatility Impact: Cryptocurrencies’ value can fluctuate dramatically within short periods; transferring assets during volatile phases might result in significant financial losses if market conditions change unexpectedly.
- Security Breaches & Fraudulent Activities: Despite advancements in cybersecurity measures—for example partnerships aimed at protecting ATMs—users remain vulnerable if they do not follow best practices such as enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) or avoiding phishing scams[5].
Understanding these risks underscores why due diligence is vital when executing crypto transfers; always verify addresses carefully and stay updated about regulatory changes affecting your jurisdiction.
Key Historical Milestones Related To Crypto Transfers
Tracking major milestones helps contextualize current practices:
- In 2008/2009: Satoshi Nakamoto proposed blockchain technology culminating with Bitcoin’s launch—the first decentralized digital currency facilitating peer-to-peer transfers without intermediaries.
- 2010: The first cryptocurrency wallet was developed shortly after Bitcoin’s inception—marking a pivotal moment toward user-friendly access.
- 2013 onwards: Scalability solutions like sharding were proposed initially but gained traction later; these innovations aim at supporting mass adoption by improving network throughput.
- May 12th ,2025 : Bullet Blockchain partnered with Sailo Technologies specifically targeting cybersecurity enhancements across U.S.-based Bitcoin ATMs demonstrates ongoing efforts toward safer transactional environments today[6].
These historical points highlight continuous innovation driven by technological needs alongside regulatory considerations shaping current standards for secure crypto asset management.
By understanding each phase—from choosing compatible wallets through leveraging recent technological advances—you gain confidence navigating cryptocurrency transfers safely effectively while being aware of potential pitfalls related both technical vulnerabilities and legal complexities involved in digital asset management today.[1]: Reference about scalability solutions[2]: Example of multi-signature security[3]: Regulatory developments overview[4]: NFT legal disputes case study[5]: Best practices for secure transactions[6]: Partnership announcement date


Lo
2025-05-15 00:46
How do you transfer cryptocurrency between wallets?
Transfer of Cryptocurrency Between Wallets: A Complete Guide
Understanding Cryptocurrency Wallets and Their Functionality
Cryptocurrency wallets are essential tools that enable users to store, send, and receive digital assets securely. These wallets come in two primary forms: hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets are connected to the internet, making them suitable for frequent transactions but more vulnerable to cyber threats. Cold wallets, on the other hand, operate offline—such as hardware devices or paper wallets—and are ideal for long-term storage due to their enhanced security features.
Each wallet is identified by a unique address—a string of alphanumeric characters—that serves as the destination or source for transactions. When transferring funds between wallets, understanding how these addresses work is crucial because sending cryptocurrency to an incorrect address can result in permanent loss of funds.
Step-by-Step Process for Transferring Cryptocurrency
Transferring cryptocurrency involves several key steps designed to ensure accuracy and security:
Selecting Compatible Wallets
Before initiating a transfer, verify that both the sender’s and recipient’s wallets support the specific cryptocurrency you intend to transfer (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum). Compatibility issues can lead to failed transactions or lost funds.Generating Recipient Address
The sender must obtain the recipient's wallet address accurately. This can be done by copying it directly from the recipient’s wallet app or scanning a QR code if available. Double-checking this address minimizes errors.Entering Transfer Amount
Specify exactly how much cryptocurrency you want to send. Many platforms allow you to include transaction fees within this amount; higher fees often result in faster confirmation times on congested networks.Reviewing Transaction Details
Carefully review all details before confirming—recipient's address, amount, transaction fee—to prevent mistakes that could lead to loss of funds or delays.Confirming and Broadcasting Transaction
Once confirmed, your wallet will broadcast the transaction across the blockchain network where miners/nodes verify it before adding it permanently into blocks on the chain.
The entire process relies heavily on blockchain technology's transparency and decentralization principles—once confirmed by miners/nodes through consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake—the transfer becomes irreversible.
Recent Innovations Enhancing Cryptocurrency Transfers
Advancements in blockchain technology have significantly improved how transfers are executed:
- Blockchain Scalability Solutions: To handle increasing transaction volumes efficiently without congestion delays or high fees, solutions such as sharding (dividing data into smaller pieces) and layer 2 protocols like Lightning Network (for Bitcoin) have been developed[1]. These innovations enable faster processing times and lower costs.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: As cyber threats evolve rapidly, security measures have become more sophisticated—examples include multi-signature authentication processes requiring multiple approvals before executing transfers[2]. Partnerships like Bullet Blockchain with Sailo Technologies aim at safeguarding U.S.-based Bitcoin ATMs against hacking attempts.
- Regulatory Clarity: Governments worldwide are establishing clearer guidelines around AML (Anti-Money Laundering) & KYC (Know Your Customer), which help legitimize transfers while preventing illicit activities such as money laundering or fraud[3].
These developments not only streamline user experience but also bolster trustworthiness within crypto ecosystems—a critical factor for mainstream adoption.
Risks Associated with Transferring Cryptocurrency
While transferring cryptocurrencies offers numerous benefits—including speediness compared with traditional banking—it also carries inherent risks:
- Legal Disputes Over Digital Assets: Cases involving intellectual property rights over NFTs exemplify potential legal complications when ownership disputes arise post-transfer[4].
- Market Volatility Impact: Cryptocurrencies’ value can fluctuate dramatically within short periods; transferring assets during volatile phases might result in significant financial losses if market conditions change unexpectedly.
- Security Breaches & Fraudulent Activities: Despite advancements in cybersecurity measures—for example partnerships aimed at protecting ATMs—users remain vulnerable if they do not follow best practices such as enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) or avoiding phishing scams[5].
Understanding these risks underscores why due diligence is vital when executing crypto transfers; always verify addresses carefully and stay updated about regulatory changes affecting your jurisdiction.
Key Historical Milestones Related To Crypto Transfers
Tracking major milestones helps contextualize current practices:
- In 2008/2009: Satoshi Nakamoto proposed blockchain technology culminating with Bitcoin’s launch—the first decentralized digital currency facilitating peer-to-peer transfers without intermediaries.
- 2010: The first cryptocurrency wallet was developed shortly after Bitcoin’s inception—marking a pivotal moment toward user-friendly access.
- 2013 onwards: Scalability solutions like sharding were proposed initially but gained traction later; these innovations aim at supporting mass adoption by improving network throughput.
- May 12th ,2025 : Bullet Blockchain partnered with Sailo Technologies specifically targeting cybersecurity enhancements across U.S.-based Bitcoin ATMs demonstrates ongoing efforts toward safer transactional environments today[6].
These historical points highlight continuous innovation driven by technological needs alongside regulatory considerations shaping current standards for secure crypto asset management.
By understanding each phase—from choosing compatible wallets through leveraging recent technological advances—you gain confidence navigating cryptocurrency transfers safely effectively while being aware of potential pitfalls related both technical vulnerabilities and legal complexities involved in digital asset management today.[1]: Reference about scalability solutions[2]: Example of multi-signature security[3]: Regulatory developments overview[4]: NFT legal disputes case study[5]: Best practices for secure transactions[6]: Partnership announcement date
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Error executing ChatgptTask


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-14 11:38
How are gas tokens (e.g., GST2) used to reduce fees?
Error executing ChatgptTask
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Main Uses of Cryptocurrency Today
Cryptocurrencies have transitioned from niche digital assets to integral components of the global financial ecosystem. Their diverse applications span investment, payments, decentralized finance, smart contracts, and digital ownership through NFTs. Understanding these core uses provides insight into how crypto technology is shaping modern finance and digital interactions.
Investment and Trading in Cryptocurrencies
One of the most prominent uses of cryptocurrencies today is for investment purposes. Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) are widely recognized as leading assets within this space. Investors often buy these digital currencies with the expectation that their value will increase over time, aiming for high returns. However, due to their inherent volatility—where prices can fluctuate dramatically within short periods—they are considered high-risk investments. This volatility attracts traders seeking quick profits through buying low and selling high on various exchanges.
The trading landscape has also expanded beyond simple buy-and-hold strategies to include derivatives such as futures and options tied to cryptocurrencies. These financial instruments allow traders to hedge positions or speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset directly. As a result, cryptocurrency trading has become more sophisticated but also riskier, emphasizing the importance of market knowledge and risk management.
Cryptocurrencies as a Payment Method
Another significant application is using cryptocurrencies for everyday transactions. Companies like WonderFi Technologies Inc., which operates platforms integrating crypto payments into traditional financial systems, are paving the way for mainstream adoption. Digital currencies offer benefits such as faster transaction times compared to conventional banking methods and lower cross-border transfer fees.
Many merchants now accept cryptocurrencies directly or via third-party payment processors that convert crypto into fiat currency instantly at checkout points—both online and in physical stores. This trend enhances transaction security by reducing reliance on intermediaries like banks while providing users with greater privacy options compared to traditional payment methods.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance—or DeFi—is revolutionizing how individuals access financial services without relying on centralized institutions like banks or brokerages. Built primarily on blockchain platforms such as Ethereum, DeFi applications enable users to lend money (lending protocols), borrow funds (borrowing platforms), earn interest through yield farming strategies, or trade assets via decentralized exchanges.
DeFi's appeal lies in its transparency—since all transactions are recorded openly on blockchain—and its accessibility; anyone with an internet connection can participate regardless of geographic location or credit history. While still evolving rapidly—with new projects launching regularly—the sector faces challenges related to security vulnerabilities that require ongoing attention from developers and regulators alike.
Smart Contracts: Automating Transactions
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded onto blockchain networks that automatically enforce terms once predefined conditions are met. They eliminate intermediaries by executing transactions transparently without human intervention once triggered.
For example:
- In real estate deals: transferring property ownership upon receipt of payment.
- In supply chain management: tracking product provenance automatically.
- In insurance: releasing payouts when specific criteria occur (e.g., flight delays).
Smart contracts enhance efficiency by reducing processing times and minimizing errors associated with manual handling while increasing trust among parties involved in complex transactions across various industries including logistics, healthcare, legal services—and increasingly within decentralized applications themselves.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Digital Ownership Rights
NFTs have gained widespread popularity as unique digital tokens representing ownership rights over art pieces, collectibles, music tracks—and even virtual real estate—in online environments known as metaverses or virtual worlds.
Unlike fungible tokens such as Bitcoin—which are interchangeable—NFTs possess distinct attributes making each one unique; they’re stored securely using blockchain technology ensuring provenance verification and scarcity control—a key factor driving their value proposition in art markets where authenticity matters greatly.
Beyond art collecting:
- Artists monetize their work directly via NFT sales.
- Creators establish royalties automatically upon secondary sales.
- Virtual worlds utilize NFTs for land parcels or avatar accessories ownership rights.
This innovation opens new revenue streams but also raises questions about copyright enforcement & environmental impact due to energy-intensive minting processes associated with some blockchains like Ethereum’s current proof-of-work model.
How These Uses Are Evolving
Recent developments indicate a growing integration between these main uses:
- Platforms expanding support for multiple cryptocurrencies facilitate broader adoption.
- Regulatory clarity begins shaping industry standards around securities classification & consumer protections.
- Technological advancements improve scalability & security—making crypto more practical for daily use cases than ever before.
Furthermore,companies continue exploring innovative ways—for instance combining DeFi lending with NFT collateralization—to unlock new liquidity pools while addressing issues related to market volatility & security risks prevalent across sectors.
Addressing Challenges While Embracing Opportunities
Despite promising growth trajectories:regulatory uncertainties remain a concern; governments worldwide craft policies aimed at preventing illicit activities but sometimes create barriers impacting legitimate innovation efforts[1]. Security breaches targeting DeFi protocols & NFT marketplaces highlight ongoing vulnerabilities requiring robust cybersecurity measures[2].
Environmental concerns linked mainly to energy consumption during mining processes prompt industry shifts toward greener alternatives—including proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms—that aim at sustainable growth[3].
By understanding these core uses alongside emerging trends & challenges faced by the industry today—including regulatory evolution—it becomes clear that cryptocurrency technology continues transforming how we think about money—from investment vehicles through everyday payments—to complex contractual agreements enabled seamlessly via blockchain innovations.
References
- [Research Source 1]
- [Research Source 2]
- [Research Source 3]4–5 – Additional insights based on recent reports


Lo
2025-05-11 10:00
What are its main uses right now?
Main Uses of Cryptocurrency Today
Cryptocurrencies have transitioned from niche digital assets to integral components of the global financial ecosystem. Their diverse applications span investment, payments, decentralized finance, smart contracts, and digital ownership through NFTs. Understanding these core uses provides insight into how crypto technology is shaping modern finance and digital interactions.
Investment and Trading in Cryptocurrencies
One of the most prominent uses of cryptocurrencies today is for investment purposes. Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) are widely recognized as leading assets within this space. Investors often buy these digital currencies with the expectation that their value will increase over time, aiming for high returns. However, due to their inherent volatility—where prices can fluctuate dramatically within short periods—they are considered high-risk investments. This volatility attracts traders seeking quick profits through buying low and selling high on various exchanges.
The trading landscape has also expanded beyond simple buy-and-hold strategies to include derivatives such as futures and options tied to cryptocurrencies. These financial instruments allow traders to hedge positions or speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset directly. As a result, cryptocurrency trading has become more sophisticated but also riskier, emphasizing the importance of market knowledge and risk management.
Cryptocurrencies as a Payment Method
Another significant application is using cryptocurrencies for everyday transactions. Companies like WonderFi Technologies Inc., which operates platforms integrating crypto payments into traditional financial systems, are paving the way for mainstream adoption. Digital currencies offer benefits such as faster transaction times compared to conventional banking methods and lower cross-border transfer fees.
Many merchants now accept cryptocurrencies directly or via third-party payment processors that convert crypto into fiat currency instantly at checkout points—both online and in physical stores. This trend enhances transaction security by reducing reliance on intermediaries like banks while providing users with greater privacy options compared to traditional payment methods.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance—or DeFi—is revolutionizing how individuals access financial services without relying on centralized institutions like banks or brokerages. Built primarily on blockchain platforms such as Ethereum, DeFi applications enable users to lend money (lending protocols), borrow funds (borrowing platforms), earn interest through yield farming strategies, or trade assets via decentralized exchanges.
DeFi's appeal lies in its transparency—since all transactions are recorded openly on blockchain—and its accessibility; anyone with an internet connection can participate regardless of geographic location or credit history. While still evolving rapidly—with new projects launching regularly—the sector faces challenges related to security vulnerabilities that require ongoing attention from developers and regulators alike.
Smart Contracts: Automating Transactions
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded onto blockchain networks that automatically enforce terms once predefined conditions are met. They eliminate intermediaries by executing transactions transparently without human intervention once triggered.
For example:
- In real estate deals: transferring property ownership upon receipt of payment.
- In supply chain management: tracking product provenance automatically.
- In insurance: releasing payouts when specific criteria occur (e.g., flight delays).
Smart contracts enhance efficiency by reducing processing times and minimizing errors associated with manual handling while increasing trust among parties involved in complex transactions across various industries including logistics, healthcare, legal services—and increasingly within decentralized applications themselves.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Digital Ownership Rights
NFTs have gained widespread popularity as unique digital tokens representing ownership rights over art pieces, collectibles, music tracks—and even virtual real estate—in online environments known as metaverses or virtual worlds.
Unlike fungible tokens such as Bitcoin—which are interchangeable—NFTs possess distinct attributes making each one unique; they’re stored securely using blockchain technology ensuring provenance verification and scarcity control—a key factor driving their value proposition in art markets where authenticity matters greatly.
Beyond art collecting:
- Artists monetize their work directly via NFT sales.
- Creators establish royalties automatically upon secondary sales.
- Virtual worlds utilize NFTs for land parcels or avatar accessories ownership rights.
This innovation opens new revenue streams but also raises questions about copyright enforcement & environmental impact due to energy-intensive minting processes associated with some blockchains like Ethereum’s current proof-of-work model.
How These Uses Are Evolving
Recent developments indicate a growing integration between these main uses:
- Platforms expanding support for multiple cryptocurrencies facilitate broader adoption.
- Regulatory clarity begins shaping industry standards around securities classification & consumer protections.
- Technological advancements improve scalability & security—making crypto more practical for daily use cases than ever before.
Furthermore,companies continue exploring innovative ways—for instance combining DeFi lending with NFT collateralization—to unlock new liquidity pools while addressing issues related to market volatility & security risks prevalent across sectors.
Addressing Challenges While Embracing Opportunities
Despite promising growth trajectories:regulatory uncertainties remain a concern; governments worldwide craft policies aimed at preventing illicit activities but sometimes create barriers impacting legitimate innovation efforts[1]. Security breaches targeting DeFi protocols & NFT marketplaces highlight ongoing vulnerabilities requiring robust cybersecurity measures[2].
Environmental concerns linked mainly to energy consumption during mining processes prompt industry shifts toward greener alternatives—including proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms—that aim at sustainable growth[3].
By understanding these core uses alongside emerging trends & challenges faced by the industry today—including regulatory evolution—it becomes clear that cryptocurrency technology continues transforming how we think about money—from investment vehicles through everyday payments—to complex contractual agreements enabled seamlessly via blockchain innovations.
References
- [Research Source 1]
- [Research Source 2]
- [Research Source 3]4–5 – Additional insights based on recent reports
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Privacy Tools Can Users Employ on Ethereum?
Ethereum’s rise as a leading blockchain platform has revolutionized decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contract applications. However, its inherent transparency—where every transaction is publicly recorded—poses significant privacy challenges for users. As adoption grows, so does the need for effective privacy tools that enable users to protect their financial data and personal information without compromising security or network integrity. This article explores the key privacy solutions available on Ethereum, recent technological advancements, and how they impact user security and regulatory considerations.
Understanding Ethereum’s Transparency and Privacy Challenges
Ethereum operates as a decentralized ledger where all transactions are visible to anyone with access to the blockchain explorer. While this transparency ensures trustlessness and immutability, it also means that transaction details such as sender addresses, recipient addresses, amounts transferred, and timestamps are accessible publicly. For individual users or institutions handling sensitive data or large transactions, this openness can be a deterrent due to concerns over privacy breaches or targeted attacks.
The tension between transparency and privacy has prompted developers to create specialized tools aimed at masking transaction details while maintaining the network's security features. These solutions aim not only to enhance user confidentiality but also to comply with evolving regulatory standards around financial data protection.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: The Backbone of Privacy on Ethereum
One of the most promising cryptographic innovations in enhancing Ethereum privacy is Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs). ZKPs allow one party—the prover—to demonstrate knowledge of certain information without revealing the actual data itself. This technology enables private verification processes that do not compromise underlying details.
Recent developments from companies like zkSync by Matter Labs and StarkWare have advanced ZKP implementations tailored for Ethereum's ecosystem. These platforms facilitate private transactions where users can prove ownership or validity without exposing sensitive information such as wallet balances or transaction specifics.
Key benefits include:
- Confidentiality of transaction amounts
- Anonymity of sender/recipient addresses
- Reduced on-chain data footprint
By integrating ZKPs into layer 2 scaling solutions like zkSync and Optimism, developers have significantly improved both scalability and privacy simultaneously—a critical step toward mainstream adoption.
Private Transactions Through Cryptographic Techniques
Beyond ZKPs, other cryptographic methods underpin private transactions on Ethereum:
Tornado Cash: A widely used mixer service that employs zero-knowledge proofs to obfuscate transaction trails by pooling multiple deposits before withdrawal—making it difficult for observers to trace funds back to specific sources.
Aztec Network: An innovative protocol offering confidential transfers within DeFi applications using advanced cryptography techniques like bulletproofs—a form of succinct zero-knowledge proof—to conceal transfer details while ensuring correctness.
These tools serve different use cases—from simple fund mixing for individual privacy needs to complex confidential DeFi operations—highlighting how cryptography underpins modern efforts toward transactional anonymity.
Layer 2 Solutions Enhancing Privacy
Layer 2 scaling solutions such as Optimism and Polygon aim primarily at increasing throughput but increasingly incorporate features supporting user privacy:
Optimism: Recently integrated ZKP technology into its layer 2 framework in March 2024; this allows private transactions processed off-chain before being settled securely on mainnet.
Polygon: Offers various sidechains with optional encryption features designed for enterprise-grade confidentiality in DeFi operations.
Layer 2 solutions reduce congestion fees while enabling more flexible implementation of private protocols—making them attractive options for both individual users seeking anonymity—and enterprises requiring compliance with strict confidentiality standards.
Recent Developments in Ethereum Privacy Technologies
The landscape is rapidly evolving with notable updates:
In April 2023, zkSync partnered with StarkWare—a leader in scalable zero-knowledge proofs—to integrate their respective technologies seamlessly into existing networks.
Tornado Cash released an update in January 2024 improving mixing capabilities further; these enhancements make tracing more difficult even against sophisticated analysis techniques.
Optimism announced successful integration of advanced ZKP protocols into its layer 2 environment during March 2024 — marking a significant milestone toward widespread adoption of confidential transactions within scalable infrastructure frameworks.
These developments reflect ongoing efforts by industry leaders aiming at balancing usability with robust security guarantees necessary for broader acceptance across sectors including finance, healthcare, supply chain management—and potentially regulatory environments demanding compliance measures aligned with anti-money laundering (AML) standards.
Regulatory Considerations & Security Risks
While these innovative tools bolster user sovereignty over personal data—and support compliance initiatives—they also attract scrutiny from regulators concerned about illicit activities facilitated through anonymous channels:
Regulatory Scrutiny
Governments worldwide are increasingly examining how privacy-enhancing technologies could be exploited for money laundering or tax evasion purposes. Platforms like Tornado Cash faced bans in some jurisdictions due to misuse allegations despite their legitimate uses within legal boundaries; similar concerns apply broadly across crypto ecosystems employing strong anonymization techniques.
Security Risks
Cryptography-based systems inherently carry risks if improperly implemented:
- Vulnerabilities may emerge through bugs or design flaws
- Sophisticated attackers might exploit weaknesses leading to loss of funds
Ensuring rigorous audits alongside continuous updates remains essential when deploying these complex systems at scale.
Impact on Market Dynamics
As more participants adopt enhanced privacy measures:
- DeFi protocols may see shifts towards more confidential lending/borrowing models,
- Asset flows could become less transparent,
- Competition might intensify among platforms offering superior anonymity features,
which could reshape market strategies around trustless interactions versus user confidentiality needs.
Embracing Privacy While Navigating Challenges
Ethereum’s suite of emerging privacy tools demonstrates a clear trajectory toward balancing decentralization’s transparency benefits against individual rights’ demands for confidentiality. Zero-Knowledge Proofs stand out as foundational technology enabling secure yet private interactions—not only protecting user identities but also fostering broader trustworthiness essential for institutional adoption.
However, stakeholders must remain vigilant regarding regulatory landscapes' evolution—including potential restrictions—and prioritize security best practices when deploying cryptographic solutions at scale.
Final Thoughts: The Future Pathway Toward Private Blockchain Interactions
As blockchain innovation accelerates—with ongoing improvements in scalability via Layer 2 integrations—the focus increasingly shifts toward making these networks both fast AND private by design rather than afterthoughts alone. Developers continue refining cryptographic techniques like ZKPs alongside practical implementations such as mixers (e.g., Tornado Cash) and confidential DeFi protocols (e.g., Aztec).
For everyday users interested in safeguarding their financial activities without sacrificing decentralization principles—or risking exposure—they now have access through multiple layers—from simple mixers up through sophisticated zero-knowledge-based systems—that cater specifically to varying levels of technical expertise yet uphold core principles rooted in trustlessness & censorship resistance.
References
For further reading:


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 15:41
What privacy tools can users employ on Ethereum?
What Privacy Tools Can Users Employ on Ethereum?
Ethereum’s rise as a leading blockchain platform has revolutionized decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contract applications. However, its inherent transparency—where every transaction is publicly recorded—poses significant privacy challenges for users. As adoption grows, so does the need for effective privacy tools that enable users to protect their financial data and personal information without compromising security or network integrity. This article explores the key privacy solutions available on Ethereum, recent technological advancements, and how they impact user security and regulatory considerations.
Understanding Ethereum’s Transparency and Privacy Challenges
Ethereum operates as a decentralized ledger where all transactions are visible to anyone with access to the blockchain explorer. While this transparency ensures trustlessness and immutability, it also means that transaction details such as sender addresses, recipient addresses, amounts transferred, and timestamps are accessible publicly. For individual users or institutions handling sensitive data or large transactions, this openness can be a deterrent due to concerns over privacy breaches or targeted attacks.
The tension between transparency and privacy has prompted developers to create specialized tools aimed at masking transaction details while maintaining the network's security features. These solutions aim not only to enhance user confidentiality but also to comply with evolving regulatory standards around financial data protection.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: The Backbone of Privacy on Ethereum
One of the most promising cryptographic innovations in enhancing Ethereum privacy is Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs). ZKPs allow one party—the prover—to demonstrate knowledge of certain information without revealing the actual data itself. This technology enables private verification processes that do not compromise underlying details.
Recent developments from companies like zkSync by Matter Labs and StarkWare have advanced ZKP implementations tailored for Ethereum's ecosystem. These platforms facilitate private transactions where users can prove ownership or validity without exposing sensitive information such as wallet balances or transaction specifics.
Key benefits include:
- Confidentiality of transaction amounts
- Anonymity of sender/recipient addresses
- Reduced on-chain data footprint
By integrating ZKPs into layer 2 scaling solutions like zkSync and Optimism, developers have significantly improved both scalability and privacy simultaneously—a critical step toward mainstream adoption.
Private Transactions Through Cryptographic Techniques
Beyond ZKPs, other cryptographic methods underpin private transactions on Ethereum:
Tornado Cash: A widely used mixer service that employs zero-knowledge proofs to obfuscate transaction trails by pooling multiple deposits before withdrawal—making it difficult for observers to trace funds back to specific sources.
Aztec Network: An innovative protocol offering confidential transfers within DeFi applications using advanced cryptography techniques like bulletproofs—a form of succinct zero-knowledge proof—to conceal transfer details while ensuring correctness.
These tools serve different use cases—from simple fund mixing for individual privacy needs to complex confidential DeFi operations—highlighting how cryptography underpins modern efforts toward transactional anonymity.
Layer 2 Solutions Enhancing Privacy
Layer 2 scaling solutions such as Optimism and Polygon aim primarily at increasing throughput but increasingly incorporate features supporting user privacy:
Optimism: Recently integrated ZKP technology into its layer 2 framework in March 2024; this allows private transactions processed off-chain before being settled securely on mainnet.
Polygon: Offers various sidechains with optional encryption features designed for enterprise-grade confidentiality in DeFi operations.
Layer 2 solutions reduce congestion fees while enabling more flexible implementation of private protocols—making them attractive options for both individual users seeking anonymity—and enterprises requiring compliance with strict confidentiality standards.
Recent Developments in Ethereum Privacy Technologies
The landscape is rapidly evolving with notable updates:
In April 2023, zkSync partnered with StarkWare—a leader in scalable zero-knowledge proofs—to integrate their respective technologies seamlessly into existing networks.
Tornado Cash released an update in January 2024 improving mixing capabilities further; these enhancements make tracing more difficult even against sophisticated analysis techniques.
Optimism announced successful integration of advanced ZKP protocols into its layer 2 environment during March 2024 — marking a significant milestone toward widespread adoption of confidential transactions within scalable infrastructure frameworks.
These developments reflect ongoing efforts by industry leaders aiming at balancing usability with robust security guarantees necessary for broader acceptance across sectors including finance, healthcare, supply chain management—and potentially regulatory environments demanding compliance measures aligned with anti-money laundering (AML) standards.
Regulatory Considerations & Security Risks
While these innovative tools bolster user sovereignty over personal data—and support compliance initiatives—they also attract scrutiny from regulators concerned about illicit activities facilitated through anonymous channels:
Regulatory Scrutiny
Governments worldwide are increasingly examining how privacy-enhancing technologies could be exploited for money laundering or tax evasion purposes. Platforms like Tornado Cash faced bans in some jurisdictions due to misuse allegations despite their legitimate uses within legal boundaries; similar concerns apply broadly across crypto ecosystems employing strong anonymization techniques.
Security Risks
Cryptography-based systems inherently carry risks if improperly implemented:
- Vulnerabilities may emerge through bugs or design flaws
- Sophisticated attackers might exploit weaknesses leading to loss of funds
Ensuring rigorous audits alongside continuous updates remains essential when deploying these complex systems at scale.
Impact on Market Dynamics
As more participants adopt enhanced privacy measures:
- DeFi protocols may see shifts towards more confidential lending/borrowing models,
- Asset flows could become less transparent,
- Competition might intensify among platforms offering superior anonymity features,
which could reshape market strategies around trustless interactions versus user confidentiality needs.
Embracing Privacy While Navigating Challenges
Ethereum’s suite of emerging privacy tools demonstrates a clear trajectory toward balancing decentralization’s transparency benefits against individual rights’ demands for confidentiality. Zero-Knowledge Proofs stand out as foundational technology enabling secure yet private interactions—not only protecting user identities but also fostering broader trustworthiness essential for institutional adoption.
However, stakeholders must remain vigilant regarding regulatory landscapes' evolution—including potential restrictions—and prioritize security best practices when deploying cryptographic solutions at scale.
Final Thoughts: The Future Pathway Toward Private Blockchain Interactions
As blockchain innovation accelerates—with ongoing improvements in scalability via Layer 2 integrations—the focus increasingly shifts toward making these networks both fast AND private by design rather than afterthoughts alone. Developers continue refining cryptographic techniques like ZKPs alongside practical implementations such as mixers (e.g., Tornado Cash) and confidential DeFi protocols (e.g., Aztec).
For everyday users interested in safeguarding their financial activities without sacrificing decentralization principles—or risking exposure—they now have access through multiple layers—from simple mixers up through sophisticated zero-knowledge-based systems—that cater specifically to varying levels of technical expertise yet uphold core principles rooted in trustlessness & censorship resistance.
References
For further reading:
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📅 August 4 2025
🎉 Stay updated with the latest crypto market trends!
👉 Trade on:https://bit.ly/3DFYq30
👉 X:https://twitter.com/Jucoinex
👉 APP download: https://www.jucoin.com/en/community-downloads
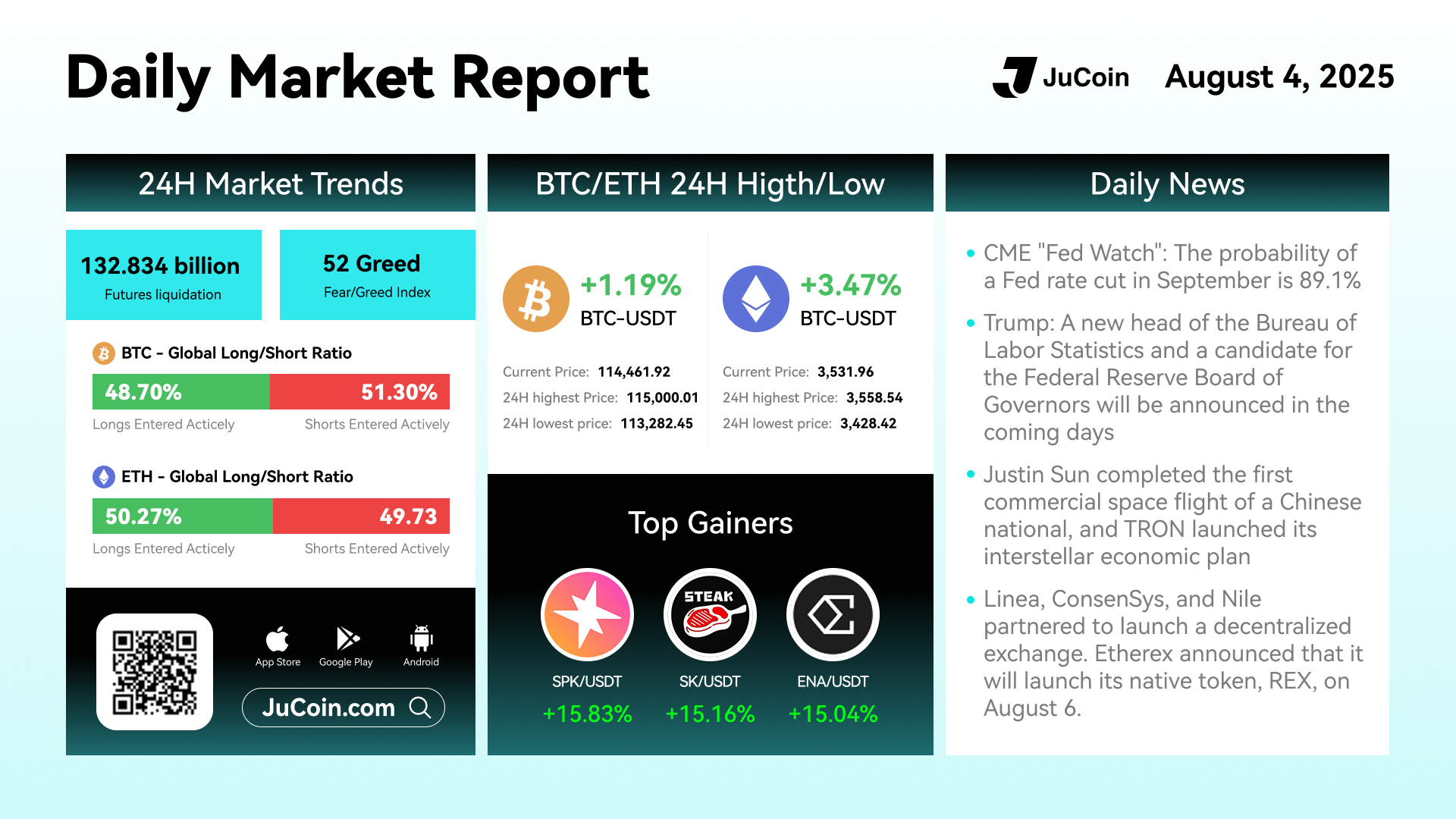


JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 04:34
🚀 #JuCoin Daily Market Report
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
When to Use Credit Spreads in Investment and Risk Management
Understanding credit spreads is essential for investors, financial analysts, and portfolio managers aiming to assess credit risk, optimize investment strategies, or hedge against market volatility. These spreads serve as a vital indicator of market sentiment and economic outlooks, guiding decision-making across various scenarios.
Assessing Credit Risk in Bond Investments
One of the primary uses of credit spreads is evaluating the relative risk associated with different bonds. When considering high-yield (junk) bonds versus safer government securities like U.S. Treasuries, the spread quantifies how much extra return an investor demands for taking on additional risk. A widening spread indicates increased perceived risk—perhaps due to deteriorating issuer fundamentals or broader economic concerns—prompting investors to reconsider their holdings or adjust their portfolios accordingly.
Conversely, narrowing credit spreads suggest improving confidence in corporate borrowers' ability to meet debt obligations. Investors can leverage this information when selecting bonds that align with their risk appetite or when reallocating assets during changing market conditions.
Timing Market Entry and Exit Points
Credit spreads are valuable tools for timing investment decisions. For instance:
- Entry Point: Narrowing spreads may signal a period of economic recovery or stability, making it an opportune moment to increase exposure to higher-yield assets before risks re-emerge.
- Exit Point: Conversely, widening spreads often precede downturns or heightened uncertainty; recognizing this trend allows investors to reduce exposure in risky asset classes proactively.
Monitoring these shifts helps manage downside risks while capitalizing on favorable market phases.
Evaluating Economic Conditions and Business Cycles
Credit spread movements often reflect underlying macroeconomic trends. During periods of economic expansion, credit spreads tend to narrow as companies demonstrate stronger financial health and default risks diminish. In contrast, during recessions or times of financial stress—such as geopolitical tensions or policy uncertainties—spreads typically widen due to increased default fears.
Investors use these signals not only for individual bond selection but also as early warning indicators of potential economic downturns. For example:
- Persistent widening could foreshadow recessionary pressures.
- Sudden narrowing might indicate overly optimistic sentiment that could lead to inflated asset prices.
By integrating credit spread analysis into macroeconomic assessments, stakeholders can better anticipate shifts in the business cycle.
Managing Portfolio Risks During Market Volatility
Market volatility influences credit spreads significantly; periods marked by turbulence often see wider spreads across high-yield sectors while investment-grade bonds remain relatively stable initially. Recognizing these patterns enables portfolio managers to implement hedging strategies effectively—for example:
- Increasing allocations toward safer assets like government bonds during uncertain times.
- Using derivatives such as options on bond ETFs that track changes in credit premiums.
This proactive approach helps mitigate losses from sudden market swings driven by geopolitical events, monetary policy changes, or fiscal uncertainties.
Making Informed Decisions with Regulatory Changes
Policy developments related to fiscal policies and trade agreements can impact investor confidence and thus influence credit spreads substantially. For instance:
- Announcements of new tariffs may cause immediate widening due to anticipated supply chain disruptions.
- Fiscal stimulus measures might temporarily narrow spreads if they bolster corporate earnings prospects.
Investors monitoring regulatory environments should incorporate real-time changes into their analysis framework using credit spread data—a practice that enhances decision-making accuracy amid evolving policy landscapes.
Practical Scenarios Where Credit Spreads Are Most Useful
Here are some specific situations where analyzing credit spreads provides tangible benefits:
Risk Assessment Before Bond Purchases: Before investing in high-yield bonds during periods of uncertainty—or when markets are volatile—review current spread levels relative to historical averages ensures informed choices aligned with your risk tolerance.
Portfolio Rebalancing: During times when broad markets experience fluctuations (e.g., rising interest rates), tracking how different segments' credits behave helps decide whether shifting toward safer assets is prudent.
Monitoring Economic Indicators: Regularly observing shifts in overall market-wide credit premiums offers insights into potential upcoming recessions or recoveries—not just at an individual security level but across entire sectors.
Hedging Strategies: If you hold a significant position exposed directly through corporate bonds or ETFs sensitive to changing credits (like CLO funds), understanding current trends allows you timely adjustments via derivatives contracts designed around expected movements in yields.
Final Thoughts on Using Credit Spreads Effectively
Incorporating the analysis of credit spreads into your investment toolkit enhances both strategic planning and tactical responses within dynamic markets. Whether assessing individual securities’ risks during turbulent times—or gauging broader macroeconomic signals—they provide crucial insights grounded in real-time data reflecting investor sentiment about future defaults and economic health.
By staying attentive not only at specific points but also over longer-term cycles—watching how these premiums evolve—you position yourself better for navigating complex financial landscapes while managing downside risks effectively.
Note: Always consider combining multiple indicators—including macroeconomic data—and consult with financial professionals before making significant investment decisions based solely on changes in credit spreds for comprehensive risk management tailored specifically for your goals.*


Lo
2025-06-09 22:00
In what scenarios would you use credit spreads?
When to Use Credit Spreads in Investment and Risk Management
Understanding credit spreads is essential for investors, financial analysts, and portfolio managers aiming to assess credit risk, optimize investment strategies, or hedge against market volatility. These spreads serve as a vital indicator of market sentiment and economic outlooks, guiding decision-making across various scenarios.
Assessing Credit Risk in Bond Investments
One of the primary uses of credit spreads is evaluating the relative risk associated with different bonds. When considering high-yield (junk) bonds versus safer government securities like U.S. Treasuries, the spread quantifies how much extra return an investor demands for taking on additional risk. A widening spread indicates increased perceived risk—perhaps due to deteriorating issuer fundamentals or broader economic concerns—prompting investors to reconsider their holdings or adjust their portfolios accordingly.
Conversely, narrowing credit spreads suggest improving confidence in corporate borrowers' ability to meet debt obligations. Investors can leverage this information when selecting bonds that align with their risk appetite or when reallocating assets during changing market conditions.
Timing Market Entry and Exit Points
Credit spreads are valuable tools for timing investment decisions. For instance:
- Entry Point: Narrowing spreads may signal a period of economic recovery or stability, making it an opportune moment to increase exposure to higher-yield assets before risks re-emerge.
- Exit Point: Conversely, widening spreads often precede downturns or heightened uncertainty; recognizing this trend allows investors to reduce exposure in risky asset classes proactively.
Monitoring these shifts helps manage downside risks while capitalizing on favorable market phases.
Evaluating Economic Conditions and Business Cycles
Credit spread movements often reflect underlying macroeconomic trends. During periods of economic expansion, credit spreads tend to narrow as companies demonstrate stronger financial health and default risks diminish. In contrast, during recessions or times of financial stress—such as geopolitical tensions or policy uncertainties—spreads typically widen due to increased default fears.
Investors use these signals not only for individual bond selection but also as early warning indicators of potential economic downturns. For example:
- Persistent widening could foreshadow recessionary pressures.
- Sudden narrowing might indicate overly optimistic sentiment that could lead to inflated asset prices.
By integrating credit spread analysis into macroeconomic assessments, stakeholders can better anticipate shifts in the business cycle.
Managing Portfolio Risks During Market Volatility
Market volatility influences credit spreads significantly; periods marked by turbulence often see wider spreads across high-yield sectors while investment-grade bonds remain relatively stable initially. Recognizing these patterns enables portfolio managers to implement hedging strategies effectively—for example:
- Increasing allocations toward safer assets like government bonds during uncertain times.
- Using derivatives such as options on bond ETFs that track changes in credit premiums.
This proactive approach helps mitigate losses from sudden market swings driven by geopolitical events, monetary policy changes, or fiscal uncertainties.
Making Informed Decisions with Regulatory Changes
Policy developments related to fiscal policies and trade agreements can impact investor confidence and thus influence credit spreads substantially. For instance:
- Announcements of new tariffs may cause immediate widening due to anticipated supply chain disruptions.
- Fiscal stimulus measures might temporarily narrow spreads if they bolster corporate earnings prospects.
Investors monitoring regulatory environments should incorporate real-time changes into their analysis framework using credit spread data—a practice that enhances decision-making accuracy amid evolving policy landscapes.
Practical Scenarios Where Credit Spreads Are Most Useful
Here are some specific situations where analyzing credit spreads provides tangible benefits:
Risk Assessment Before Bond Purchases: Before investing in high-yield bonds during periods of uncertainty—or when markets are volatile—review current spread levels relative to historical averages ensures informed choices aligned with your risk tolerance.
Portfolio Rebalancing: During times when broad markets experience fluctuations (e.g., rising interest rates), tracking how different segments' credits behave helps decide whether shifting toward safer assets is prudent.
Monitoring Economic Indicators: Regularly observing shifts in overall market-wide credit premiums offers insights into potential upcoming recessions or recoveries—not just at an individual security level but across entire sectors.
Hedging Strategies: If you hold a significant position exposed directly through corporate bonds or ETFs sensitive to changing credits (like CLO funds), understanding current trends allows you timely adjustments via derivatives contracts designed around expected movements in yields.
Final Thoughts on Using Credit Spreads Effectively
Incorporating the analysis of credit spreads into your investment toolkit enhances both strategic planning and tactical responses within dynamic markets. Whether assessing individual securities’ risks during turbulent times—or gauging broader macroeconomic signals—they provide crucial insights grounded in real-time data reflecting investor sentiment about future defaults and economic health.
By staying attentive not only at specific points but also over longer-term cycles—watching how these premiums evolve—you position yourself better for navigating complex financial landscapes while managing downside risks effectively.
Note: Always consider combining multiple indicators—including macroeconomic data—and consult with financial professionals before making significant investment decisions based solely on changes in credit spreds for comprehensive risk management tailored specifically for your goals.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Why Is Bithumb Warning Users About Bitcoin Gold?
Bithumb, one of South Korea’s leading cryptocurrency exchanges, has recently issued a warning to its users regarding Bitcoin Gold (BTG). This move has sparked curiosity and concern among traders and investors. To understand the implications fully, it’s essential to explore the background of Bitcoin Gold, the reasons behind Bithumb's cautionary stance, and what this means for the broader crypto community.
Understanding Bitcoin Gold: A Brief History
Bitcoin Gold was launched in October 2017 as a hard fork of the original Bitcoin blockchain. The primary motivation behind BTG was to create a more decentralized mining environment by making it resistant to ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) hardware. Unlike traditional Bitcoin mining that relies heavily on specialized equipment, BTG aimed to enable GPU-based mining—allowing individual miners with standard graphics cards to participate more easily.
This vision resonated with many in the crypto community who believed that decentralization is fundamental for maintaining security and fairness within blockchain networks. However, despite its initial promise, Bitcoin Gold has faced numerous challenges over time.
Security Concerns Surrounding Bitcoin Gold
One of the most significant issues associated with BTG is security vulnerabilities. In 2018, BTG suffered a major hacking incident where approximately 17,000 coins were stolen—valued at around $18 million at that time. Hackers exploited weaknesses in its network or wallet infrastructure to carry out this theft.
Such incidents have raised red flags about BTG's security protocols and overall resilience against cyberattacks. For exchanges like Bithumb operating in highly regulated environments such as South Korea—which enforces strict compliance standards—supporting or even listing cryptocurrencies with known security issues can pose substantial risks.
Regulatory Environment Impact on Cryptocurrency Support
South Korea maintains rigorous regulations concerning cryptocurrency trading platforms. The government emphasizes investor protection and anti-money laundering measures while closely monitoring digital assets' compliance status.
In this context, exchanges like Bithumb are cautious about supporting cryptocurrencies that might attract regulatory scrutiny due to past security breaches or ambiguous legal standing. Supporting an asset like BTG—which has experienced notable hacks—could potentially expose them to legal liabilities or reputational damage if users suffer losses linked directly or indirectly from these vulnerabilities.
Market Volatility and Investor Risks
Cryptocurrencies are inherently volatile; prices can fluctuate dramatically within short periods due to market sentiment shifts or external events. For coins like BTG—with relatively lower liquidity compared to mainstream assets—the volatility can be even more pronounced.
Investors holding BTG may face sudden value drops during market downturns or after negative news reports related to security concerns or governance disputes within its community. Such instability makes it less attractive for risk-averse traders seeking safer investment options on platforms like Bithumb.
Community Disputes Affecting Trustworthiness
The development community behind Bitcoin Gold has experienced internal disagreements over governance decisions and future development directions. These controversies sometimes lead to skepticism among users regarding project transparency and long-term viability.
When trust diminishes within a cryptocurrency’s ecosystem due to internal conflicts—or perceived mismanagement—it often results in decreased user confidence across trading platforms supporting that coin—a factor likely influencing Bithumb's decision-making process when issuing warnings about BTG support.
Recent Developments Without Major Security Breaches
As of June 2025, there have been no recent major hacks targeting Bithumb’s holdings specifically related directly to BTC holdings; however, ongoing market trends continue affecting perceptions around BTC-related assets including BTG:
- Fluctuating prices driven by macroeconomic factors
- Regulatory updates impacting how exchanges handle certain tokens
- Community debates influencing project credibility
These elements contribute cumulatively toward cautious stances taken by prominent exchanges such as Bithumb regarding specific cryptocurrencies like BTC-Gold.
Potential Impacts of Bithumb’s Warning on Users & Markets
Bithumb's warning could influence various aspects of trading activity:
User Confidence: Traders might become hesitant about holding or trading BTG through Bithumb if they perceive increased risk.
Market Dynamics: Negative sentiment stemming from warnings can lead investors toward liquidating their positions faster than usual—potentially causing price declines.
Regulatory Scrutiny: Authorities may interpret such warnings as signals indicating potential issues within certain tokens’ ecosystems—prompting further investigations.
Community Reactions: Supporters of Bitcoin Gold might respond defensively against perceived unfair treatment from major exchanges which could impact future project developments or collaborations.
Understanding these potential outcomes helps investors make informed decisions aligned with their risk appetite while recognizing broader industry trends influenced by exchange policies.
Key Takeaways for Investors:
- Always verify an exchange’s official communications before making trades involving high-risk tokens.
- Be aware that past security breaches significantly influence current regulatory attitudes towards specific cryptocurrencies.
- Diversify holdings across different assets rather than concentrating investments solely in volatile tokens like BTG.
In summary, BithUMB's warning about Bitcoin Gold reflects ongoing concerns surrounding its security history, regulatory environment considerations in South Korea, market volatility risks, and internal community disputes affecting trustworthiness—all critical factors for traders evaluating whether support for such assets aligns with their safety standards and investment goals. Staying informed through credible sources remains essential amid evolving developments within the crypto landscape.
Keywords: bitcoin gold warning bithubb | btg hack history | south korea crypto regulation | cryptocurrency market volatility | crypto community disputes


kai
2025-06-05 07:05
Why is Bithumb warning users about Bitcoin Gold?
Why Is Bithumb Warning Users About Bitcoin Gold?
Bithumb, one of South Korea’s leading cryptocurrency exchanges, has recently issued a warning to its users regarding Bitcoin Gold (BTG). This move has sparked curiosity and concern among traders and investors. To understand the implications fully, it’s essential to explore the background of Bitcoin Gold, the reasons behind Bithumb's cautionary stance, and what this means for the broader crypto community.
Understanding Bitcoin Gold: A Brief History
Bitcoin Gold was launched in October 2017 as a hard fork of the original Bitcoin blockchain. The primary motivation behind BTG was to create a more decentralized mining environment by making it resistant to ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) hardware. Unlike traditional Bitcoin mining that relies heavily on specialized equipment, BTG aimed to enable GPU-based mining—allowing individual miners with standard graphics cards to participate more easily.
This vision resonated with many in the crypto community who believed that decentralization is fundamental for maintaining security and fairness within blockchain networks. However, despite its initial promise, Bitcoin Gold has faced numerous challenges over time.
Security Concerns Surrounding Bitcoin Gold
One of the most significant issues associated with BTG is security vulnerabilities. In 2018, BTG suffered a major hacking incident where approximately 17,000 coins were stolen—valued at around $18 million at that time. Hackers exploited weaknesses in its network or wallet infrastructure to carry out this theft.
Such incidents have raised red flags about BTG's security protocols and overall resilience against cyberattacks. For exchanges like Bithumb operating in highly regulated environments such as South Korea—which enforces strict compliance standards—supporting or even listing cryptocurrencies with known security issues can pose substantial risks.
Regulatory Environment Impact on Cryptocurrency Support
South Korea maintains rigorous regulations concerning cryptocurrency trading platforms. The government emphasizes investor protection and anti-money laundering measures while closely monitoring digital assets' compliance status.
In this context, exchanges like Bithumb are cautious about supporting cryptocurrencies that might attract regulatory scrutiny due to past security breaches or ambiguous legal standing. Supporting an asset like BTG—which has experienced notable hacks—could potentially expose them to legal liabilities or reputational damage if users suffer losses linked directly or indirectly from these vulnerabilities.
Market Volatility and Investor Risks
Cryptocurrencies are inherently volatile; prices can fluctuate dramatically within short periods due to market sentiment shifts or external events. For coins like BTG—with relatively lower liquidity compared to mainstream assets—the volatility can be even more pronounced.
Investors holding BTG may face sudden value drops during market downturns or after negative news reports related to security concerns or governance disputes within its community. Such instability makes it less attractive for risk-averse traders seeking safer investment options on platforms like Bithumb.
Community Disputes Affecting Trustworthiness
The development community behind Bitcoin Gold has experienced internal disagreements over governance decisions and future development directions. These controversies sometimes lead to skepticism among users regarding project transparency and long-term viability.
When trust diminishes within a cryptocurrency’s ecosystem due to internal conflicts—or perceived mismanagement—it often results in decreased user confidence across trading platforms supporting that coin—a factor likely influencing Bithumb's decision-making process when issuing warnings about BTG support.
Recent Developments Without Major Security Breaches
As of June 2025, there have been no recent major hacks targeting Bithumb’s holdings specifically related directly to BTC holdings; however, ongoing market trends continue affecting perceptions around BTC-related assets including BTG:
- Fluctuating prices driven by macroeconomic factors
- Regulatory updates impacting how exchanges handle certain tokens
- Community debates influencing project credibility
These elements contribute cumulatively toward cautious stances taken by prominent exchanges such as Bithumb regarding specific cryptocurrencies like BTC-Gold.
Potential Impacts of Bithumb’s Warning on Users & Markets
Bithumb's warning could influence various aspects of trading activity:
User Confidence: Traders might become hesitant about holding or trading BTG through Bithumb if they perceive increased risk.
Market Dynamics: Negative sentiment stemming from warnings can lead investors toward liquidating their positions faster than usual—potentially causing price declines.
Regulatory Scrutiny: Authorities may interpret such warnings as signals indicating potential issues within certain tokens’ ecosystems—prompting further investigations.
Community Reactions: Supporters of Bitcoin Gold might respond defensively against perceived unfair treatment from major exchanges which could impact future project developments or collaborations.
Understanding these potential outcomes helps investors make informed decisions aligned with their risk appetite while recognizing broader industry trends influenced by exchange policies.
Key Takeaways for Investors:
- Always verify an exchange’s official communications before making trades involving high-risk tokens.
- Be aware that past security breaches significantly influence current regulatory attitudes towards specific cryptocurrencies.
- Diversify holdings across different assets rather than concentrating investments solely in volatile tokens like BTG.
In summary, BithUMB's warning about Bitcoin Gold reflects ongoing concerns surrounding its security history, regulatory environment considerations in South Korea, market volatility risks, and internal community disputes affecting trustworthiness—all critical factors for traders evaluating whether support for such assets aligns with their safety standards and investment goals. Staying informed through credible sources remains essential amid evolving developments within the crypto landscape.
Keywords: bitcoin gold warning bithubb | btg hack history | south korea crypto regulation | cryptocurrency market volatility | crypto community disputes
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Sets Wave 3 Apart in Cryptocurrency and Investment?
Understanding the evolution of cryptocurrency markets is essential for investors, developers, and enthusiasts alike. Among the various phases or "waves" that have marked this journey, Wave 3 stands out as a transformative period characterized by technological innovation, regulatory maturation, and mainstream acceptance. This article explores what distinguishes Wave 3 from previous phases and why these differences matter for the future of digital assets.
Technological Breakthroughs Define Wave 3
One of the most notable features setting Wave 3 apart is its focus on technological advancements aimed at solving longstanding issues such as scalability and usability. During this phase, blockchain projects introduced solutions like sharding—dividing networks into smaller parts to process transactions more efficiently—and layer 2 scaling protocols such as Lightning Network or Optimistic Rollups. These innovations significantly increased transaction speeds while reducing costs, making cryptocurrencies more practical for everyday use.
Additionally, smart contracts became mainstream during this period. Originally popularized by Ethereum, smart contracts enable self-executing agreements without intermediaries. This capability has led to an explosion of decentralized applications (dApps) across finance (DeFi), gaming, supply chain management, and more sectors—broadening the scope of blockchain utility beyond simple peer-to-peer transfers.
Regulatory Maturity and Institutional Involvement
Unlike earlier waves driven primarily by retail investors’ hype or speculative trading, Wave 3 witnesses a shift toward regulatory clarity and institutional participation. Governments worldwide began establishing clearer guidelines for exchanges operating within their jurisdictions—covering anti-money laundering (AML) measures and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures—to foster safer environments for investors.
The rise of stablecoins—cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies like USD or EUR—also exemplifies this maturation process. Stablecoins provide stability amid volatile markets; their adoption has facilitated smoother transactions between traditional finance systems and crypto platforms. As a result, institutional players such as hedge funds or asset managers started allocating significant capital into cryptocurrencies during this phase.
Mainstream Adoption Accelerates
Wave 3 marks a turning point where cryptocurrencies transition from niche assets to widely accepted financial instruments across various sectors—including retail businesses accepting crypto payments or governments exploring digital currencies. The increasing involvement of large corporations in blockchain projects further legitimizes digital assets’ role in global economies.
This broader acceptance is partly driven by consumer demand but also supported by infrastructure improvements like user-friendly wallets and integrated payment solutions that make buying or spending crypto easier than ever before.
Security Enhancements Respond to Growing Risks
As market value surged during Wave 3—with Bitcoin halving events reducing supply—the importance of security intensified accordingly. Developers prioritized implementing robust security protocols to protect against hacking attempts targeting exchanges or individual wallets—a critical step given high-profile breaches in earlier years had shaken investor confidence.
These efforts include multi-signature wallets, advanced encryption methods, regular audits of smart contract codebases—and ongoing education initiatives aimed at raising awareness about best practices among users.
Recent Developments That Highlight Distinctiveness
Several key developments underscore how different Wave 3 is compared to prior phases:
- Bitcoin Halving Events: Occurring approximately every four years during this wave have historically led to price rallies due to reduced mining rewards—a phenomenon that influences market sentiment significantly.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The rapid growth of DeFi platforms like Compound or Aave exemplifies innovative financial services built on blockchain technology—offering lending/borrowing without traditional banks.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Multiple countries announced plans for CBDCs during this period; these government-backed digital currencies aim at modernizing monetary systems while potentially challenging existing banking models.
- Environmental Concerns: Increased scrutiny over energy consumption associated with proof-of-work mining prompted development toward greener consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-stake—which are now gaining traction within the industry.
Potential Challenges Unique To This Phase
Despite its many strengths—the technological progressions alone mark a significant leap forward—Wave 3 faces specific hurdles:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: While regulations are becoming clearer overall, ongoing debates around compliance could lead some projects into legal gray areas—or even shutdowns if they fail to meet new standards.
- Market Volatility: Rapid adoption can cause sharp price swings that may deter risk-averse investors but also attract speculative traders seeking quick gains.
- Security Risks: As user bases grow exponentially with increased mainstream access—including institutional investments—the attack surface expands correspondingly; cyber threats remain an ongoing concern requiring constant vigilance.
- Environmental Impact: Despite efforts toward sustainable mining practices—and shifts towards energy-efficient consensus algorithms—the environmental footprint remains under scrutiny which could influence future regulations affecting certain cryptocurrencies' viability.
How Differentiating Features Shape Future Trends
Wave 3’s defining characteristics set it apart from Waves 1 & 2 not only through technological innovation but also via evolving market dynamics involving regulation and societal acceptance—all factors likely influencing subsequent phases' development trajectories.
For example:
- The integration of CBDCs might redefine central banking operations,
- Continued improvements in scalability could facilitate mass adoption,
- Enhanced security measures will be crucial as competition intensifies,
- Environmental considerations may drive further innovation towards eco-friendly consensus mechanisms.
Why Recognizing These Differences Matters
Understanding what makes Wave 3 unique helps stakeholders—from individual investors to policymakers—to navigate risks effectively while capitalizing on emerging opportunities within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. It highlights how technological progress combined with regulatory clarity fosters trustworthiness—a vital component when considering long-term investments in digital assets.
In summary,
Wave 3 represents a pivotal era marked by groundbreaking innovations like scalable blockchains and widespread use cases enabled through smart contracts; increased regulatory oversight coupled with growing institutional involvement; broader societal acceptance leading towards mainstream integration; alongside challenges related to security risks & environmental impact management—all shaping today’s rapidly evolving crypto landscape.
Keywords:cryptocurrency waves | wave three cryptocurrency | blockchain technology advancements | DeFi boom | stablecoins regulation | Bitcoin halving effect | CBDC development | crypto market volatility


Lo
2025-05-29 07:11
What distinguishes Wave 3 from other waves?
What Sets Wave 3 Apart in Cryptocurrency and Investment?
Understanding the evolution of cryptocurrency markets is essential for investors, developers, and enthusiasts alike. Among the various phases or "waves" that have marked this journey, Wave 3 stands out as a transformative period characterized by technological innovation, regulatory maturation, and mainstream acceptance. This article explores what distinguishes Wave 3 from previous phases and why these differences matter for the future of digital assets.
Technological Breakthroughs Define Wave 3
One of the most notable features setting Wave 3 apart is its focus on technological advancements aimed at solving longstanding issues such as scalability and usability. During this phase, blockchain projects introduced solutions like sharding—dividing networks into smaller parts to process transactions more efficiently—and layer 2 scaling protocols such as Lightning Network or Optimistic Rollups. These innovations significantly increased transaction speeds while reducing costs, making cryptocurrencies more practical for everyday use.
Additionally, smart contracts became mainstream during this period. Originally popularized by Ethereum, smart contracts enable self-executing agreements without intermediaries. This capability has led to an explosion of decentralized applications (dApps) across finance (DeFi), gaming, supply chain management, and more sectors—broadening the scope of blockchain utility beyond simple peer-to-peer transfers.
Regulatory Maturity and Institutional Involvement
Unlike earlier waves driven primarily by retail investors’ hype or speculative trading, Wave 3 witnesses a shift toward regulatory clarity and institutional participation. Governments worldwide began establishing clearer guidelines for exchanges operating within their jurisdictions—covering anti-money laundering (AML) measures and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures—to foster safer environments for investors.
The rise of stablecoins—cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies like USD or EUR—also exemplifies this maturation process. Stablecoins provide stability amid volatile markets; their adoption has facilitated smoother transactions between traditional finance systems and crypto platforms. As a result, institutional players such as hedge funds or asset managers started allocating significant capital into cryptocurrencies during this phase.
Mainstream Adoption Accelerates
Wave 3 marks a turning point where cryptocurrencies transition from niche assets to widely accepted financial instruments across various sectors—including retail businesses accepting crypto payments or governments exploring digital currencies. The increasing involvement of large corporations in blockchain projects further legitimizes digital assets’ role in global economies.
This broader acceptance is partly driven by consumer demand but also supported by infrastructure improvements like user-friendly wallets and integrated payment solutions that make buying or spending crypto easier than ever before.
Security Enhancements Respond to Growing Risks
As market value surged during Wave 3—with Bitcoin halving events reducing supply—the importance of security intensified accordingly. Developers prioritized implementing robust security protocols to protect against hacking attempts targeting exchanges or individual wallets—a critical step given high-profile breaches in earlier years had shaken investor confidence.
These efforts include multi-signature wallets, advanced encryption methods, regular audits of smart contract codebases—and ongoing education initiatives aimed at raising awareness about best practices among users.
Recent Developments That Highlight Distinctiveness
Several key developments underscore how different Wave 3 is compared to prior phases:
- Bitcoin Halving Events: Occurring approximately every four years during this wave have historically led to price rallies due to reduced mining rewards—a phenomenon that influences market sentiment significantly.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The rapid growth of DeFi platforms like Compound or Aave exemplifies innovative financial services built on blockchain technology—offering lending/borrowing without traditional banks.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Multiple countries announced plans for CBDCs during this period; these government-backed digital currencies aim at modernizing monetary systems while potentially challenging existing banking models.
- Environmental Concerns: Increased scrutiny over energy consumption associated with proof-of-work mining prompted development toward greener consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-stake—which are now gaining traction within the industry.
Potential Challenges Unique To This Phase
Despite its many strengths—the technological progressions alone mark a significant leap forward—Wave 3 faces specific hurdles:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: While regulations are becoming clearer overall, ongoing debates around compliance could lead some projects into legal gray areas—or even shutdowns if they fail to meet new standards.
- Market Volatility: Rapid adoption can cause sharp price swings that may deter risk-averse investors but also attract speculative traders seeking quick gains.
- Security Risks: As user bases grow exponentially with increased mainstream access—including institutional investments—the attack surface expands correspondingly; cyber threats remain an ongoing concern requiring constant vigilance.
- Environmental Impact: Despite efforts toward sustainable mining practices—and shifts towards energy-efficient consensus algorithms—the environmental footprint remains under scrutiny which could influence future regulations affecting certain cryptocurrencies' viability.
How Differentiating Features Shape Future Trends
Wave 3’s defining characteristics set it apart from Waves 1 & 2 not only through technological innovation but also via evolving market dynamics involving regulation and societal acceptance—all factors likely influencing subsequent phases' development trajectories.
For example:
- The integration of CBDCs might redefine central banking operations,
- Continued improvements in scalability could facilitate mass adoption,
- Enhanced security measures will be crucial as competition intensifies,
- Environmental considerations may drive further innovation towards eco-friendly consensus mechanisms.
Why Recognizing These Differences Matters
Understanding what makes Wave 3 unique helps stakeholders—from individual investors to policymakers—to navigate risks effectively while capitalizing on emerging opportunities within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. It highlights how technological progress combined with regulatory clarity fosters trustworthiness—a vital component when considering long-term investments in digital assets.
In summary,
Wave 3 represents a pivotal era marked by groundbreaking innovations like scalable blockchains and widespread use cases enabled through smart contracts; increased regulatory oversight coupled with growing institutional involvement; broader societal acceptance leading towards mainstream integration; alongside challenges related to security risks & environmental impact management—all shaping today’s rapidly evolving crypto landscape.
Keywords:cryptocurrency waves | wave three cryptocurrency | blockchain technology advancements | DeFi boom | stablecoins regulation | Bitcoin halving effect | CBDC development | crypto market volatility
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Chainlink (LINK) and How Does It Differ from Other Oracles?
Understanding the core differences between Chainlink (LINK) and other oracle networks is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, decentralized finance (DeFi), or smart contract development. While all oracles serve the fundamental purpose of connecting blockchain applications with real-world data, their architectures, security models, and ecosystem integrations vary significantly. This article explores these distinctions to provide a clear picture of what sets Chainlink apart.
How Chainlink Works as a Decentralized Oracle Network
Chainlink operates as a decentralized oracle network (DON), which means it relies on multiple independent nodes to gather, validate, and deliver external data to smart contracts on various blockchain platforms like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. Unlike traditional centralized oracles—where a single entity supplies data—Chainlink’s architecture distributes trust across numerous nodes. This decentralization reduces risks associated with data manipulation or single points of failure.
Nodes in the Chainlink network are incentivized through LINK tokens to provide accurate information consistently. They participate in economic mechanisms that reward correct data submission while penalizing inaccuracies via staking protocols. This system enhances trustworthiness and ensures that smart contracts receive reliable inputs for executing complex operations such as financial derivatives, insurance claims, or supply chain tracking.
Key Features That Distinguish Chainlink from Other Oracles
Decentralized Data Validation: Unlike some oracle solutions that rely on one source or node for data provision, Chainlink aggregates inputs from multiple sources before delivering them to the blockchain. This multi-source approach minimizes the risk of false information entering smart contracts.
Wide Range of Data Feeds: Chainlink offers an extensive array of pre-built data feeds—including price indices for cryptocurrencies and commodities, weather reports for agriculture-related applications, IoT sensor readings for industrial use cases—and supports custom integrations via APIs.
Security Protocols: The network employs cryptographic proofs like Verifiable Random Functions (VRF) and secure aggregation techniques to ensure integrity and tamper-resistance in its outputs—a critical feature especially when dealing with sensitive financial transactions.
Integration Flexibility: Supporting multiple blockchains beyond Ethereum allows developers greater flexibility when building cross-chain applications that require real-world inputs without being limited by platform-specific constraints.
Comparing Architecture & Security Models
While many decentralized oracle providers aim at similar goals—trustless access to off-chain data—their underlying architectures differ:
Chainlink's Multi-Source Model: By aggregating responses from numerous independent nodes across diverse locations and operators worldwide, it creates a robust consensus mechanism that makes it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate results.
Other Oracles' Approaches:
- Some utilize single-source models where one trusted provider supplies all necessary data.
- Others employ hybrid systems combining centralized elements with decentralization layers but may lack comprehensive validation processes.
This architectural choice directly impacts security; decentralized models like Chainlink tend to offer higher resilience against attacks but can be more complex and costly compared to simpler centralized solutions.
The Role of Incentives & Tokenomics
A defining characteristic of Chainlink is its use of LINK tokens not only as a utility token but also as an incentive mechanism within its ecosystem:
- Node operators stake LINK tokens as collateral.
- They earn rewards in LINK based on their accuracy.
- Penalties are imposed if they submit incorrect information—a process known as slashing—that discourages malicious behavior.
This economic design aligns incentives among participants while fostering trustworthiness—a feature less emphasized by some competing oracle networks which may rely solely on reputation systems without token-based staking mechanisms.
Market Position & Ecosystem Integration
Chainlink’s extensive partnerships—including collaborations with major organizations like the International Olympic Committee—and support across multiple blockchains give it an edge over many competitors who operate within narrower ecosystems or specific platforms only. Its ability to integrate seamlessly into existing DeFi projects has made it the go-to choice for developers seeking reliable off-chain data sources at scale.
In contrast, other oracle providers such as Band Protocol focus heavily on interoperability within specific ecosystems like Cosmos-based chains but might lack broader adoption outside those environments unless they expand their integrations further.
Emerging Challenges & Competitive Landscape
Despite its leadership position today, several challenges threaten long-term dominance:
Increased competition from newer players such as Band Protocol—which emphasizes lightweight architecture—and The Graph—which specializes in indexing blockchain data—could erode market share.
Regulatory scrutiny around DeFi projects utilizing oracles raises questions about compliance standards; although not yet heavily targeted specifically at Oracle providers like Chainlink,regulatory developments could influence operational frameworks moving forward.
Additionally, security remains paramount; any significant breach affecting node integrity could undermine confidence not just in individual networks but also broadly impact perceptions around decentralized oracle reliability overall.
Why Choosing Between Different Oracles Matters
For developers designing smart contracts requiring external inputs—from price feeds used in trading algorithms to weather conditions impacting crop insurance—the choice between different oracle solutions can significantly influence project success:
Opting for decentralized options like Chainlink provides higher security guarantees due to multi-source validation processes.
Simpler centralized alternatives might offer faster deployment at lower costs but introduce vulnerabilities related to single points of failure.
Ultimately, understanding these differences helps align technical requirements with risk appetite—especially crucial when handling high-stakes financial transactions where trustworthiness is non-negotiable.
What Sets ChainLink Apart From Competitors?
While several other projects aim at providing off-chain data access through various methods—including Band Protocol’s lightweight design focused on interoperability or The Graph’s indexing services—ChainLink's comprehensive approach makes it stand out:
- Its broad ecosystem support across multiple blockchains
- Extensive partnership network
- Proven track record through large-scale deployments
- Advanced security features leveraging cryptography
These factors collectively contribute toward establishing chain link's reputation as a leader among decentralized oracle networks capable of powering next-generation dApps securely.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between different types of blockchain oracles depends largely on project needs concerning security levels versus cost-efficiency considerations. While alternative solutions might suit smaller-scale applications requiring less stringent validation protocols—or specialized environments—they often fall short when high reliability is essential—for example—in DeFi lending platforms where accurate asset prices are critical.
By understanding how each solution operates—from architecture design principles down to incentive structures—you can make informed decisions aligned with your project's goals while appreciating what makes each unique within this rapidly evolving space.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-29 02:34
What is the difference between Chainlink (LINK) and other oracles?
What Is Chainlink (LINK) and How Does It Differ from Other Oracles?
Understanding the core differences between Chainlink (LINK) and other oracle networks is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, decentralized finance (DeFi), or smart contract development. While all oracles serve the fundamental purpose of connecting blockchain applications with real-world data, their architectures, security models, and ecosystem integrations vary significantly. This article explores these distinctions to provide a clear picture of what sets Chainlink apart.
How Chainlink Works as a Decentralized Oracle Network
Chainlink operates as a decentralized oracle network (DON), which means it relies on multiple independent nodes to gather, validate, and deliver external data to smart contracts on various blockchain platforms like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. Unlike traditional centralized oracles—where a single entity supplies data—Chainlink’s architecture distributes trust across numerous nodes. This decentralization reduces risks associated with data manipulation or single points of failure.
Nodes in the Chainlink network are incentivized through LINK tokens to provide accurate information consistently. They participate in economic mechanisms that reward correct data submission while penalizing inaccuracies via staking protocols. This system enhances trustworthiness and ensures that smart contracts receive reliable inputs for executing complex operations such as financial derivatives, insurance claims, or supply chain tracking.
Key Features That Distinguish Chainlink from Other Oracles
Decentralized Data Validation: Unlike some oracle solutions that rely on one source or node for data provision, Chainlink aggregates inputs from multiple sources before delivering them to the blockchain. This multi-source approach minimizes the risk of false information entering smart contracts.
Wide Range of Data Feeds: Chainlink offers an extensive array of pre-built data feeds—including price indices for cryptocurrencies and commodities, weather reports for agriculture-related applications, IoT sensor readings for industrial use cases—and supports custom integrations via APIs.
Security Protocols: The network employs cryptographic proofs like Verifiable Random Functions (VRF) and secure aggregation techniques to ensure integrity and tamper-resistance in its outputs—a critical feature especially when dealing with sensitive financial transactions.
Integration Flexibility: Supporting multiple blockchains beyond Ethereum allows developers greater flexibility when building cross-chain applications that require real-world inputs without being limited by platform-specific constraints.
Comparing Architecture & Security Models
While many decentralized oracle providers aim at similar goals—trustless access to off-chain data—their underlying architectures differ:
Chainlink's Multi-Source Model: By aggregating responses from numerous independent nodes across diverse locations and operators worldwide, it creates a robust consensus mechanism that makes it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate results.
Other Oracles' Approaches:
- Some utilize single-source models where one trusted provider supplies all necessary data.
- Others employ hybrid systems combining centralized elements with decentralization layers but may lack comprehensive validation processes.
This architectural choice directly impacts security; decentralized models like Chainlink tend to offer higher resilience against attacks but can be more complex and costly compared to simpler centralized solutions.
The Role of Incentives & Tokenomics
A defining characteristic of Chainlink is its use of LINK tokens not only as a utility token but also as an incentive mechanism within its ecosystem:
- Node operators stake LINK tokens as collateral.
- They earn rewards in LINK based on their accuracy.
- Penalties are imposed if they submit incorrect information—a process known as slashing—that discourages malicious behavior.
This economic design aligns incentives among participants while fostering trustworthiness—a feature less emphasized by some competing oracle networks which may rely solely on reputation systems without token-based staking mechanisms.
Market Position & Ecosystem Integration
Chainlink’s extensive partnerships—including collaborations with major organizations like the International Olympic Committee—and support across multiple blockchains give it an edge over many competitors who operate within narrower ecosystems or specific platforms only. Its ability to integrate seamlessly into existing DeFi projects has made it the go-to choice for developers seeking reliable off-chain data sources at scale.
In contrast, other oracle providers such as Band Protocol focus heavily on interoperability within specific ecosystems like Cosmos-based chains but might lack broader adoption outside those environments unless they expand their integrations further.
Emerging Challenges & Competitive Landscape
Despite its leadership position today, several challenges threaten long-term dominance:
Increased competition from newer players such as Band Protocol—which emphasizes lightweight architecture—and The Graph—which specializes in indexing blockchain data—could erode market share.
Regulatory scrutiny around DeFi projects utilizing oracles raises questions about compliance standards; although not yet heavily targeted specifically at Oracle providers like Chainlink,regulatory developments could influence operational frameworks moving forward.
Additionally, security remains paramount; any significant breach affecting node integrity could undermine confidence not just in individual networks but also broadly impact perceptions around decentralized oracle reliability overall.
Why Choosing Between Different Oracles Matters
For developers designing smart contracts requiring external inputs—from price feeds used in trading algorithms to weather conditions impacting crop insurance—the choice between different oracle solutions can significantly influence project success:
Opting for decentralized options like Chainlink provides higher security guarantees due to multi-source validation processes.
Simpler centralized alternatives might offer faster deployment at lower costs but introduce vulnerabilities related to single points of failure.
Ultimately, understanding these differences helps align technical requirements with risk appetite—especially crucial when handling high-stakes financial transactions where trustworthiness is non-negotiable.
What Sets ChainLink Apart From Competitors?
While several other projects aim at providing off-chain data access through various methods—including Band Protocol’s lightweight design focused on interoperability or The Graph’s indexing services—ChainLink's comprehensive approach makes it stand out:
- Its broad ecosystem support across multiple blockchains
- Extensive partnership network
- Proven track record through large-scale deployments
- Advanced security features leveraging cryptography
These factors collectively contribute toward establishing chain link's reputation as a leader among decentralized oracle networks capable of powering next-generation dApps securely.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between different types of blockchain oracles depends largely on project needs concerning security levels versus cost-efficiency considerations. While alternative solutions might suit smaller-scale applications requiring less stringent validation protocols—or specialized environments—they often fall short when high reliability is essential—for example—in DeFi lending platforms where accurate asset prices are critical.
By understanding how each solution operates—from architecture design principles down to incentive structures—you can make informed decisions aligned with your project's goals while appreciating what makes each unique within this rapidly evolving space.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is Investing.com? A Comprehensive Overview
Investing.com is a widely recognized online platform that serves as a comprehensive resource for financial news, data, and analysis. Established in 2007, it has grown to become one of the most trusted sources for both individual investors and professional traders worldwide. The platform’s primary goal is to provide users with real-time market information, insightful analysis, and useful tools to facilitate informed investment decisions across various asset classes.
The platform covers a broad spectrum of financial markets including stocks, commodities such as gold and oil, foreign exchange (forex) markets, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, and emerging digital assets. Its extensive coverage makes it an invaluable resource for those seeking up-to-date information on global economic developments or specific market movements.
Investing.com’s core offerings include real-time data feeds that display live prices through interactive charts. These tools allow users to analyze trends visually and make timely trading decisions. Additionally, the site features in-depth news articles written by experienced journalists who track market-moving events around the world. This combination of current data and expert insights helps users stay ahead in fast-moving markets.
Beyond news and data services, Investing.com provides various analytical tools designed for technical analysis—such as indicators like moving averages or RSI—and fundamental analysis resources including economic calendars that highlight upcoming macroeconomic releases affecting markets globally. These features are complemented by calculators for risk management or profit estimation.
Community engagement also plays a significant role on Investing.com through forums where traders share strategies or ask questions about specific assets or market conditions. This social aspect fosters knowledge exchange among diverse user groups—from novice investors learning the ropes to seasoned professionals discussing complex trading ideas.
Recent Developments Enhancing User Experience
Over recent years, Investing.com has made notable strides in expanding its coverage areas to meet evolving investor interests. One key development has been its increased focus on emerging markets—regions experiencing rapid economic growth but often underrepresented in mainstream financial media—as well as cryptocurrencies which have gained immense popularity among retail investors since the early 2020s[1].
Technological upgrades have also played a crucial role in improving user experience (UX). The platform continuously updates its mobile applications ensuring smoother navigation across devices while enhancing data visualization capabilities with more sophisticated charts and customizable dashboards[2]. Faster loading times contribute significantly toward reducing user frustration during high-volatility periods when timely access to information is critical.
User engagement metrics indicate rising participation levels among younger demographics who prefer digital-first platforms over traditional media outlets[3]. To cater specifically to this audience segment—which values educational content—the site offers tutorials on technical analysis basics or how macroeconomic factors influence asset prices.
Regulatory compliance remains vital for maintaining credibility; Investing.com adheres strictly to international standards governing online financial services[4]. This commitment ensures transparency regarding data accuracy while safeguarding user privacy—a factor increasingly important amid growing cybersecurity concerns.
Focus on Cryptocurrency Markets
As digital currencies continue their ascent into mainstream finance, investing platforms like Investing.com have responded by dedicating more resources toward crypto coverage[5]. Users can now access detailed price charts spanning multiple timeframes alongside breaking news updates relevant specifically to blockchain technology developments or regulatory changes impacting virtual assets.
This specialized focus includes providing educational materials aimed at demystifying complex topics such as decentralized finance (DeFi), initial coin offerings (ICOs), or security tokens—helping newcomers understand these innovative yet often volatile sectors better. Such initiatives position Investing.com not only as an information hub but also as an educational partner supporting responsible investing within rapidly evolving digital asset ecosystems.
Key Facts About Investing.com
- Founded: 2007
- Headquarters: Cyprus
- Services Offered: Real-time quotes; comprehensive news coverage; technical & fundamental analysis tools; economic calendars; community forums
- User Base: Global reach with significant audiences across Europe & North America
Potential Challenges Facing the Platform
Despite its strengths, investing platforms like Investing.com face ongoing challenges related primarily to market volatility—where sudden price swings can impact both user sentiment and data reliability during turbulent periods[6]. Regulatory landscapes are also shifting rapidly worldwide; new rules concerning online trading disclosures or anti-money laundering measures require constant adaptation from service providers[4].
Technological evolution presents another hurdle: maintaining cutting-edge features without compromising usability demands continuous investment into infrastructure upgrades.[2] Cybersecurity remains paramount given increasing threats targeting sensitive personal & financial information stored within these systems—a responsibility requiring robust security protocols against breaches [7].
By proactively addressing these issues through innovation-driven strategies combined with strict compliance measures—and fostering transparent communication with their community—Investing.com's reputation continues strengthening amid dynamic global markets.
References
- Recent expansion into cryptocurrency coverage reflects broader industry trends.
- Upgrades improve mobile app performance & visual analytics.
- Increased engagement among younger investors driven by intuitive design.
- Compliance ensures adherence to international regulations.
- Growing interest in digital assets prompts dedicated crypto sections.
- Market volatility impacts real-time data accuracy during crises.7.Cybersecurity risks necessitate advanced protection measures.
Keywords: investing website overview | financial markets data | cryptocurrency coverage | real-time stock quotes | investment tools | online trading platforms


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-26 19:37
What is Investing.com?
What is Investing.com? A Comprehensive Overview
Investing.com is a widely recognized online platform that serves as a comprehensive resource for financial news, data, and analysis. Established in 2007, it has grown to become one of the most trusted sources for both individual investors and professional traders worldwide. The platform’s primary goal is to provide users with real-time market information, insightful analysis, and useful tools to facilitate informed investment decisions across various asset classes.
The platform covers a broad spectrum of financial markets including stocks, commodities such as gold and oil, foreign exchange (forex) markets, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, and emerging digital assets. Its extensive coverage makes it an invaluable resource for those seeking up-to-date information on global economic developments or specific market movements.
Investing.com’s core offerings include real-time data feeds that display live prices through interactive charts. These tools allow users to analyze trends visually and make timely trading decisions. Additionally, the site features in-depth news articles written by experienced journalists who track market-moving events around the world. This combination of current data and expert insights helps users stay ahead in fast-moving markets.
Beyond news and data services, Investing.com provides various analytical tools designed for technical analysis—such as indicators like moving averages or RSI—and fundamental analysis resources including economic calendars that highlight upcoming macroeconomic releases affecting markets globally. These features are complemented by calculators for risk management or profit estimation.
Community engagement also plays a significant role on Investing.com through forums where traders share strategies or ask questions about specific assets or market conditions. This social aspect fosters knowledge exchange among diverse user groups—from novice investors learning the ropes to seasoned professionals discussing complex trading ideas.
Recent Developments Enhancing User Experience
Over recent years, Investing.com has made notable strides in expanding its coverage areas to meet evolving investor interests. One key development has been its increased focus on emerging markets—regions experiencing rapid economic growth but often underrepresented in mainstream financial media—as well as cryptocurrencies which have gained immense popularity among retail investors since the early 2020s[1].
Technological upgrades have also played a crucial role in improving user experience (UX). The platform continuously updates its mobile applications ensuring smoother navigation across devices while enhancing data visualization capabilities with more sophisticated charts and customizable dashboards[2]. Faster loading times contribute significantly toward reducing user frustration during high-volatility periods when timely access to information is critical.
User engagement metrics indicate rising participation levels among younger demographics who prefer digital-first platforms over traditional media outlets[3]. To cater specifically to this audience segment—which values educational content—the site offers tutorials on technical analysis basics or how macroeconomic factors influence asset prices.
Regulatory compliance remains vital for maintaining credibility; Investing.com adheres strictly to international standards governing online financial services[4]. This commitment ensures transparency regarding data accuracy while safeguarding user privacy—a factor increasingly important amid growing cybersecurity concerns.
Focus on Cryptocurrency Markets
As digital currencies continue their ascent into mainstream finance, investing platforms like Investing.com have responded by dedicating more resources toward crypto coverage[5]. Users can now access detailed price charts spanning multiple timeframes alongside breaking news updates relevant specifically to blockchain technology developments or regulatory changes impacting virtual assets.
This specialized focus includes providing educational materials aimed at demystifying complex topics such as decentralized finance (DeFi), initial coin offerings (ICOs), or security tokens—helping newcomers understand these innovative yet often volatile sectors better. Such initiatives position Investing.com not only as an information hub but also as an educational partner supporting responsible investing within rapidly evolving digital asset ecosystems.
Key Facts About Investing.com
- Founded: 2007
- Headquarters: Cyprus
- Services Offered: Real-time quotes; comprehensive news coverage; technical & fundamental analysis tools; economic calendars; community forums
- User Base: Global reach with significant audiences across Europe & North America
Potential Challenges Facing the Platform
Despite its strengths, investing platforms like Investing.com face ongoing challenges related primarily to market volatility—where sudden price swings can impact both user sentiment and data reliability during turbulent periods[6]. Regulatory landscapes are also shifting rapidly worldwide; new rules concerning online trading disclosures or anti-money laundering measures require constant adaptation from service providers[4].
Technological evolution presents another hurdle: maintaining cutting-edge features without compromising usability demands continuous investment into infrastructure upgrades.[2] Cybersecurity remains paramount given increasing threats targeting sensitive personal & financial information stored within these systems—a responsibility requiring robust security protocols against breaches [7].
By proactively addressing these issues through innovation-driven strategies combined with strict compliance measures—and fostering transparent communication with their community—Investing.com's reputation continues strengthening amid dynamic global markets.
References
- Recent expansion into cryptocurrency coverage reflects broader industry trends.
- Upgrades improve mobile app performance & visual analytics.
- Increased engagement among younger investors driven by intuitive design.
- Compliance ensures adherence to international regulations.
- Growing interest in digital assets prompts dedicated crypto sections.
- Market volatility impacts real-time data accuracy during crises.7.Cybersecurity risks necessitate advanced protection measures.
Keywords: investing website overview | financial markets data | cryptocurrency coverage | real-time stock quotes | investment tools | online trading platforms
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Where Can You Find TradingView’s Roadmap? A Complete Guide
Understanding the future direction of TradingView is essential for traders, investors, and financial technology enthusiasts. The platform’s roadmap provides insights into upcoming features, technological advancements, and strategic initiatives that shape its growth. If you're wondering where to access this vital document or overview, this guide will help clarify how and where to find TradingView’s roadmap while offering context on its importance.
Accessing TradingView’s Roadmap: Official Sources
TradingView does not publish a detailed, publicly accessible roadmap in the traditional sense like some tech companies do. Instead, users can find information about the platform's future plans through several official channels:
Company Announcements and Blog Posts: TradingView regularly shares updates about new features or strategic initiatives via their official blog or news section on their website. These posts often highlight upcoming developments aligned with their broader roadmap.
Product Updates Section: Within the platform itself or on their support pages, there are dedicated sections where they announce new releases and improvements. While not a comprehensive roadmap per se, these updates reflect ongoing projects.
Social Media Channels: Platforms such as Twitter and LinkedIn serve as channels for real-time announcements from TradingView leadership regarding upcoming features or partnerships that hint at future directions.
Investor Relations (if applicable): For publicly traded companies or those with investor relations pages—though TradingView is privately held—they may occasionally share strategic outlooks during earnings calls or investor presentations.
Why Is It Important to Know Where to Find the Roadmap?
Having access to a company's roadmap helps users understand what innovations are coming next and how they might benefit from them. For traders relying heavily on technical analysis tools like advanced charting capabilities or AI-powered insights—knowing when these features will be released allows better planning of trading strategies.
Moreover, transparency about development priorities builds trust among users who want assurance that the platform remains competitive amid rapid technological changes in fintech sectors such as cryptocurrency integration and machine learning enhancements.
How Does TradingView Communicate Its Future Plans?
While an explicit public-facing detailed roadmap isn't always available in one centralized document online—like some software giants provide—TradingView communicates its strategic focus through various channels:
Feature Rollouts & Announcements: Regularly updating users via email newsletters and within-platform notifications about new tools like crypto-specific indicators.
Community Engagement Initiatives: Soliciting feedback through forums ensures user needs influence development priorities; this indirect insight hints at future plans.
Partnership Announcements: Collaborations with data providers or fintech firms often signal areas of expansion reflected in upcoming features.
Event Participation & Industry Conferences: Presentations at industry events sometimes reveal long-term visions for product evolution.
Where Can Traders See Upcoming Features?
For traders eager to anticipate what improvements are around the corner:
Check out TradingView's Official Blog for detailed articles discussing recent upgrades which often include hints toward future developments.
Follow TradingView's social media profiles for quick updates on feature launches.
Review community forums such as TradingView Community, where beta testers sometimes share insights into forthcoming functionalities based on early access programs.
The Role of User Feedback in Shaping Future Developments
A key aspect of understanding where you can find parts of TradingView’s evolving plan lies in recognizing how user input influences development priorities. The company actively seeks feedback via surveys and forum discussions; many planned enhancements stem directly from community suggestions—especially around mobile app improvements, crypto integrations, or AI-driven analysis tools.
By participating actively within these platforms—and staying informed—you gain insight into potential feature releases before they become widely available.
Monitoring Market Trends Through Public Disclosures
Although specific details may not be published openly as a formal "roadmap," observing industry trends helps infer possible directions:
The surge in cryptocurrency trading has prompted extensive crypto-specific indicator additions recently announced by TradingView.
Advances in artificial intelligence suggest ongoing investments aimed at predictive analytics enhancement.
Strategic partnerships indicate potential integrations with other fintech services expanding overall functionality.
In summary,
While you might not find a single downloadable "Trading View Roadmap" document readily available online, multiple sources collectively provide valuable insights into its developmental trajectory—from official blogs and social media updates to community forums emphasizing user-driven innovation efforts. Staying engaged across these platforms ensures you remain informed about upcoming features that could impact your trading strategies significantly.
Key Takeaways
Official Channels: Keep an eye on Trading View's blog posts, social media accounts (Twitter/LinkedIn), support pages, and community forums for latest announcements related to product upgrades.*
Community Insights: Active participation allows you to gauge user sentiment influencing future developments.*
Market Trends & Partnerships: Observing industry shifts offers clues regarding potential feature expansions.*
By understanding where these communications occur—and engaging regularly—you position yourself advantageously within an evolving ecosystem designed around trader success.
Semantic & LSI Keywords:
Trade Platform Development Timeline | Financial Technology Innovation | Cryptocurrency Market Integration | Technical Analysis Tools Updates | Trader Community Feedback | Fintech Partnerships News | Real-Time Market Data Enhancements


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-26 17:00
Where can you find TradingView’s roadmap?
Where Can You Find TradingView’s Roadmap? A Complete Guide
Understanding the future direction of TradingView is essential for traders, investors, and financial technology enthusiasts. The platform’s roadmap provides insights into upcoming features, technological advancements, and strategic initiatives that shape its growth. If you're wondering where to access this vital document or overview, this guide will help clarify how and where to find TradingView’s roadmap while offering context on its importance.
Accessing TradingView’s Roadmap: Official Sources
TradingView does not publish a detailed, publicly accessible roadmap in the traditional sense like some tech companies do. Instead, users can find information about the platform's future plans through several official channels:
Company Announcements and Blog Posts: TradingView regularly shares updates about new features or strategic initiatives via their official blog or news section on their website. These posts often highlight upcoming developments aligned with their broader roadmap.
Product Updates Section: Within the platform itself or on their support pages, there are dedicated sections where they announce new releases and improvements. While not a comprehensive roadmap per se, these updates reflect ongoing projects.
Social Media Channels: Platforms such as Twitter and LinkedIn serve as channels for real-time announcements from TradingView leadership regarding upcoming features or partnerships that hint at future directions.
Investor Relations (if applicable): For publicly traded companies or those with investor relations pages—though TradingView is privately held—they may occasionally share strategic outlooks during earnings calls or investor presentations.
Why Is It Important to Know Where to Find the Roadmap?
Having access to a company's roadmap helps users understand what innovations are coming next and how they might benefit from them. For traders relying heavily on technical analysis tools like advanced charting capabilities or AI-powered insights—knowing when these features will be released allows better planning of trading strategies.
Moreover, transparency about development priorities builds trust among users who want assurance that the platform remains competitive amid rapid technological changes in fintech sectors such as cryptocurrency integration and machine learning enhancements.
How Does TradingView Communicate Its Future Plans?
While an explicit public-facing detailed roadmap isn't always available in one centralized document online—like some software giants provide—TradingView communicates its strategic focus through various channels:
Feature Rollouts & Announcements: Regularly updating users via email newsletters and within-platform notifications about new tools like crypto-specific indicators.
Community Engagement Initiatives: Soliciting feedback through forums ensures user needs influence development priorities; this indirect insight hints at future plans.
Partnership Announcements: Collaborations with data providers or fintech firms often signal areas of expansion reflected in upcoming features.
Event Participation & Industry Conferences: Presentations at industry events sometimes reveal long-term visions for product evolution.
Where Can Traders See Upcoming Features?
For traders eager to anticipate what improvements are around the corner:
Check out TradingView's Official Blog for detailed articles discussing recent upgrades which often include hints toward future developments.
Follow TradingView's social media profiles for quick updates on feature launches.
Review community forums such as TradingView Community, where beta testers sometimes share insights into forthcoming functionalities based on early access programs.
The Role of User Feedback in Shaping Future Developments
A key aspect of understanding where you can find parts of TradingView’s evolving plan lies in recognizing how user input influences development priorities. The company actively seeks feedback via surveys and forum discussions; many planned enhancements stem directly from community suggestions—especially around mobile app improvements, crypto integrations, or AI-driven analysis tools.
By participating actively within these platforms—and staying informed—you gain insight into potential feature releases before they become widely available.
Monitoring Market Trends Through Public Disclosures
Although specific details may not be published openly as a formal "roadmap," observing industry trends helps infer possible directions:
The surge in cryptocurrency trading has prompted extensive crypto-specific indicator additions recently announced by TradingView.
Advances in artificial intelligence suggest ongoing investments aimed at predictive analytics enhancement.
Strategic partnerships indicate potential integrations with other fintech services expanding overall functionality.
In summary,
While you might not find a single downloadable "Trading View Roadmap" document readily available online, multiple sources collectively provide valuable insights into its developmental trajectory—from official blogs and social media updates to community forums emphasizing user-driven innovation efforts. Staying engaged across these platforms ensures you remain informed about upcoming features that could impact your trading strategies significantly.
Key Takeaways
Official Channels: Keep an eye on Trading View's blog posts, social media accounts (Twitter/LinkedIn), support pages, and community forums for latest announcements related to product upgrades.*
Community Insights: Active participation allows you to gauge user sentiment influencing future developments.*
Market Trends & Partnerships: Observing industry shifts offers clues regarding potential feature expansions.*
By understanding where these communications occur—and engaging regularly—you position yourself advantageously within an evolving ecosystem designed around trader success.
Semantic & LSI Keywords:
Trade Platform Development Timeline | Financial Technology Innovation | Cryptocurrency Market Integration | Technical Analysis Tools Updates | Trader Community Feedback | Fintech Partnerships News | Real-Time Market Data Enhancements
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Many Chains Does Zapper Support?
Understanding the scope of blockchain compatibility in DeFi platforms is essential for investors and developers alike. Zapper, a prominent player in the decentralized finance ecosystem, has gained recognition for its ability to streamline asset management across multiple blockchain networks. This article explores how many chains Zapper supports, the significance of this multi-chain functionality, recent updates, and potential challenges associated with supporting numerous blockchains.
What Is Zapper and Its Role in DeFi?
Zapper functions as an all-in-one dashboard designed to simplify interaction with various DeFi protocols. It provides users with a centralized interface to view their crypto holdings, manage liquidity pools, yield farming positions, and lending activities without navigating multiple platforms or wallets. By integrating numerous blockchain networks into one platform, Zapper enhances user experience and promotes portfolio diversification—a core principle in risk management within decentralized finance.
The platform's primary appeal lies in its ability to connect different chains seamlessly. This cross-chain support allows users to access opportunities on Ethereum’s vast ecosystem while also exploring emerging protocols on other blockchains like Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Polygon (MATIC), Avalanche (AVAX), Solana (SOL), Polkadot (DOT), and Cosmos (ATOM).
How Many Blockchain Networks Does Zapper Support?
As of recent updates—up through 2025—Zapper supports over seven major blockchain networks:
- Ethereum (ETH): The foundational network for most DeFi activity.
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC): Known for low transaction fees and fast processing times.
- Polygon (MATIC): A layer 2 scaling solution that reduces congestion on Ethereum.
- Avalanche (AVAX): Offers high throughput with quick finality.
- Solana (SOL): Recognized for high performance and rapid transactions.
- Polkadot (DOT): Focused on interoperability between different blockchains.
- Cosmos (ATOM): A network facilitating communication among independent chains.
This list reflects a strategic focus on both established giants like Ethereum and emerging ecosystems such as Solana or Avalanche that are gaining traction due to their scalability advantages.
The Importance of Multi-Chain Support in DeFi
Supporting multiple chains is not merely a technical feature but a strategic necessity within the broader context of decentralized finance. Investors increasingly seek diversified exposure across various tokens and protocols hosted on different blockchains. Multi-chain compatibility enables them to:
- Access diverse investment opportunities
- Reduce dependency on any single network
- Optimize transaction costs by choosing cheaper networks
- Participate in niche ecosystems that may offer higher yields or unique assets
For platforms like Zapper, this multi-chain approach broadens their user base by accommodating users from different regions who prefer specific chains due to regulatory reasons or local infrastructure preferences.
Recent Developments Enhancing Chain Support
Over recent years, Zapper has actively expanded its chain support through several key initiatives:
Expansion into New Blockchains
In 2023–2024, Zapper extended support beyond traditional Ethereum-based assets by integrating with newer ecosystems such as Avalanche and Solana—both known for their scalability solutions tailored toward high-performance applications.
Protocol Integrations
The platform has also incorporated popular lending protocols like Aave and Compound during 2024—allowing users not only to view assets but also seamlessly lend or borrow cryptocurrencies directly from within the interface.
User Interface Improvements
To enhance usability amid increasing complexity from supporting more chains:
- Real-time price tracking
- Simplified navigation
- Enhanced security features
have been introduced progressively throughout 2024–2025.
These upgrades aim at maintaining performance standards despite expanding protocol integrations across diverse networks.
Challenges Associated With Supporting Multiple Chains
While multi-chain support offers significant benefits—including increased flexibility—it introduces notable risks:
Security Concerns
Each added chain presents unique vulnerabilities; smart contract bugs or exploits can compromise user funds if not properly managed or audited thoroughly across all supported networks.
Regulatory Risks
DeFi’s evolving legal landscape could impact certain chains differently depending upon jurisdictional regulations concerning tokens or protocol operations—potentially limiting access based on geographic location or compliance issues.
Scalability & Performance Issues
Handling data from several active blockchains demands robust infrastructure; failure here could lead to delays in portfolio updates or transaction processing errors affecting user trustworthiness over time.
Future Outlook: Expanding Cross-Chain Capabilities
Looking ahead into 2025–2026, platforms like Zapper are expected to further broaden their chain integrations as new ecosystems emerge—and existing ones improve scalability features—for example:
- Integration with additional Layer 2 solutions such as Arbitrum
- Inclusion of other interoperability-focused projects
- Enhanced security measures leveraging cross-chain bridges
Such developments will likely make multi-chain management even more seamless while addressing current limitations related to security risks.
By understanding how many chains ZAPPER supports—and why this matters—you gain insight into its role within the broader DeFi landscape. As it continues expanding its reach across diverse blockchain environments while balancing security concerns—a critical aspect rooted deeply in industry best practices—it remains well-positioned as an essential tool for modern crypto investors seeking comprehensive asset management solutions across multiple ecosystems.
If you’re considering using platforms like ZAPPER for managing your digital assets efficiently across various blockchains—or evaluating future investment opportunities—their ongoing expansion underscores the importance of versatile tools capable of navigating today’s complex decentralized environment effectively.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-26 16:24
How many chains does Zapper support?
How Many Chains Does Zapper Support?
Understanding the scope of blockchain compatibility in DeFi platforms is essential for investors and developers alike. Zapper, a prominent player in the decentralized finance ecosystem, has gained recognition for its ability to streamline asset management across multiple blockchain networks. This article explores how many chains Zapper supports, the significance of this multi-chain functionality, recent updates, and potential challenges associated with supporting numerous blockchains.
What Is Zapper and Its Role in DeFi?
Zapper functions as an all-in-one dashboard designed to simplify interaction with various DeFi protocols. It provides users with a centralized interface to view their crypto holdings, manage liquidity pools, yield farming positions, and lending activities without navigating multiple platforms or wallets. By integrating numerous blockchain networks into one platform, Zapper enhances user experience and promotes portfolio diversification—a core principle in risk management within decentralized finance.
The platform's primary appeal lies in its ability to connect different chains seamlessly. This cross-chain support allows users to access opportunities on Ethereum’s vast ecosystem while also exploring emerging protocols on other blockchains like Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Polygon (MATIC), Avalanche (AVAX), Solana (SOL), Polkadot (DOT), and Cosmos (ATOM).
How Many Blockchain Networks Does Zapper Support?
As of recent updates—up through 2025—Zapper supports over seven major blockchain networks:
- Ethereum (ETH): The foundational network for most DeFi activity.
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC): Known for low transaction fees and fast processing times.
- Polygon (MATIC): A layer 2 scaling solution that reduces congestion on Ethereum.
- Avalanche (AVAX): Offers high throughput with quick finality.
- Solana (SOL): Recognized for high performance and rapid transactions.
- Polkadot (DOT): Focused on interoperability between different blockchains.
- Cosmos (ATOM): A network facilitating communication among independent chains.
This list reflects a strategic focus on both established giants like Ethereum and emerging ecosystems such as Solana or Avalanche that are gaining traction due to their scalability advantages.
The Importance of Multi-Chain Support in DeFi
Supporting multiple chains is not merely a technical feature but a strategic necessity within the broader context of decentralized finance. Investors increasingly seek diversified exposure across various tokens and protocols hosted on different blockchains. Multi-chain compatibility enables them to:
- Access diverse investment opportunities
- Reduce dependency on any single network
- Optimize transaction costs by choosing cheaper networks
- Participate in niche ecosystems that may offer higher yields or unique assets
For platforms like Zapper, this multi-chain approach broadens their user base by accommodating users from different regions who prefer specific chains due to regulatory reasons or local infrastructure preferences.
Recent Developments Enhancing Chain Support
Over recent years, Zapper has actively expanded its chain support through several key initiatives:
Expansion into New Blockchains
In 2023–2024, Zapper extended support beyond traditional Ethereum-based assets by integrating with newer ecosystems such as Avalanche and Solana—both known for their scalability solutions tailored toward high-performance applications.
Protocol Integrations
The platform has also incorporated popular lending protocols like Aave and Compound during 2024—allowing users not only to view assets but also seamlessly lend or borrow cryptocurrencies directly from within the interface.
User Interface Improvements
To enhance usability amid increasing complexity from supporting more chains:
- Real-time price tracking
- Simplified navigation
- Enhanced security features
have been introduced progressively throughout 2024–2025.
These upgrades aim at maintaining performance standards despite expanding protocol integrations across diverse networks.
Challenges Associated With Supporting Multiple Chains
While multi-chain support offers significant benefits—including increased flexibility—it introduces notable risks:
Security Concerns
Each added chain presents unique vulnerabilities; smart contract bugs or exploits can compromise user funds if not properly managed or audited thoroughly across all supported networks.
Regulatory Risks
DeFi’s evolving legal landscape could impact certain chains differently depending upon jurisdictional regulations concerning tokens or protocol operations—potentially limiting access based on geographic location or compliance issues.
Scalability & Performance Issues
Handling data from several active blockchains demands robust infrastructure; failure here could lead to delays in portfolio updates or transaction processing errors affecting user trustworthiness over time.
Future Outlook: Expanding Cross-Chain Capabilities
Looking ahead into 2025–2026, platforms like Zapper are expected to further broaden their chain integrations as new ecosystems emerge—and existing ones improve scalability features—for example:
- Integration with additional Layer 2 solutions such as Arbitrum
- Inclusion of other interoperability-focused projects
- Enhanced security measures leveraging cross-chain bridges
Such developments will likely make multi-chain management even more seamless while addressing current limitations related to security risks.
By understanding how many chains ZAPPER supports—and why this matters—you gain insight into its role within the broader DeFi landscape. As it continues expanding its reach across diverse blockchain environments while balancing security concerns—a critical aspect rooted deeply in industry best practices—it remains well-positioned as an essential tool for modern crypto investors seeking comprehensive asset management solutions across multiple ecosystems.
If you’re considering using platforms like ZAPPER for managing your digital assets efficiently across various blockchains—or evaluating future investment opportunities—their ongoing expansion underscores the importance of versatile tools capable of navigating today’s complex decentralized environment effectively.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Customizable Are TradingView Notifications?
TradingView has become a go-to platform for traders and investors worldwide, thanks to its powerful charting tools, social trading features, and real-time data. One of its standout features is the notification system, which helps users stay informed about market movements without constantly monitoring their screens. But just how customizable are these notifications? Let’s explore the depth of TradingView’s alert options, recent updates enhancing their flexibility, and some best practices to maximize their effectiveness.
Understanding TradingView's Notification System
At its core, TradingView offers a versatile notification system designed to keep traders updated on critical market events. Whether you're tracking specific price levels or technical indicator signals, the platform allows you to set alerts tailored precisely to your trading strategy. These notifications can be delivered via multiple channels—email alerts, mobile push notifications through the app, or third-party integrations like Discord and Telegram—making it easier for users to stay connected regardless of location.
This multi-channel approach ensures that traders receive timely updates in formats they prefer. For example, a day trader might rely on instant push notifications during active hours while an investor with longer-term positions might prefer email summaries sent after market close.
Customization Options for Alerts
TradingView provides several layers of customization that cater both to novice traders and advanced users:
Price Movement Alerts
One of the most straightforward alert types involves setting thresholds based on asset prices. Users can specify exact price points or ranges where they want alerts triggered—for instance, when a stock hits a support level or breaks through resistance.
Technical Indicator Alerts
For those who base decisions on technical analysis indicators such as RSI (Relative Strength Index), Moving Averages (MA), Bollinger Bands, etc., TradingView allows setting alerts when certain indicator conditions are met. For example:
- RSI crossing above 70 indicating overbought conditions.
- Moving average crossover signaling potential trend reversals.These enable more nuanced monitoring aligned with technical strategies.
Custom Scripts Using Pine Script
Advanced users can leverage Pine Script—a proprietary scripting language—to create highly personalized alerts based on complex criteria not covered by default options. This flexibility empowers traders who develop custom indicators or strategies tailored specifically to their trading style.
Notification Channels & Sensitivity Settings
Beyond what triggers an alert is how it's delivered:
- Channels: Email notifications for detailed summaries; mobile push for instant updates; third-party apps like Telegram or Discord for community sharing.
- Sensitivity Levels: Users can adjust alert sensitivity—such as setting wider thresholds—to reduce false positives caused by minor fluctuations in volatile markets.
Time-Based & Scheduled Alerts
Another layer of customization involves scheduling alerts at specific times—during particular hours or days—ensuring you’re notified only when it matters most during your active trading periods.
Recent Enhancements Improving Alert Flexibility
TradingView continually evolves its notification capabilities:
Enhanced Pine Script Features: Recent updates have expanded Pine Script functionalities allowing developers and advanced traders to craft more sophisticated scripts that generate precise alerts based on complex conditions.
Third-Party Integration Expansion: The platform now supports seamless integration with popular messaging services like Discord and Telegram — enabling real-time sharing within communities or automated workflows.
User Interface Improvements: Setting up and managing alerts has become more intuitive thanks to streamlined UI changes aimed at reducing complexity for new users while providing granular control for experienced ones.
Community Contributions: The vibrant TradingView community regularly shares custom scripts and strategies that include pre-built alert systems—these resources help less experienced traders implement advanced notification setups quickly.
Risks & Limitations of Highly Customized Notifications
While extensive customization enhances usability significantly—and offers tailored insights—it also introduces some risks:
Information Overload: Setting too many alerts across various assets may lead to constant interruptions—a phenomenon known as “alert fatigue.” This overload can cause important signals being missed amid noise.
False Positives & Sensitivity Issues: Improperly calibrated sensitivity settings may trigger unnecessary alarms due to minor price swings or indicator fluctuations—not reflective of meaningful market moves—which wastes time investigating irrelevant events.
Security Concerns: Although TradingView employs robust security measures—including encrypted data transmission—the use of custom scripts introduces potential vulnerabilities if malicious code is inadvertently integrated into user-created scripts.
Dependence on Platform Stability: Relying heavily on automated notifications means any platform downtime could delay critical information delivery—a risk mitigated by having backup plans such as manual monitoring methods during outages.
Best Practices for Effective Use of Notifications
To maximize benefits while minimizing drawbacks:
- Regularly review your alert list; disable unnecessary ones that no longer serve your strategy.
- Fine-tune sensitivity levels carefully; start with broader thresholds then narrow down based on performance feedback.
- Combine multiple types (price-based + indicator-based) cautiously rather than overwhelming yourself with numerous simultaneous triggers.
- Test new scripts thoroughly before deploying them live in high-stakes environments—they should accurately reflect intended conditions without false triggers.
- Stay updated with platform enhancements so you can leverage new features effectively as they roll out.
By understanding these aspects deeply rooted in user needs—and aligning them with best practices—you ensure that TradingView’s customizable notification system becomes an effective tool rather than an overwhelming source of distraction.
In summary, TradingView offers highly flexible options for customizing notifications—from simple price level alarms all the way up to complex scripted triggers integrated across multiple channels. Its ongoing improvements continue expanding these capabilities while emphasizing ease-of-use alongside depth of control suited both beginners and seasoned professionals alike. When managed thoughtfully—with attention paid toward avoiding overloads—you gain a strategic edge through timely insights delivered exactly how you need them most in today’s fast-paced markets.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-26 14:46
How customizable are TradingView notifications?
How Customizable Are TradingView Notifications?
TradingView has become a go-to platform for traders and investors worldwide, thanks to its powerful charting tools, social trading features, and real-time data. One of its standout features is the notification system, which helps users stay informed about market movements without constantly monitoring their screens. But just how customizable are these notifications? Let’s explore the depth of TradingView’s alert options, recent updates enhancing their flexibility, and some best practices to maximize their effectiveness.
Understanding TradingView's Notification System
At its core, TradingView offers a versatile notification system designed to keep traders updated on critical market events. Whether you're tracking specific price levels or technical indicator signals, the platform allows you to set alerts tailored precisely to your trading strategy. These notifications can be delivered via multiple channels—email alerts, mobile push notifications through the app, or third-party integrations like Discord and Telegram—making it easier for users to stay connected regardless of location.
This multi-channel approach ensures that traders receive timely updates in formats they prefer. For example, a day trader might rely on instant push notifications during active hours while an investor with longer-term positions might prefer email summaries sent after market close.
Customization Options for Alerts
TradingView provides several layers of customization that cater both to novice traders and advanced users:
Price Movement Alerts
One of the most straightforward alert types involves setting thresholds based on asset prices. Users can specify exact price points or ranges where they want alerts triggered—for instance, when a stock hits a support level or breaks through resistance.
Technical Indicator Alerts
For those who base decisions on technical analysis indicators such as RSI (Relative Strength Index), Moving Averages (MA), Bollinger Bands, etc., TradingView allows setting alerts when certain indicator conditions are met. For example:
- RSI crossing above 70 indicating overbought conditions.
- Moving average crossover signaling potential trend reversals.These enable more nuanced monitoring aligned with technical strategies.
Custom Scripts Using Pine Script
Advanced users can leverage Pine Script—a proprietary scripting language—to create highly personalized alerts based on complex criteria not covered by default options. This flexibility empowers traders who develop custom indicators or strategies tailored specifically to their trading style.
Notification Channels & Sensitivity Settings
Beyond what triggers an alert is how it's delivered:
- Channels: Email notifications for detailed summaries; mobile push for instant updates; third-party apps like Telegram or Discord for community sharing.
- Sensitivity Levels: Users can adjust alert sensitivity—such as setting wider thresholds—to reduce false positives caused by minor fluctuations in volatile markets.
Time-Based & Scheduled Alerts
Another layer of customization involves scheduling alerts at specific times—during particular hours or days—ensuring you’re notified only when it matters most during your active trading periods.
Recent Enhancements Improving Alert Flexibility
TradingView continually evolves its notification capabilities:
Enhanced Pine Script Features: Recent updates have expanded Pine Script functionalities allowing developers and advanced traders to craft more sophisticated scripts that generate precise alerts based on complex conditions.
Third-Party Integration Expansion: The platform now supports seamless integration with popular messaging services like Discord and Telegram — enabling real-time sharing within communities or automated workflows.
User Interface Improvements: Setting up and managing alerts has become more intuitive thanks to streamlined UI changes aimed at reducing complexity for new users while providing granular control for experienced ones.
Community Contributions: The vibrant TradingView community regularly shares custom scripts and strategies that include pre-built alert systems—these resources help less experienced traders implement advanced notification setups quickly.
Risks & Limitations of Highly Customized Notifications
While extensive customization enhances usability significantly—and offers tailored insights—it also introduces some risks:
Information Overload: Setting too many alerts across various assets may lead to constant interruptions—a phenomenon known as “alert fatigue.” This overload can cause important signals being missed amid noise.
False Positives & Sensitivity Issues: Improperly calibrated sensitivity settings may trigger unnecessary alarms due to minor price swings or indicator fluctuations—not reflective of meaningful market moves—which wastes time investigating irrelevant events.
Security Concerns: Although TradingView employs robust security measures—including encrypted data transmission—the use of custom scripts introduces potential vulnerabilities if malicious code is inadvertently integrated into user-created scripts.
Dependence on Platform Stability: Relying heavily on automated notifications means any platform downtime could delay critical information delivery—a risk mitigated by having backup plans such as manual monitoring methods during outages.
Best Practices for Effective Use of Notifications
To maximize benefits while minimizing drawbacks:
- Regularly review your alert list; disable unnecessary ones that no longer serve your strategy.
- Fine-tune sensitivity levels carefully; start with broader thresholds then narrow down based on performance feedback.
- Combine multiple types (price-based + indicator-based) cautiously rather than overwhelming yourself with numerous simultaneous triggers.
- Test new scripts thoroughly before deploying them live in high-stakes environments—they should accurately reflect intended conditions without false triggers.
- Stay updated with platform enhancements so you can leverage new features effectively as they roll out.
By understanding these aspects deeply rooted in user needs—and aligning them with best practices—you ensure that TradingView’s customizable notification system becomes an effective tool rather than an overwhelming source of distraction.
In summary, TradingView offers highly flexible options for customizing notifications—from simple price level alarms all the way up to complex scripted triggers integrated across multiple channels. Its ongoing improvements continue expanding these capabilities while emphasizing ease-of-use alongside depth of control suited both beginners and seasoned professionals alike. When managed thoughtfully—with attention paid toward avoiding overloads—you gain a strategic edge through timely insights delivered exactly how you need them most in today’s fast-paced markets.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, represents a transformative shift in the way financial services are delivered and accessed. Unlike traditional banking and financial systems that rely on centralized institutions such as banks, credit unions, or brokerages, DeFi leverages blockchain technology to create open, permissionless financial applications accessible to anyone with an internet connection. This innovation aims to democratize finance by removing intermediaries and reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
At its core, DeFi encompasses a broad ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps) built primarily on blockchain networks like Ethereum. These applications facilitate various financial activities—lending and borrowing digital assets, trading cryptocurrencies through decentralized exchanges (DEXs), issuing stablecoins pegged to fiat currencies for stability, creating prediction markets for event outcomes, and implementing yield farming strategies that generate passive income.
The primary appeal of DeFi lies in its transparency and security. Transactions are recorded on public blockchains where they can be audited by anyone at any time. Smart contracts—self-executing code stored on the blockchain—automate processes without human intervention. This setup minimizes counterparty risk while providing users with greater control over their assets.
Key Components of DeFi
Understanding the main building blocks of DeFi helps clarify how this ecosystem functions:
Lending Protocols: Platforms like Aave and Compound enable users to lend their cryptocurrencies or borrow against collateral. These protocols operate via smart contracts that automatically manage interest rates based on supply-demand dynamics.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Uniswap and SushiSwap exemplify DEX platforms where users trade tokens directly from their wallets using liquidity pools instead of relying on centralized order books.
Stablecoins: Digital assets such as USDT (Tether) and USDC provide price stability within volatile crypto markets by being pegged 1:1 to fiat currencies like USD.
Prediction Markets: Platforms like Augur allow participants to bet on future events' outcomes—ranging from elections to sports results—in a decentralized manner.
Yield Farming: Users provide liquidity or stake tokens in protocols in exchange for rewards or interest payments—a strategy that has driven significant liquidity into DeFi platforms.
The Rise of DeFi: Context & Drivers
Several factors have fueled the rapid growth of Decentralized Finance over recent years:
Advancements in Blockchain Technology: The development of scalable smart contract platforms such as Ethereum has provided a robust foundation for building complex dApps.
Growing Cryptocurrency Adoption: As more individuals become comfortable with digital assets, demand for innovative ways to utilize these assets increases.
Favorable Regulatory Trends: While regulatory clarity remains evolving globally, increasing acceptance by some jurisdictions encourages innovation within legal frameworks.
Financial Inclusion Goals: By removing barriers associated with traditional banking—such as geographic restrictions or credit requirements—DeFi aims to serve unbanked populations worldwide.
Recent Developments Shaping the Ecosystem
The trajectory of DeFi has seen notable milestones:
The 2020 "Yield Farming Boom" marked an era where users rapidly moved funds across protocols seeking high returns through staking or liquidity provision strategies.
During "DeFi Summer" 2020—a period characterized by explosive growth—the number of active protocols surged alongside total value locked (TVL), reflecting increased user engagement.
However, this expansion exposed vulnerabilities; multiple smart contract exploits occurred during this period—including high-profile hacks—that underscored security challenges inherent in complex codebases.
Regulatory attention also intensified around 2021 when agencies like the U.S Securities and Exchange Commission issued warnings about potential risks associated with certain DeFi activities—including unregistered securities offerings—and called for greater oversight.
Meanwhile, efforts are underway integrating traditional finance elements into the ecosystem through CeFI (Centralized Finance) bridges designed to combine benefits from both worlds—for example: enabling fiat-to-DeFI conversions seamlessly while maintaining compliance standards.
Potential Challenges Facing DeFI
Despite its promising outlook—and significant innovations—the sector faces several hurdles:
Security Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities remain one of the most pressing concerns; exploits can lead to substantial asset losses—as seen during past incidents involving flash loan attacks or coding bugs—which damage trust among users.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear legal frameworks creates ambiguity around compliance obligations; stricter regulations could limit certain activities or impose new operational constraints affecting growth prospects.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices tend toward high fluctuation levels; volatile asset values can impact collateralization ratios within lending protocols or cause sudden swings in protocol TVL metrics impacting overall stability.
Scalability Issues: Current blockchain networks face congestion issues leading to higher transaction fees ("gas fees") which may deter small investors from participating actively across multiple platforms simultaneously—a challenge that solutions like layer-two scaling aim address but are still under development.
User Education & Accessibility: The complexity inherent in understanding smart contracts—even basic concepts related thereto—is often daunting for newcomers; inadequate education may result in mistakes causing loss—or mismanagement—of funds if proper precautions aren’t taken.
Building Trust Through E-A-T Principles
For readers seeking trustworthy insights into DeFi’s landscape—from investors evaluating opportunities—to developers aiming at secure protocol design—it’s essential that information is accurate (“Expertise”), transparent (“Authoritativeness”), and current (“Trustworthiness”). Recognizing reputable sources such as industry leaders’ reports—from CoinDesk's analyses to academic research published by Harvard Business Review—is vital when navigating this fast-changing environment.
Looking Ahead: Opportunities & Risks
As it continues evolving rapidly—with innovations like cross-chain interoperability expanding options—the potential benefits include increased financial inclusion worldwide along with new investment avenues beyond traditional markets. However—and equally important—it’s crucial not overlook risks related especially to security breaches or regulatory crackdowns which could hinder progress if not managed proactively.
Summary
Decentralized Finance stands at an exciting crossroads: offering unprecedented access points into global finance while challenging established institutions’ dominance. Its success depends heavily upon addressing key issues surrounding security vulnerabilities, regulatory clarity—and ensuring user education keeps pace with technological advancements—all critical factors shaping its future trajectory within mainstream finance ecosystems


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 19:45
What exactly is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, represents a transformative shift in the way financial services are delivered and accessed. Unlike traditional banking and financial systems that rely on centralized institutions such as banks, credit unions, or brokerages, DeFi leverages blockchain technology to create open, permissionless financial applications accessible to anyone with an internet connection. This innovation aims to democratize finance by removing intermediaries and reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
At its core, DeFi encompasses a broad ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps) built primarily on blockchain networks like Ethereum. These applications facilitate various financial activities—lending and borrowing digital assets, trading cryptocurrencies through decentralized exchanges (DEXs), issuing stablecoins pegged to fiat currencies for stability, creating prediction markets for event outcomes, and implementing yield farming strategies that generate passive income.
The primary appeal of DeFi lies in its transparency and security. Transactions are recorded on public blockchains where they can be audited by anyone at any time. Smart contracts—self-executing code stored on the blockchain—automate processes without human intervention. This setup minimizes counterparty risk while providing users with greater control over their assets.
Key Components of DeFi
Understanding the main building blocks of DeFi helps clarify how this ecosystem functions:
Lending Protocols: Platforms like Aave and Compound enable users to lend their cryptocurrencies or borrow against collateral. These protocols operate via smart contracts that automatically manage interest rates based on supply-demand dynamics.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Uniswap and SushiSwap exemplify DEX platforms where users trade tokens directly from their wallets using liquidity pools instead of relying on centralized order books.
Stablecoins: Digital assets such as USDT (Tether) and USDC provide price stability within volatile crypto markets by being pegged 1:1 to fiat currencies like USD.
Prediction Markets: Platforms like Augur allow participants to bet on future events' outcomes—ranging from elections to sports results—in a decentralized manner.
Yield Farming: Users provide liquidity or stake tokens in protocols in exchange for rewards or interest payments—a strategy that has driven significant liquidity into DeFi platforms.
The Rise of DeFi: Context & Drivers
Several factors have fueled the rapid growth of Decentralized Finance over recent years:
Advancements in Blockchain Technology: The development of scalable smart contract platforms such as Ethereum has provided a robust foundation for building complex dApps.
Growing Cryptocurrency Adoption: As more individuals become comfortable with digital assets, demand for innovative ways to utilize these assets increases.
Favorable Regulatory Trends: While regulatory clarity remains evolving globally, increasing acceptance by some jurisdictions encourages innovation within legal frameworks.
Financial Inclusion Goals: By removing barriers associated with traditional banking—such as geographic restrictions or credit requirements—DeFi aims to serve unbanked populations worldwide.
Recent Developments Shaping the Ecosystem
The trajectory of DeFi has seen notable milestones:
The 2020 "Yield Farming Boom" marked an era where users rapidly moved funds across protocols seeking high returns through staking or liquidity provision strategies.
During "DeFi Summer" 2020—a period characterized by explosive growth—the number of active protocols surged alongside total value locked (TVL), reflecting increased user engagement.
However, this expansion exposed vulnerabilities; multiple smart contract exploits occurred during this period—including high-profile hacks—that underscored security challenges inherent in complex codebases.
Regulatory attention also intensified around 2021 when agencies like the U.S Securities and Exchange Commission issued warnings about potential risks associated with certain DeFi activities—including unregistered securities offerings—and called for greater oversight.
Meanwhile, efforts are underway integrating traditional finance elements into the ecosystem through CeFI (Centralized Finance) bridges designed to combine benefits from both worlds—for example: enabling fiat-to-DeFI conversions seamlessly while maintaining compliance standards.
Potential Challenges Facing DeFI
Despite its promising outlook—and significant innovations—the sector faces several hurdles:
Security Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities remain one of the most pressing concerns; exploits can lead to substantial asset losses—as seen during past incidents involving flash loan attacks or coding bugs—which damage trust among users.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear legal frameworks creates ambiguity around compliance obligations; stricter regulations could limit certain activities or impose new operational constraints affecting growth prospects.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices tend toward high fluctuation levels; volatile asset values can impact collateralization ratios within lending protocols or cause sudden swings in protocol TVL metrics impacting overall stability.
Scalability Issues: Current blockchain networks face congestion issues leading to higher transaction fees ("gas fees") which may deter small investors from participating actively across multiple platforms simultaneously—a challenge that solutions like layer-two scaling aim address but are still under development.
User Education & Accessibility: The complexity inherent in understanding smart contracts—even basic concepts related thereto—is often daunting for newcomers; inadequate education may result in mistakes causing loss—or mismanagement—of funds if proper precautions aren’t taken.
Building Trust Through E-A-T Principles
For readers seeking trustworthy insights into DeFi’s landscape—from investors evaluating opportunities—to developers aiming at secure protocol design—it’s essential that information is accurate (“Expertise”), transparent (“Authoritativeness”), and current (“Trustworthiness”). Recognizing reputable sources such as industry leaders’ reports—from CoinDesk's analyses to academic research published by Harvard Business Review—is vital when navigating this fast-changing environment.
Looking Ahead: Opportunities & Risks
As it continues evolving rapidly—with innovations like cross-chain interoperability expanding options—the potential benefits include increased financial inclusion worldwide along with new investment avenues beyond traditional markets. However—and equally important—it’s crucial not overlook risks related especially to security breaches or regulatory crackdowns which could hinder progress if not managed proactively.
Summary
Decentralized Finance stands at an exciting crossroads: offering unprecedented access points into global finance while challenging established institutions’ dominance. Its success depends heavily upon addressing key issues surrounding security vulnerabilities, regulatory clarity—and ensuring user education keeps pace with technological advancements—all critical factors shaping its future trajectory within mainstream finance ecosystems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Key Metrics Should You Track in Cryptocurrency and Investment?
Understanding the fundamentals of cryptocurrency markets requires more than just watching price charts. To make informed investment decisions, it’s essential to monitor key metrics that reflect the health, activity, and potential of digital assets. Among these, market capitalization (market cap), trading volume, and total value locked (TVL) stand out as critical indicators. This article explores each metric in detail to help investors grasp their significance and how they can be used effectively.
Market Capitalization: Gauging Size and Stability
Market cap is a straightforward yet powerful metric that indicates the total value of all circulating coins for a given cryptocurrency. It is calculated by multiplying the current price per coin by the total number of coins in circulation. For example, Bitcoin’s market cap reflects its dominance as a leading digital asset—often considered a benchmark for the entire crypto space.
Investors use market cap to assess relative size among cryptocurrencies. Larger market caps generally suggest greater stability because these assets tend to be less volatile compared to smaller ones. Bitcoin's position at the top exemplifies this trend; its extensive adoption and liquidity contribute to its status as a 'safe' choice within volatile markets.
However, it's important to recognize that market cap alone doesn't tell the full story about an asset's potential or risk profile. Rapid changes in price can cause significant fluctuations in market cap rankings—altcoins may surge or decline quickly due to speculative activity or technological developments.
Trading Volume: Measuring Market Activity
Trading volume refers to how many units of a cryptocurrency are bought and sold over a specific period—typically 24 hours. This metric provides insight into liquidity—the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without impacting its price significantly—and overall market interest.
High trading volumes often indicate strong investor interest or increased participation from traders seeking short-term gains through technical analysis strategies. For instance, during periods of heightened buying activity—such as bullish runs—trading volume tends to spike alongside rising prices, signaling robust demand.
Conversely, low trading volumes may suggest limited liquidity which can lead to slippage—a situation where executing large trades causes unfavorable price movements—and increased volatility risks. Traders frequently analyze volume patterns together with other indicators like moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index) for better prediction accuracy regarding future price trends.
Regulatory developments also influence trading volumes; stricter regulations might suppress activity temporarily while regulatory clarity could boost confidence and participation over time.
Total Value Locked: Assessing DeFi Ecosystem Health
While traditional cryptocurrencies focus on their circulating supply and valuation metrics like market cap, decentralized finance (DeFi) introduces another vital indicator: Total Value Locked (TVL). TVL measures how much capital—in USD equivalent—is actively staked or deposited across various DeFi protocols such as lending platforms (Aave), decentralized exchanges (Uniswap), yield farming projects, among others.
This metric serves as an indicator of ecosystem vitality; higher TVL suggests active user engagement with DeFi applications indicating trustworthiness and growth potential within these platforms. Ethereum remains dominant here due to its extensive network supporting numerous protocols; however, alternative blockchains like Binance Smart Chain have gained traction thanks to lower transaction fees attracting more users seeking yield opportunities.
Monitoring TVL helps investors understand not only ecosystem adoption but also risk exposure since high TVL levels could mean larger pools susceptible if security breaches occur—or conversely signal healthy protocol usage that supports long-term sustainability when managed properly.
Recent Trends Impacting These Metrics
The landscape of cryptocurrency markets is dynamic—with fluctuations driven by macroeconomic factors such as global economic uncertainty during events like COVID-19 pandemic periods boosting Bitcoin’s appeal as a store-of-value asset leading up increases in both market caps and trading volumes globally.
Regulatory shifts continue shaping investor behavior; stricter rules introduced by governments can reduce trading activities temporarily but might also legitimize certain assets over time—potentially stabilizing markets once compliance frameworks are established.
In DeFi sectors specifically, Ethereum’s dominance persists owing largely to its rich ecosystem supporting innovative financial products—but newer chains like Binance Smart Chain have rapidly grown their TVLs due mainly to cost advantages attracting retail investors looking for yield farming opportunities.
Risks Associated With These Metrics
While tracking these key indicators offers valuable insights into crypto markets’ health:
Market volatility remains high due primarily because prices—and consequently metrics like market cap—can swing dramatically within short periods.
Regulatory risks threaten both traditional exchanges’ operations and DeFi protocols’ legality—which could impact trade volumes significantly.
Security vulnerabilities pose serious threats especially when high TVLs attract malicious actors aiming at protocol exploits resulting in substantial financial losses for users involved.
How Investors Can Use These Metrics Effectively
To leverage these metrics optimally:
Combine multiple data points—for example:
- A rising market cap coupled with increasing trading volume signals strong momentum.
- High TVL alongside stable prices indicates healthy ecosystem growth.
Stay updated on regulatory news affecting specific assets or regions—they directly influence trade activity levels.
Use technical analysis tools alongside fundamental metrics for comprehensive decision-making—for instance:
- Volume spikes combined with chart patterns may forecast upcoming trend reversals.
Be cautious about over-reliance on any single indicator; always consider broader macroeconomic factors influencing crypto markets.
Tracking Market Cap, Volume & TVL: The Foundation Of Informed Crypto Investing
In summary—from assessing whether an asset has enough liquidity via trading volume,to understanding overall size through market capitalization,and evaluating ecosystem health using Total Value Locked—the right combination of these key metrics provides deep insights into current conditions within cryptocurrency markets.
By integrating this knowledge into your investment approach while remaining aware of associated risks—including volatility swings,regulatory impacts,and security concerns—you position yourself better prepared for navigating this fast-evolving landscape confidently.
Keywords: Cryptocurrency metrics , Market capitalization , Trading volume , Total value locked , Crypto investing tips , Blockchain analytics , DeFi ecosystems


kai
2025-05-22 12:47
What key metrics—market cap, volume, TVL—should you track?
What Key Metrics Should You Track in Cryptocurrency and Investment?
Understanding the fundamentals of cryptocurrency markets requires more than just watching price charts. To make informed investment decisions, it’s essential to monitor key metrics that reflect the health, activity, and potential of digital assets. Among these, market capitalization (market cap), trading volume, and total value locked (TVL) stand out as critical indicators. This article explores each metric in detail to help investors grasp their significance and how they can be used effectively.
Market Capitalization: Gauging Size and Stability
Market cap is a straightforward yet powerful metric that indicates the total value of all circulating coins for a given cryptocurrency. It is calculated by multiplying the current price per coin by the total number of coins in circulation. For example, Bitcoin’s market cap reflects its dominance as a leading digital asset—often considered a benchmark for the entire crypto space.
Investors use market cap to assess relative size among cryptocurrencies. Larger market caps generally suggest greater stability because these assets tend to be less volatile compared to smaller ones. Bitcoin's position at the top exemplifies this trend; its extensive adoption and liquidity contribute to its status as a 'safe' choice within volatile markets.
However, it's important to recognize that market cap alone doesn't tell the full story about an asset's potential or risk profile. Rapid changes in price can cause significant fluctuations in market cap rankings—altcoins may surge or decline quickly due to speculative activity or technological developments.
Trading Volume: Measuring Market Activity
Trading volume refers to how many units of a cryptocurrency are bought and sold over a specific period—typically 24 hours. This metric provides insight into liquidity—the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without impacting its price significantly—and overall market interest.
High trading volumes often indicate strong investor interest or increased participation from traders seeking short-term gains through technical analysis strategies. For instance, during periods of heightened buying activity—such as bullish runs—trading volume tends to spike alongside rising prices, signaling robust demand.
Conversely, low trading volumes may suggest limited liquidity which can lead to slippage—a situation where executing large trades causes unfavorable price movements—and increased volatility risks. Traders frequently analyze volume patterns together with other indicators like moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index) for better prediction accuracy regarding future price trends.
Regulatory developments also influence trading volumes; stricter regulations might suppress activity temporarily while regulatory clarity could boost confidence and participation over time.
Total Value Locked: Assessing DeFi Ecosystem Health
While traditional cryptocurrencies focus on their circulating supply and valuation metrics like market cap, decentralized finance (DeFi) introduces another vital indicator: Total Value Locked (TVL). TVL measures how much capital—in USD equivalent—is actively staked or deposited across various DeFi protocols such as lending platforms (Aave), decentralized exchanges (Uniswap), yield farming projects, among others.
This metric serves as an indicator of ecosystem vitality; higher TVL suggests active user engagement with DeFi applications indicating trustworthiness and growth potential within these platforms. Ethereum remains dominant here due to its extensive network supporting numerous protocols; however, alternative blockchains like Binance Smart Chain have gained traction thanks to lower transaction fees attracting more users seeking yield opportunities.
Monitoring TVL helps investors understand not only ecosystem adoption but also risk exposure since high TVL levels could mean larger pools susceptible if security breaches occur—or conversely signal healthy protocol usage that supports long-term sustainability when managed properly.
Recent Trends Impacting These Metrics
The landscape of cryptocurrency markets is dynamic—with fluctuations driven by macroeconomic factors such as global economic uncertainty during events like COVID-19 pandemic periods boosting Bitcoin’s appeal as a store-of-value asset leading up increases in both market caps and trading volumes globally.
Regulatory shifts continue shaping investor behavior; stricter rules introduced by governments can reduce trading activities temporarily but might also legitimize certain assets over time—potentially stabilizing markets once compliance frameworks are established.
In DeFi sectors specifically, Ethereum’s dominance persists owing largely to its rich ecosystem supporting innovative financial products—but newer chains like Binance Smart Chain have rapidly grown their TVLs due mainly to cost advantages attracting retail investors looking for yield farming opportunities.
Risks Associated With These Metrics
While tracking these key indicators offers valuable insights into crypto markets’ health:
Market volatility remains high due primarily because prices—and consequently metrics like market cap—can swing dramatically within short periods.
Regulatory risks threaten both traditional exchanges’ operations and DeFi protocols’ legality—which could impact trade volumes significantly.
Security vulnerabilities pose serious threats especially when high TVLs attract malicious actors aiming at protocol exploits resulting in substantial financial losses for users involved.
How Investors Can Use These Metrics Effectively
To leverage these metrics optimally:
Combine multiple data points—for example:
- A rising market cap coupled with increasing trading volume signals strong momentum.
- High TVL alongside stable prices indicates healthy ecosystem growth.
Stay updated on regulatory news affecting specific assets or regions—they directly influence trade activity levels.
Use technical analysis tools alongside fundamental metrics for comprehensive decision-making—for instance:
- Volume spikes combined with chart patterns may forecast upcoming trend reversals.
Be cautious about over-reliance on any single indicator; always consider broader macroeconomic factors influencing crypto markets.
Tracking Market Cap, Volume & TVL: The Foundation Of Informed Crypto Investing
In summary—from assessing whether an asset has enough liquidity via trading volume,to understanding overall size through market capitalization,and evaluating ecosystem health using Total Value Locked—the right combination of these key metrics provides deep insights into current conditions within cryptocurrency markets.
By integrating this knowledge into your investment approach while remaining aware of associated risks—including volatility swings,regulatory impacts,and security concerns—you position yourself better prepared for navigating this fast-evolving landscape confidently.
Keywords: Cryptocurrency metrics , Market capitalization , Trading volume , Total value locked , Crypto investing tips , Blockchain analytics , DeFi ecosystems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
