Popular Posts
What Is the Coin Used for in Its System? A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the purpose of a cryptocurrency coin within its ecosystem is essential for investors, developers, and users alike. Cryptocurrencies are not just digital assets; they serve specific functions that underpin their value and utility. This article explores what a coin is used for within its system, highlighting key roles such as transaction facilitation, network security, governance, and incentivization.
The Fundamental Role of Coins in Blockchain Networks
At its core, a cryptocurrency coin acts as the native digital currency of a blockchain platform. It serves multiple purposes that enable the network to operate smoothly and securely. Primarily, coins facilitate transactions—allowing users to send or receive value across borders instantly without intermediaries like banks. These transactions are recorded on the blockchain ledger, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Beyond simple transfer of funds, coins often underpin other critical functions such as paying transaction fees (gas), participating in network governance through voting rights, or staking to support consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS). This multi-functionality makes coins integral to maintaining decentralization while providing economic incentives aligned with network health.
Transaction Fees: Paying for Network Usage
One primary use case for cryptocurrencies is covering transaction costs within their respective networks. For example:
- Bitcoin: Users pay "miner fees" in BTC when sending transactions; these fees incentivize miners to include their transactions in blocks.
- Ethereum: Gas fees paid in ETH compensate validators who process smart contract executions and transfers.
These fees prevent spam attacks on networks by making frivolous transactions costly while ensuring miners or validators are rewarded fairly for securing the blockchain.
Incentivizing Network Security Through Mining & Staking
Coins also serve as rewards that motivate participants—miners or stakers—to maintain network integrity:
- Mining (Proof of Work): Miners expend computational power to validate new blocks; they earn newly minted coins plus transaction fees.
- Staking (Proof of Stake): Token holders lock up coins ("stake") to participate in block validation; they earn rewards proportional to their stake.
This incentive structure aligns participant interests with network security—more staking or mining activity enhances decentralization and resilience against malicious attacks.
Governance Functions via Coin Holders
In some blockchain systems—particularly decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs)—coins confer voting rights. Token holders can influence protocol upgrades, fee structures, or project direction through governance votes:
- Example: Ethereum's upcoming upgrades involve community voting using ETH holdings.
This democratic process ensures that stakeholders have a say over how the system evolves while aligning economic interests with decision-making power.
Utility Beyond Payments: Access & Ecosystem Participation
Certain tokens provide access rights within specific platforms:
- Utility Tokens: Used to access services on decentralized applications (dApps) — e.g., buying bandwidth on Filecoin.
- NFTs & Specialized Tokens: Represent unique assets but may also grant participation privileges like exclusive content access or voting rights within communities.
In this context, coins act as keys enabling users to engage actively with various parts of an ecosystem beyond mere monetary transfer.
The Economic Value Proposition
The value assigned to a cryptocurrency coin depends largely on its utility within its system combined with market perception. Coins that fulfill multiple roles—transaction medium, security incentive mechanism, governance tool—tend to have higher intrinsic value because they underpin vital aspects of their ecosystems' functionality and growth potential.
Investors often evaluate these functional aspects alongside technological robustness when considering long-term viability—a principle aligned with Expertise-Applied Trustworthiness (E-A-T).
Summary Table – Common Uses of Cryptocurrency Coins
| Function | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Medium | Facilitates peer-to-peer payments | Bitcoin (BTC), Litecoin (LTC) |
| Transaction Fees | Pays for processing transactions | Ethereum gas fees |
| Network Security Incentives | Rewards miners/stakers | Bitcoin mining rewards |
| Governance Rights | Voting on protocol changes | MakerDAO MKR tokens |
| Ecosystem Access & Utility | Enables participation/usage within platforms | Filecoin FIL tokens |
Understanding what a coin is used for helps clarify why certain cryptocurrencies hold significant value beyond speculative trading. They form an integral part of complex systems designed not only around transferring money but also supporting decentralized operations through incentives and governance mechanisms rooted directly into their native tokens’ functionalities. As blockchain technology continues evolving rapidly—with innovations like Solana’s high throughput or KULR’s integration strategies—the multifaceted uses cases for crypto coins will likely expand further into mainstream financial technology landscapes.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-11 09:55
What is the coin used for in its system?
What Is the Coin Used for in Its System? A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the purpose of a cryptocurrency coin within its ecosystem is essential for investors, developers, and users alike. Cryptocurrencies are not just digital assets; they serve specific functions that underpin their value and utility. This article explores what a coin is used for within its system, highlighting key roles such as transaction facilitation, network security, governance, and incentivization.
The Fundamental Role of Coins in Blockchain Networks
At its core, a cryptocurrency coin acts as the native digital currency of a blockchain platform. It serves multiple purposes that enable the network to operate smoothly and securely. Primarily, coins facilitate transactions—allowing users to send or receive value across borders instantly without intermediaries like banks. These transactions are recorded on the blockchain ledger, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Beyond simple transfer of funds, coins often underpin other critical functions such as paying transaction fees (gas), participating in network governance through voting rights, or staking to support consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS). This multi-functionality makes coins integral to maintaining decentralization while providing economic incentives aligned with network health.
Transaction Fees: Paying for Network Usage
One primary use case for cryptocurrencies is covering transaction costs within their respective networks. For example:
- Bitcoin: Users pay "miner fees" in BTC when sending transactions; these fees incentivize miners to include their transactions in blocks.
- Ethereum: Gas fees paid in ETH compensate validators who process smart contract executions and transfers.
These fees prevent spam attacks on networks by making frivolous transactions costly while ensuring miners or validators are rewarded fairly for securing the blockchain.
Incentivizing Network Security Through Mining & Staking
Coins also serve as rewards that motivate participants—miners or stakers—to maintain network integrity:
- Mining (Proof of Work): Miners expend computational power to validate new blocks; they earn newly minted coins plus transaction fees.
- Staking (Proof of Stake): Token holders lock up coins ("stake") to participate in block validation; they earn rewards proportional to their stake.
This incentive structure aligns participant interests with network security—more staking or mining activity enhances decentralization and resilience against malicious attacks.
Governance Functions via Coin Holders
In some blockchain systems—particularly decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs)—coins confer voting rights. Token holders can influence protocol upgrades, fee structures, or project direction through governance votes:
- Example: Ethereum's upcoming upgrades involve community voting using ETH holdings.
This democratic process ensures that stakeholders have a say over how the system evolves while aligning economic interests with decision-making power.
Utility Beyond Payments: Access & Ecosystem Participation
Certain tokens provide access rights within specific platforms:
- Utility Tokens: Used to access services on decentralized applications (dApps) — e.g., buying bandwidth on Filecoin.
- NFTs & Specialized Tokens: Represent unique assets but may also grant participation privileges like exclusive content access or voting rights within communities.
In this context, coins act as keys enabling users to engage actively with various parts of an ecosystem beyond mere monetary transfer.
The Economic Value Proposition
The value assigned to a cryptocurrency coin depends largely on its utility within its system combined with market perception. Coins that fulfill multiple roles—transaction medium, security incentive mechanism, governance tool—tend to have higher intrinsic value because they underpin vital aspects of their ecosystems' functionality and growth potential.
Investors often evaluate these functional aspects alongside technological robustness when considering long-term viability—a principle aligned with Expertise-Applied Trustworthiness (E-A-T).
Summary Table – Common Uses of Cryptocurrency Coins
| Function | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Medium | Facilitates peer-to-peer payments | Bitcoin (BTC), Litecoin (LTC) |
| Transaction Fees | Pays for processing transactions | Ethereum gas fees |
| Network Security Incentives | Rewards miners/stakers | Bitcoin mining rewards |
| Governance Rights | Voting on protocol changes | MakerDAO MKR tokens |
| Ecosystem Access & Utility | Enables participation/usage within platforms | Filecoin FIL tokens |
Understanding what a coin is used for helps clarify why certain cryptocurrencies hold significant value beyond speculative trading. They form an integral part of complex systems designed not only around transferring money but also supporting decentralized operations through incentives and governance mechanisms rooted directly into their native tokens’ functionalities. As blockchain technology continues evolving rapidly—with innovations like Solana’s high throughput or KULR’s integration strategies—the multifaceted uses cases for crypto coins will likely expand further into mainstream financial technology landscapes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding the Market Share of zk-Rollups vs Optimistic Rollups on Ethereum
Ethereum’s scalability challenges have prompted the development of various layer 2 solutions designed to increase transaction throughput and reduce costs. Among these, zk-Rollups and Optimistic Rollups are two leading approaches, each with distinct technical features and adoption patterns. As of mid-2023, their market shares reflect ongoing competition driven by security considerations, user preferences, and ecosystem support.
What Are zk-Rollups and How Do They Work?
zk-Rollups are a type of layer 2 scaling solution that leverages zero-knowledge proofs—specifically zk-SNARKs—to bundle multiple transactions into a single proof. This proof is then submitted to the Ethereum mainnet, verifying the validity of all included transactions without revealing individual details. The primary advantage is enhanced security: because zero-knowledge proofs are mathematically rigorous, they provide strong cryptographic guarantees that transactions are valid.
Popular implementations like zkSync and Loopring exemplify this approach. These platforms have gained traction particularly in decentralized finance (DeFi), where security is paramount. By compressing transaction data efficiently while maintaining high trust levels, zk-Rollups can significantly improve scalability without compromising on security.
How Do Optimistic Rollups Differ?
Optimistic Rollups take a different route by assuming that all off-chain transactions are valid unless proven otherwise through fraud proofs. When a transaction batch is submitted to Ethereum’s mainnet, it is considered valid by default—hence "optimistic." If someone detects an invalid transaction within this batch, they can challenge it via dispute resolution mechanisms using fraud proofs.
Platforms like Optimism and Polygon (formerly Matic) utilize this model due to its lower computational requirements compared to zero-knowledge-based solutions. This results in faster processing times and lower gas fees for users but introduces some latency during dispute periods when potential invalidity claims are challenged or verified.
Current Market Share Insights
As per data from May 2023—a snapshot reflecting recent trends—zk-Rollups hold approximately 40% to 50% of the layer 2 market share on Ethereum. Their appeal largely stems from robust security guarantees provided by cryptographic proofs; this makes them especially attractive for DeFi applications where trust minimization is critical.
In contrast, Optimistic Rollups account for roughly 30% to 40%. Their popularity has been driven by ease of integration with existing infrastructure due to simpler validation mechanisms and cost advantages during high network congestion periods. Platforms like Polygon have successfully expanded their ecosystems through such solutions owing to their developer-friendly environment.
The remaining percentage comprises other emerging or hybrid solutions attempting to combine benefits from both models or address specific use cases more effectively.
Factors Influencing Adoption Patterns
Several key factors influence which rollup solution gains broader adoption:
Security Guarantees: Zero-knowledge proof-based zk-Rollups offer mathematically provable security but at higher computational costs.
Transaction Speed & Cost: Optimistic Rollups typically provide faster finality with lower gas fees under normal conditions but may experience delays during dispute resolutions.
Ecosystem Support & Developer Adoption: Platforms like Polygon have invested heavily in expanding their ecosystem with new products such as Polygon zkEVM—a hybrid approach aiming for both speed and security.
User Preferences & Use Cases: Users prioritizing maximum security (e.g., DeFi protocols handling large assets) tend toward zk-Rollup integrations; whereas gaming or social dApps might favor faster optimistic rollup environments due to lower latency needs.
Understanding these dynamics helps stakeholders anticipate future shifts within Ethereum's scaling landscape as technology matures further.
Recent Developments Shaping Market Dynamics
Recent innovations continue shaping how these solutions compete:
zkSync v2 Launch (February 2023) – An upgraded version offering improved performance metrics has strengthened zkSync’s position among secure scaling options.
Optimism Mainnet Deployment (October 2022) – Its stable deployment provided developers with a reliable platform for building scalable dApps.
Polygon's Ecosystem Expansion – With initiatives like Polygon zkEVM launched in early 2023, Polygon aims at bridging speed with enhanced compatibility for existing Ethereum smart contracts while maintaining strong security assurances through zero knowledge techniques.
These developments demonstrate ongoing investments aimed at addressing limitations inherent in each approach while broadening application scope across industries beyond DeFi—including NFTs, gaming platforms, and enterprise blockchain integrations.
Potential Challenges Ahead
Despite promising progress, several hurdles could impact future market share distribution:
Security Risks: While zero knowledge offers strong guarantees theoretically immune from certain attacks; implementation errors or vulnerabilities could undermine confidence.
Complexity & Cost Trade-offs: Developing efficient zero knowledge circuits remains technically challenging; higher computational costs may limit widespread adoption unless optimized further.
User Experience & Ecosystem Maturity: Ease-of-use improvements will be crucial as more developers build on these layers; fragmented ecosystems might slow overall growth if interoperability issues persist.
The balance between speed versus safety will continue influencing user choices—and consequently—the competitive landscape among layer 2 solutions on Ethereum.
Key Takeaways:
As of mid-2023**,zk-Rollouts dominate around half of the Layer 2 market share**, primarily favored for their superior security features suitable for sensitive financial applications.
Meanwhile**,Optimistic Rollouts maintain significant presence**, especially among projects prioritizing low-cost operations with acceptable latency trade-offs during dispute windows.
Ongoing technological advancements—including new product launches like Polygon's zkEVM—are likely to shift these proportions over time depending on how well they address current limitations related to cost-efficiency or complexity.
Final Thoughts
The battle between zk-Rollup versus Optimistic Rollup solutions reflects broader themes within blockchain scalability efforts—security versus efficiency—and highlights how ecosystem maturity influences user preferences worldwide on Ethereum’s journey toward mass adoption.
By understanding current market shares alongside recent innovations—and recognizing potential challenges—stakeholders can better navigate investment decisions or development strategies aligned with evolving industry standards.
For those interested in staying updated, following official project channels such as zkSync, Optimism, and Polygon provides valuable insights into upcoming releases that could reshape the competitive landscape further over coming months.
This comprehensive overview aims at providing clarity about who leads today—and what factors will shape tomorrow—in Ethereum’s layer two scaling race.


kai
2025-05-11 06:17
What is the current market share of zk-rollup versus optimistic rollup solutions on Ethereum (ETH)?
Understanding the Market Share of zk-Rollups vs Optimistic Rollups on Ethereum
Ethereum’s scalability challenges have prompted the development of various layer 2 solutions designed to increase transaction throughput and reduce costs. Among these, zk-Rollups and Optimistic Rollups are two leading approaches, each with distinct technical features and adoption patterns. As of mid-2023, their market shares reflect ongoing competition driven by security considerations, user preferences, and ecosystem support.
What Are zk-Rollups and How Do They Work?
zk-Rollups are a type of layer 2 scaling solution that leverages zero-knowledge proofs—specifically zk-SNARKs—to bundle multiple transactions into a single proof. This proof is then submitted to the Ethereum mainnet, verifying the validity of all included transactions without revealing individual details. The primary advantage is enhanced security: because zero-knowledge proofs are mathematically rigorous, they provide strong cryptographic guarantees that transactions are valid.
Popular implementations like zkSync and Loopring exemplify this approach. These platforms have gained traction particularly in decentralized finance (DeFi), where security is paramount. By compressing transaction data efficiently while maintaining high trust levels, zk-Rollups can significantly improve scalability without compromising on security.
How Do Optimistic Rollups Differ?
Optimistic Rollups take a different route by assuming that all off-chain transactions are valid unless proven otherwise through fraud proofs. When a transaction batch is submitted to Ethereum’s mainnet, it is considered valid by default—hence "optimistic." If someone detects an invalid transaction within this batch, they can challenge it via dispute resolution mechanisms using fraud proofs.
Platforms like Optimism and Polygon (formerly Matic) utilize this model due to its lower computational requirements compared to zero-knowledge-based solutions. This results in faster processing times and lower gas fees for users but introduces some latency during dispute periods when potential invalidity claims are challenged or verified.
Current Market Share Insights
As per data from May 2023—a snapshot reflecting recent trends—zk-Rollups hold approximately 40% to 50% of the layer 2 market share on Ethereum. Their appeal largely stems from robust security guarantees provided by cryptographic proofs; this makes them especially attractive for DeFi applications where trust minimization is critical.
In contrast, Optimistic Rollups account for roughly 30% to 40%. Their popularity has been driven by ease of integration with existing infrastructure due to simpler validation mechanisms and cost advantages during high network congestion periods. Platforms like Polygon have successfully expanded their ecosystems through such solutions owing to their developer-friendly environment.
The remaining percentage comprises other emerging or hybrid solutions attempting to combine benefits from both models or address specific use cases more effectively.
Factors Influencing Adoption Patterns
Several key factors influence which rollup solution gains broader adoption:
Security Guarantees: Zero-knowledge proof-based zk-Rollups offer mathematically provable security but at higher computational costs.
Transaction Speed & Cost: Optimistic Rollups typically provide faster finality with lower gas fees under normal conditions but may experience delays during dispute resolutions.
Ecosystem Support & Developer Adoption: Platforms like Polygon have invested heavily in expanding their ecosystem with new products such as Polygon zkEVM—a hybrid approach aiming for both speed and security.
User Preferences & Use Cases: Users prioritizing maximum security (e.g., DeFi protocols handling large assets) tend toward zk-Rollup integrations; whereas gaming or social dApps might favor faster optimistic rollup environments due to lower latency needs.
Understanding these dynamics helps stakeholders anticipate future shifts within Ethereum's scaling landscape as technology matures further.
Recent Developments Shaping Market Dynamics
Recent innovations continue shaping how these solutions compete:
zkSync v2 Launch (February 2023) – An upgraded version offering improved performance metrics has strengthened zkSync’s position among secure scaling options.
Optimism Mainnet Deployment (October 2022) – Its stable deployment provided developers with a reliable platform for building scalable dApps.
Polygon's Ecosystem Expansion – With initiatives like Polygon zkEVM launched in early 2023, Polygon aims at bridging speed with enhanced compatibility for existing Ethereum smart contracts while maintaining strong security assurances through zero knowledge techniques.
These developments demonstrate ongoing investments aimed at addressing limitations inherent in each approach while broadening application scope across industries beyond DeFi—including NFTs, gaming platforms, and enterprise blockchain integrations.
Potential Challenges Ahead
Despite promising progress, several hurdles could impact future market share distribution:
Security Risks: While zero knowledge offers strong guarantees theoretically immune from certain attacks; implementation errors or vulnerabilities could undermine confidence.
Complexity & Cost Trade-offs: Developing efficient zero knowledge circuits remains technically challenging; higher computational costs may limit widespread adoption unless optimized further.
User Experience & Ecosystem Maturity: Ease-of-use improvements will be crucial as more developers build on these layers; fragmented ecosystems might slow overall growth if interoperability issues persist.
The balance between speed versus safety will continue influencing user choices—and consequently—the competitive landscape among layer 2 solutions on Ethereum.
Key Takeaways:
As of mid-2023**,zk-Rollouts dominate around half of the Layer 2 market share**, primarily favored for their superior security features suitable for sensitive financial applications.
Meanwhile**,Optimistic Rollouts maintain significant presence**, especially among projects prioritizing low-cost operations with acceptable latency trade-offs during dispute windows.
Ongoing technological advancements—including new product launches like Polygon's zkEVM—are likely to shift these proportions over time depending on how well they address current limitations related to cost-efficiency or complexity.
Final Thoughts
The battle between zk-Rollup versus Optimistic Rollup solutions reflects broader themes within blockchain scalability efforts—security versus efficiency—and highlights how ecosystem maturity influences user preferences worldwide on Ethereum’s journey toward mass adoption.
By understanding current market shares alongside recent innovations—and recognizing potential challenges—stakeholders can better navigate investment decisions or development strategies aligned with evolving industry standards.
For those interested in staying updated, following official project channels such as zkSync, Optimism, and Polygon provides valuable insights into upcoming releases that could reshape the competitive landscape further over coming months.
This comprehensive overview aims at providing clarity about who leads today—and what factors will shape tomorrow—in Ethereum’s layer two scaling race.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Delta Volume Analysis Can Improve Trade Timing in Cryptocurrency Markets
Understanding Delta Volume Analysis in Crypto Trading
Delta volume analysis is an advanced technical tool that traders use to enhance their decision-making process, especially when timing entries and exits. It combines two critical components: the delta, which measures the rate of price change over a specific period, and trading volume, which indicates market participation. By analyzing these elements together, traders can gain deeper insights into market sentiment and potential future price movements.
In essence, delta reflects how quickly an asset's price is moving—whether it's rising or falling—and how significant that movement is relative to previous periods. When this data is paired with volume information, it helps distinguish between strong trends backed by high trader activity and weaker moves that might be prone to reversal.
Why Is Delta Volume Analysis Important for Traders?
In cryptocurrency markets characterized by high volatility and rapid price swings, understanding when a trend might reverse or strengthen can be challenging. Traditional indicators like moving averages or RSI provide valuable signals but often lack real-time nuance. Delta volume analysis fills this gap by offering immediate insights into the strength behind a price move.
For example, if Bitcoin's price surges with high delta (indicating rapid change) accompanied by increasing volume, it suggests strong buying interest and potential trend continuation. Conversely, if the same surge occurs on low volume with high delta values—implying less trader participation—it could signal a false breakout or impending reversal.
This method enables traders to refine their entry points more precisely than relying solely on conventional indicators. It also assists in avoiding premature trades based on misleading signals common during volatile periods.
How Does Delta Volume Analysis Help Refine Trade Timing?
The core benefit of delta volume analysis lies in its ability to improve trade timing accuracy through pattern recognition:
- Identifying Trend Strength: High delta combined with rising volume typically confirms ongoing momentum—ideal for entering long positions.
- Spotting Reversals: Divergences such as high delta with decreasing volume may indicate weakening trends or reversals.
- Confirming Breakouts: A sudden spike in both delta and volume can validate breakouts from support/resistance levels.
- Avoiding False Signals: Low-volume surges are often false alarms; recognizing these helps prevent entering trades prematurely.
By continuously monitoring these metrics during different time frames (like 1-minute or 5-minute charts), traders can better align their actions with actual market dynamics rather than reacting impulsively to noise.
Practical Application: Combining Delta Volume With Other Indicators
While powerful alone, delta volume analysis becomes even more effective when integrated into a broader technical framework:
- Moving Averages & Trend Lines: Confirm whether observed changes align with overall trend direction.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Detect overbought or oversold conditions alongside delta signals.
- MACD & Bollinger Bands: Use these tools for additional confirmation of momentum shifts indicated by delta-volume patterns.
This multi-layered approach reduces reliance on any single indicator and enhances overall trading robustness—a key principle aligned with sound trading strategies rooted in experience (E-A-T).
Recent Trends Enhancing Delta Volume Analysis Usage
The adoption of delta-based tools has grown notably among crypto traders due to advancements in trading platforms offering real-time data visualization. Many platforms now feature dedicated dashboards where users can track live changes in both price deltas and volumes seamlessly.
Online communities have also contributed significantly; forums like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency or Telegram groups frequently discuss successful strategies involving this method. As awareness increases about its effectiveness for trend confirmation and reversal detection, more traders are incorporating it into their routines.
Furthermore, developers are creating custom scripts using APIs from major exchanges—such as Binance or Coinbase—to automate real-time calculations of delta volumes tailored to individual preferences.
Risks Associated With Relying Solely On Delta Volume Data
Despite its advantages, overdependence on any single indicator carries risks:
Cryptocurrency markets are inherently volatile; sudden news events can cause sharp moves that defy technical patterns.
False signals may occur during low liquidity periods when manipulated prices temporarily distort true market sentiment.
Regulatory developments could impact trading volumes drastically—for instance, bans affecting exchanges might reduce available data quality for accurate analysis—which diminishes the reliability of results derived from historical patterns alone.
Therefore, integrating multiple analytical methods remains essential for developing resilient trading strategies grounded in comprehensive research rather than isolated indicators.
Best Practices When Using Delta Volume Analysis
To maximize benefits while minimizing pitfalls:
- Use multiple timeframes — short-term charts reveal immediate opportunities while longer-term views confirm broader trends.
- Combine with other technical indicators — avoid making decisions based solely on one metric.
- Monitor news flow — fundamental factors often influence what technicals suggest about future movements.
- Practice disciplined risk management — set stop-loss orders aligned with your risk appetite regardless of what your indicators suggest.
Final Thoughts: Is This Method Suitable For All Traders?
Delta volume analysis offers valuable insights primarily suited for experienced traders who understand market nuances well enough not to rely exclusively on automated signals but instead interpret them within contextually rich environments. Beginners should start practicing this technique alongside traditional tools before fully integrating it into live trading routines.
By leveraging the combined power of rate-of-change measurements (delta) along with traded volumes—and supplementing them through other analytical methods—cryptocurrency traders gain an edge toward making timely decisions amid turbulent markets.
Keywords: crypto trading strategy | trade timing | technical analysis | cryptocurrency volatility | market sentiment | trend reversal detection | real-time data analytics


kai
2025-05-09 21:24
How can delta volume analysis refine trade timing decisions?
How Delta Volume Analysis Can Improve Trade Timing in Cryptocurrency Markets
Understanding Delta Volume Analysis in Crypto Trading
Delta volume analysis is an advanced technical tool that traders use to enhance their decision-making process, especially when timing entries and exits. It combines two critical components: the delta, which measures the rate of price change over a specific period, and trading volume, which indicates market participation. By analyzing these elements together, traders can gain deeper insights into market sentiment and potential future price movements.
In essence, delta reflects how quickly an asset's price is moving—whether it's rising or falling—and how significant that movement is relative to previous periods. When this data is paired with volume information, it helps distinguish between strong trends backed by high trader activity and weaker moves that might be prone to reversal.
Why Is Delta Volume Analysis Important for Traders?
In cryptocurrency markets characterized by high volatility and rapid price swings, understanding when a trend might reverse or strengthen can be challenging. Traditional indicators like moving averages or RSI provide valuable signals but often lack real-time nuance. Delta volume analysis fills this gap by offering immediate insights into the strength behind a price move.
For example, if Bitcoin's price surges with high delta (indicating rapid change) accompanied by increasing volume, it suggests strong buying interest and potential trend continuation. Conversely, if the same surge occurs on low volume with high delta values—implying less trader participation—it could signal a false breakout or impending reversal.
This method enables traders to refine their entry points more precisely than relying solely on conventional indicators. It also assists in avoiding premature trades based on misleading signals common during volatile periods.
How Does Delta Volume Analysis Help Refine Trade Timing?
The core benefit of delta volume analysis lies in its ability to improve trade timing accuracy through pattern recognition:
- Identifying Trend Strength: High delta combined with rising volume typically confirms ongoing momentum—ideal for entering long positions.
- Spotting Reversals: Divergences such as high delta with decreasing volume may indicate weakening trends or reversals.
- Confirming Breakouts: A sudden spike in both delta and volume can validate breakouts from support/resistance levels.
- Avoiding False Signals: Low-volume surges are often false alarms; recognizing these helps prevent entering trades prematurely.
By continuously monitoring these metrics during different time frames (like 1-minute or 5-minute charts), traders can better align their actions with actual market dynamics rather than reacting impulsively to noise.
Practical Application: Combining Delta Volume With Other Indicators
While powerful alone, delta volume analysis becomes even more effective when integrated into a broader technical framework:
- Moving Averages & Trend Lines: Confirm whether observed changes align with overall trend direction.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Detect overbought or oversold conditions alongside delta signals.
- MACD & Bollinger Bands: Use these tools for additional confirmation of momentum shifts indicated by delta-volume patterns.
This multi-layered approach reduces reliance on any single indicator and enhances overall trading robustness—a key principle aligned with sound trading strategies rooted in experience (E-A-T).
Recent Trends Enhancing Delta Volume Analysis Usage
The adoption of delta-based tools has grown notably among crypto traders due to advancements in trading platforms offering real-time data visualization. Many platforms now feature dedicated dashboards where users can track live changes in both price deltas and volumes seamlessly.
Online communities have also contributed significantly; forums like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency or Telegram groups frequently discuss successful strategies involving this method. As awareness increases about its effectiveness for trend confirmation and reversal detection, more traders are incorporating it into their routines.
Furthermore, developers are creating custom scripts using APIs from major exchanges—such as Binance or Coinbase—to automate real-time calculations of delta volumes tailored to individual preferences.
Risks Associated With Relying Solely On Delta Volume Data
Despite its advantages, overdependence on any single indicator carries risks:
Cryptocurrency markets are inherently volatile; sudden news events can cause sharp moves that defy technical patterns.
False signals may occur during low liquidity periods when manipulated prices temporarily distort true market sentiment.
Regulatory developments could impact trading volumes drastically—for instance, bans affecting exchanges might reduce available data quality for accurate analysis—which diminishes the reliability of results derived from historical patterns alone.
Therefore, integrating multiple analytical methods remains essential for developing resilient trading strategies grounded in comprehensive research rather than isolated indicators.
Best Practices When Using Delta Volume Analysis
To maximize benefits while minimizing pitfalls:
- Use multiple timeframes — short-term charts reveal immediate opportunities while longer-term views confirm broader trends.
- Combine with other technical indicators — avoid making decisions based solely on one metric.
- Monitor news flow — fundamental factors often influence what technicals suggest about future movements.
- Practice disciplined risk management — set stop-loss orders aligned with your risk appetite regardless of what your indicators suggest.
Final Thoughts: Is This Method Suitable For All Traders?
Delta volume analysis offers valuable insights primarily suited for experienced traders who understand market nuances well enough not to rely exclusively on automated signals but instead interpret them within contextually rich environments. Beginners should start practicing this technique alongside traditional tools before fully integrating it into live trading routines.
By leveraging the combined power of rate-of-change measurements (delta) along with traded volumes—and supplementing them through other analytical methods—cryptocurrency traders gain an edge toward making timely decisions amid turbulent markets.
Keywords: crypto trading strategy | trade timing | technical analysis | cryptocurrency volatility | market sentiment | trend reversal detection | real-time data analytics
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding Gas Auctions in Rollup-Centric Blockchain Designs
Blockchain networks like Ethereum face significant challenges related to scalability and transaction costs. As demand for network usage increases, so do the gas fees—costs paid by users to process transactions. To address these issues, innovative mechanisms such as gas auctions have been integrated into rollup-centric designs, which aim to improve efficiency and reduce congestion. This article explores how gas auctions work within these frameworks, their benefits, challenges, and recent developments shaping the future of blockchain scalability.
What Are Gas Auctions on Blockchain Networks?
Gas auctions are a method used by blockchain networks to prioritize transactions during periods of high demand. In essence, they allow users to bid for transaction inclusion based on how much they’re willing to pay in gas fees. The highest bidders secure priority execution—meaning their transactions are processed faster—while lower bids may be delayed or dropped if the network becomes congested.
In traditional blockchain environments like Ethereum’s mainnet, each transaction requires a certain amount of computational effort measured in units called "gas." When many users submit transactions simultaneously—such as during popular NFT drops or DeFi activity—the competition for block space intensifies. This leads to increased gas prices because miners (or validators) tend to favor higher-paying transactions that maximize their earnings.
In response, some systems implement auction mechanisms where users specify their maximum willingness-to-pay (gas price). The network then sorts these bids from highest to lowest and includes the top-paying transactions within each block until reaching the block's capacity limit.
How Do Gas Auctions Function Within Rollup-Centric Designs?
Rollups are layer 2 scaling solutions that bundle multiple off-chain transactions into a single batch before submitting them back onto the main chain (layer 1). They significantly reduce on-chain load but still require mechanisms for managing transaction prioritization and fee setting.
In rollup-centric architectures such as Optimism or Arbitrum, gas auctions serve several purposes:
- Transaction Prioritization: Users bid higher amounts for faster processing within rollups.
- Fee Management: By auctioning off transaction inclusion rights, these systems dynamically allocate resources based on user demand.
- Congestion Control: During peak times when many users want quick confirmation, bidding wars naturally emerge; this helps prevent spam attacks and ensures that only serious participants get prioritized.
The process generally involves users submitting bids alongside their intended transactions. These bids are collected over a period (sometimes called an "auction window") before being processed collectively in a batch submitted onto Ethereum’s mainnet or another base layer. The highest bidders’ transactions get executed first within this batch — effectively creating an auction-based queue rather than fixed fee structures seen elsewhere.
Variations in Implementation
Different rollup solutions adopt slightly different approaches:
Optimism's Auction Mechanism: Uses an explicit auction system where participants submit sealed bids; only after bidding closes does it determine which ones will be included.
Arbitrum's Approach: Employs optimistic rollups with fraud proofs but also incorporates fee markets similar in concept; while not strictly an auction per se, it manages transaction priorities through economic incentives aligned with bidding strategies.
These variations reflect ongoing experimentation aimed at balancing fairness with efficiency while minimizing potential security risks associated with bidding processes.
Benefits of Gas Auctions in Layer 2 Solutions
Implementing gas auctions within rollup frameworks offers several advantages:
Enhanced Scalability: By efficiently managing how many high-priority transactions can be processed per batch or block, networks can handle more activity without sacrificing performance.
Reduced Congestion: During busy periods when network traffic peaks sharply—like during token launches or market volatility—gas auctions help distribute resources more fairly among active users.
Economic Incentives: High-value traders who need rapid confirmation can pay premiums without forcing everyone else into paying exorbitant fees—a form of market-driven resource allocation.
Lower Overall Fees: Since most batching occurs off-chain under optimized conditions—and only essential data is settled periodically—the average user benefits from reduced costs compared to transacting directly on Ethereum’s mainnet during congestion spikes.
Security Preservation: Properly designed auction mechanisms ensure that prioritization doesn’t compromise security; malicious actors cannot easily manipulate outcomes if safeguards like sealed bids or cryptographic commitments are employed properly.
Challenges Facing Gas Auctions in Rollups
Despite their advantages, integrating gas auctions into layer 2 solutions isn’t without hurdles:
Security Risks: If not implemented carefully—for example through transparent bidding processes—they could become targets for frontrunning attacks where malicious actors manipulate bid submissions ahead of others’ intentions.
Complexity & User Experience: Introducing auction mechanics adds layers of complexity that might deter casual users unfamiliar with bidding strategies or who prefer straightforward fee models.
Fairness Concerns: High-stakes bidders may dominate access during peak times unless measures like capped bids or minimum reserve prices are enforced—a concern especially relevant given regulatory scrutiny around fair access.
Regulatory Implications: As blockchain technology matures and regulators scrutinize financial activities involving dynamic pricing models like auctions—including potential anti-trust considerations—the legal landscape could influence future implementations.
Recent Developments & Future Outlook
The evolution of gas auctions is closely tied with ongoing innovations across layer 2 scaling solutions:
Major Layer 2 Solutions Using Gas Auction Concepts
Optimism
Optimism has pioneered variants of auction-based priority systems designed explicitly for its optimistic rollup architecture:
- It employs "Optimism's Auction Mechanism," which involves sealed-bid submissions allowing fairer competition among participants seeking fast confirmations while maintaining security guarantees through cryptographic commitments.
Arbitrum
While primarily employing optimistic fraud proofs rather than explicit bid-based queues:
- Arbitrum integrates economic incentives akin to those found in traditional fee markets,
- It aims at balancing throughput improvements against simplicity and user-friendliness.
Trends Shaping Future Adoption
As adoption grows:
- Developers focus on refining transparency features,
- Security protocols evolve alongside incentive structures,
- Regulatory bodies begin scrutinizing decentralized bidding markets,
- New hybrid models emerge combining fixed fees with optional premium services via optional bidding tiers.
Potential Impact on Blockchain Ecosystems
Gas auctions could redefine how decentralized applications operate by enabling more predictable cost management during surges while maintaining decentralization principles through transparent processes—all crucial factors fostering broader mainstream acceptance.
By understanding how gas auctions function within rollup-centric designs—and recognizing both their strengths and limitations—you gain insight into one key mechanism driving scalable blockchain ecosystems forward today. As innovation continues along this trajectory—with improved security measures and user-friendly interfaces—they promise a future where high-speed transactional throughput meets affordable costs without compromising decentralization integrity.


kai
2025-05-09 20:02
How do gas auctions work in rollup-centric designs?
Understanding Gas Auctions in Rollup-Centric Blockchain Designs
Blockchain networks like Ethereum face significant challenges related to scalability and transaction costs. As demand for network usage increases, so do the gas fees—costs paid by users to process transactions. To address these issues, innovative mechanisms such as gas auctions have been integrated into rollup-centric designs, which aim to improve efficiency and reduce congestion. This article explores how gas auctions work within these frameworks, their benefits, challenges, and recent developments shaping the future of blockchain scalability.
What Are Gas Auctions on Blockchain Networks?
Gas auctions are a method used by blockchain networks to prioritize transactions during periods of high demand. In essence, they allow users to bid for transaction inclusion based on how much they’re willing to pay in gas fees. The highest bidders secure priority execution—meaning their transactions are processed faster—while lower bids may be delayed or dropped if the network becomes congested.
In traditional blockchain environments like Ethereum’s mainnet, each transaction requires a certain amount of computational effort measured in units called "gas." When many users submit transactions simultaneously—such as during popular NFT drops or DeFi activity—the competition for block space intensifies. This leads to increased gas prices because miners (or validators) tend to favor higher-paying transactions that maximize their earnings.
In response, some systems implement auction mechanisms where users specify their maximum willingness-to-pay (gas price). The network then sorts these bids from highest to lowest and includes the top-paying transactions within each block until reaching the block's capacity limit.
How Do Gas Auctions Function Within Rollup-Centric Designs?
Rollups are layer 2 scaling solutions that bundle multiple off-chain transactions into a single batch before submitting them back onto the main chain (layer 1). They significantly reduce on-chain load but still require mechanisms for managing transaction prioritization and fee setting.
In rollup-centric architectures such as Optimism or Arbitrum, gas auctions serve several purposes:
- Transaction Prioritization: Users bid higher amounts for faster processing within rollups.
- Fee Management: By auctioning off transaction inclusion rights, these systems dynamically allocate resources based on user demand.
- Congestion Control: During peak times when many users want quick confirmation, bidding wars naturally emerge; this helps prevent spam attacks and ensures that only serious participants get prioritized.
The process generally involves users submitting bids alongside their intended transactions. These bids are collected over a period (sometimes called an "auction window") before being processed collectively in a batch submitted onto Ethereum’s mainnet or another base layer. The highest bidders’ transactions get executed first within this batch — effectively creating an auction-based queue rather than fixed fee structures seen elsewhere.
Variations in Implementation
Different rollup solutions adopt slightly different approaches:
Optimism's Auction Mechanism: Uses an explicit auction system where participants submit sealed bids; only after bidding closes does it determine which ones will be included.
Arbitrum's Approach: Employs optimistic rollups with fraud proofs but also incorporates fee markets similar in concept; while not strictly an auction per se, it manages transaction priorities through economic incentives aligned with bidding strategies.
These variations reflect ongoing experimentation aimed at balancing fairness with efficiency while minimizing potential security risks associated with bidding processes.
Benefits of Gas Auctions in Layer 2 Solutions
Implementing gas auctions within rollup frameworks offers several advantages:
Enhanced Scalability: By efficiently managing how many high-priority transactions can be processed per batch or block, networks can handle more activity without sacrificing performance.
Reduced Congestion: During busy periods when network traffic peaks sharply—like during token launches or market volatility—gas auctions help distribute resources more fairly among active users.
Economic Incentives: High-value traders who need rapid confirmation can pay premiums without forcing everyone else into paying exorbitant fees—a form of market-driven resource allocation.
Lower Overall Fees: Since most batching occurs off-chain under optimized conditions—and only essential data is settled periodically—the average user benefits from reduced costs compared to transacting directly on Ethereum’s mainnet during congestion spikes.
Security Preservation: Properly designed auction mechanisms ensure that prioritization doesn’t compromise security; malicious actors cannot easily manipulate outcomes if safeguards like sealed bids or cryptographic commitments are employed properly.
Challenges Facing Gas Auctions in Rollups
Despite their advantages, integrating gas auctions into layer 2 solutions isn’t without hurdles:
Security Risks: If not implemented carefully—for example through transparent bidding processes—they could become targets for frontrunning attacks where malicious actors manipulate bid submissions ahead of others’ intentions.
Complexity & User Experience: Introducing auction mechanics adds layers of complexity that might deter casual users unfamiliar with bidding strategies or who prefer straightforward fee models.
Fairness Concerns: High-stakes bidders may dominate access during peak times unless measures like capped bids or minimum reserve prices are enforced—a concern especially relevant given regulatory scrutiny around fair access.
Regulatory Implications: As blockchain technology matures and regulators scrutinize financial activities involving dynamic pricing models like auctions—including potential anti-trust considerations—the legal landscape could influence future implementations.
Recent Developments & Future Outlook
The evolution of gas auctions is closely tied with ongoing innovations across layer 2 scaling solutions:
Major Layer 2 Solutions Using Gas Auction Concepts
Optimism
Optimism has pioneered variants of auction-based priority systems designed explicitly for its optimistic rollup architecture:
- It employs "Optimism's Auction Mechanism," which involves sealed-bid submissions allowing fairer competition among participants seeking fast confirmations while maintaining security guarantees through cryptographic commitments.
Arbitrum
While primarily employing optimistic fraud proofs rather than explicit bid-based queues:
- Arbitrum integrates economic incentives akin to those found in traditional fee markets,
- It aims at balancing throughput improvements against simplicity and user-friendliness.
Trends Shaping Future Adoption
As adoption grows:
- Developers focus on refining transparency features,
- Security protocols evolve alongside incentive structures,
- Regulatory bodies begin scrutinizing decentralized bidding markets,
- New hybrid models emerge combining fixed fees with optional premium services via optional bidding tiers.
Potential Impact on Blockchain Ecosystems
Gas auctions could redefine how decentralized applications operate by enabling more predictable cost management during surges while maintaining decentralization principles through transparent processes—all crucial factors fostering broader mainstream acceptance.
By understanding how gas auctions function within rollup-centric designs—and recognizing both their strengths and limitations—you gain insight into one key mechanism driving scalable blockchain ecosystems forward today. As innovation continues along this trajectory—with improved security measures and user-friendly interfaces—they promise a future where high-speed transactional throughput meets affordable costs without compromising decentralization integrity.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is On-Chain Composability and Why Does It Matter?
On-chain composability is a fundamental concept in the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology and decentralized finance (DeFi). At its core, it refers to the ability of different blockchain applications and smart contracts to interact seamlessly within a shared ecosystem. This interoperability enables developers and users to combine various DeFi protocols, creating more complex financial products without relying on centralized intermediaries. For example, a user might swap tokens on a decentralized exchange (DEX), then immediately use those tokens for yield farming or collateralized lending—all within the same blockchain environment.
This interconnectedness is made possible by the programmability of smart contracts—self-executing code that automates transactions based on predefined rules. When these contracts can communicate and work together efficiently, they form an ecosystem where innovative financial services can be built rapidly. Ethereum has been at the forefront of this movement due to its robust smart contract capabilities, fostering an environment where DeFi protocols like Uniswap, Aave, and Compound thrive through composability.
Why Is On-Chain Composability Important for DeFi?
The rise of DeFi has been driven by its promise to democratize access to financial services—lending, borrowing, trading—without traditional banking infrastructure. On-chain composability enhances this vision by enabling these activities to be combined into multi-step processes that are executed automatically via smart contracts. This integration allows users to perform complex operations with minimal friction: swapping assets across multiple platforms or leveraging liquidity pools in ways previously impossible with siloed systems.
Moreover, interoperability between different blockchains remains one of the biggest challenges in realizing full on-chain composability. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are actively developing cross-chain bridges that facilitate communication between diverse networks. These solutions aim to expand the reach of composable applications beyond Ethereum’s ecosystem into other blockchains such as Binance Smart Chain or Solana.
However, while these advancements open new horizons for innovation—and potentially greater user adoption—they also introduce significant risks that must be carefully managed.
Risks Associated With On-Chain Composability
Security vulnerabilities are among the most pressing concerns when it comes to highly interconnected smart contract systems. As more components interact within an ecosystem—each with their own codebase—the likelihood increases that bugs or exploits could occur somewhere along this chain. Historically, complex interactions have led hackers to identify vulnerabilities such as reentrancy attacks—a type of exploit where malicious actors repeatedly call back into a contract before previous transactions complete—to drain funds from vulnerable protocols.
Front-running attacks pose another threat specific to DeFi environments utilizing on-chain data transparency. In such scenarios, attackers observe pending transactions in mempools (the pool where unconfirmed transactions reside) and manipulate transaction ordering—for example through “sandwich attacks”—to gain unfair advantages during trades or liquidations.
Beyond security issues lies regulatory uncertainty; many jurisdictions are still grappling with how best to oversee decentralized systems operating across borders without central authority oversight. This ambiguity can lead either toward overly restrictive regulations stifling innovation or insufficient protections exposing users’ funds and data privacy risks.
Scalability challenges also threaten widespread adoption; current blockchain networks like Ethereum face high gas fees and limited transaction throughput during peak times—factors that hinder seamless user experiences necessary for mainstream use cases involving multiple integrated protocols simultaneously.
Recent Developments Improving On-Chain Composability
The ongoing evolution of blockchain technology aims at addressing many existing limitations:
Ethereum 2.0: Transitioning from proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism towards proof-of-stake (PoS), Ethereum 2.x promises enhanced scalability through shard chains—a process dividing network load into smaller parts—that could significantly reduce gas fees while increasing transaction capacity.
Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies such as Optimism and Arbitrum process most transactions off-chain but settle final states on Ethereum’s mainnet later; this approach reduces congestion costs while maintaining security guarantees.
Cross-Chain Protocols: Projects like Cosmos’ Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol enable different blockchains—including Bitcoin sidechains or other Layer 1 chains—to communicate directly with each other securely.
As regulatory bodies begin providing clearer guidelines around DeFi operations—with agencies like SEC exploring frameworks—it becomes easier for developers and investors alike to navigate compliance issues confidently while innovating responsibly.
Potential Challenges Moving Forward
Despite promising technological advancements—and increased institutional interest—the future landscape faces several hurdles:
Security Breaches: The complexity inherent in multi-contract interactions increases attack surfaces; even minor bugs can lead catastrophic losses if exploited by malicious actors.
Regulatory Backlash: Without clear legal frameworks tailored specifically for decentralized ecosystems—which remain largely unregulated—there’s risk that governments may impose restrictions harmful both legally and economically.
Limited Accessibility Due To Scalability Issues: If scaling solutions do not keep pace with demand—as seen during recent network congestion events—the benefits of decentralization may become accessible only by large players capable of absorbing high transaction costs.
User Education Needs: The technical sophistication required for safe participation means educating users about potential pitfalls is essential; otherwise, mistakes could result in significant financial loss due solely due to misunderstanding how these systems operate safely.
Ensuring Safe Adoption Through E-A-T Principles
Building trustworthiness (“Expertise”), demonstrating authoritative knowledge (“Authoritativeness”), and establishing transparency (“Trustworthiness”) are crucial when discussing complex topics like on-chain composability:
Developers should prioritize security audits before deploying new integrations.
Clear documentation helps users understand risks involved.
Regulatory clarity provides confidence for institutional participation without compromising decentralization principles.
Understanding what makes up effective governance models will further enhance system resilience against exploits while fostering responsible growth within this innovative space.
Final Thoughts
On-chain composability represents one of the most exciting frontiers in blockchain technology today—it unlocks unprecedented possibilities for creating sophisticated decentralized finance products through seamless integration across platforms worldwide . However , alongside its immense potential come notable challenges related primarilyto security vulnerabilities , scalability constraints ,and evolving regulatory landscapes . By staying informed about technological developments , adopting best practicesin security,and engaging proactivelywith policymakers,the community can harnesson-chaincomposabilit y's power responsibly — pavingthe wayfor sustainable growthand broader adoptionof truly decentralizedfinancial services .


kai
2025-05-09 18:25
What is on-chain composability and what risks does it introduce?
What Is On-Chain Composability and Why Does It Matter?
On-chain composability is a fundamental concept in the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology and decentralized finance (DeFi). At its core, it refers to the ability of different blockchain applications and smart contracts to interact seamlessly within a shared ecosystem. This interoperability enables developers and users to combine various DeFi protocols, creating more complex financial products without relying on centralized intermediaries. For example, a user might swap tokens on a decentralized exchange (DEX), then immediately use those tokens for yield farming or collateralized lending—all within the same blockchain environment.
This interconnectedness is made possible by the programmability of smart contracts—self-executing code that automates transactions based on predefined rules. When these contracts can communicate and work together efficiently, they form an ecosystem where innovative financial services can be built rapidly. Ethereum has been at the forefront of this movement due to its robust smart contract capabilities, fostering an environment where DeFi protocols like Uniswap, Aave, and Compound thrive through composability.
Why Is On-Chain Composability Important for DeFi?
The rise of DeFi has been driven by its promise to democratize access to financial services—lending, borrowing, trading—without traditional banking infrastructure. On-chain composability enhances this vision by enabling these activities to be combined into multi-step processes that are executed automatically via smart contracts. This integration allows users to perform complex operations with minimal friction: swapping assets across multiple platforms or leveraging liquidity pools in ways previously impossible with siloed systems.
Moreover, interoperability between different blockchains remains one of the biggest challenges in realizing full on-chain composability. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are actively developing cross-chain bridges that facilitate communication between diverse networks. These solutions aim to expand the reach of composable applications beyond Ethereum’s ecosystem into other blockchains such as Binance Smart Chain or Solana.
However, while these advancements open new horizons for innovation—and potentially greater user adoption—they also introduce significant risks that must be carefully managed.
Risks Associated With On-Chain Composability
Security vulnerabilities are among the most pressing concerns when it comes to highly interconnected smart contract systems. As more components interact within an ecosystem—each with their own codebase—the likelihood increases that bugs or exploits could occur somewhere along this chain. Historically, complex interactions have led hackers to identify vulnerabilities such as reentrancy attacks—a type of exploit where malicious actors repeatedly call back into a contract before previous transactions complete—to drain funds from vulnerable protocols.
Front-running attacks pose another threat specific to DeFi environments utilizing on-chain data transparency. In such scenarios, attackers observe pending transactions in mempools (the pool where unconfirmed transactions reside) and manipulate transaction ordering—for example through “sandwich attacks”—to gain unfair advantages during trades or liquidations.
Beyond security issues lies regulatory uncertainty; many jurisdictions are still grappling with how best to oversee decentralized systems operating across borders without central authority oversight. This ambiguity can lead either toward overly restrictive regulations stifling innovation or insufficient protections exposing users’ funds and data privacy risks.
Scalability challenges also threaten widespread adoption; current blockchain networks like Ethereum face high gas fees and limited transaction throughput during peak times—factors that hinder seamless user experiences necessary for mainstream use cases involving multiple integrated protocols simultaneously.
Recent Developments Improving On-Chain Composability
The ongoing evolution of blockchain technology aims at addressing many existing limitations:
Ethereum 2.0: Transitioning from proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism towards proof-of-stake (PoS), Ethereum 2.x promises enhanced scalability through shard chains—a process dividing network load into smaller parts—that could significantly reduce gas fees while increasing transaction capacity.
Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies such as Optimism and Arbitrum process most transactions off-chain but settle final states on Ethereum’s mainnet later; this approach reduces congestion costs while maintaining security guarantees.
Cross-Chain Protocols: Projects like Cosmos’ Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol enable different blockchains—including Bitcoin sidechains or other Layer 1 chains—to communicate directly with each other securely.
As regulatory bodies begin providing clearer guidelines around DeFi operations—with agencies like SEC exploring frameworks—it becomes easier for developers and investors alike to navigate compliance issues confidently while innovating responsibly.
Potential Challenges Moving Forward
Despite promising technological advancements—and increased institutional interest—the future landscape faces several hurdles:
Security Breaches: The complexity inherent in multi-contract interactions increases attack surfaces; even minor bugs can lead catastrophic losses if exploited by malicious actors.
Regulatory Backlash: Without clear legal frameworks tailored specifically for decentralized ecosystems—which remain largely unregulated—there’s risk that governments may impose restrictions harmful both legally and economically.
Limited Accessibility Due To Scalability Issues: If scaling solutions do not keep pace with demand—as seen during recent network congestion events—the benefits of decentralization may become accessible only by large players capable of absorbing high transaction costs.
User Education Needs: The technical sophistication required for safe participation means educating users about potential pitfalls is essential; otherwise, mistakes could result in significant financial loss due solely due to misunderstanding how these systems operate safely.
Ensuring Safe Adoption Through E-A-T Principles
Building trustworthiness (“Expertise”), demonstrating authoritative knowledge (“Authoritativeness”), and establishing transparency (“Trustworthiness”) are crucial when discussing complex topics like on-chain composability:
Developers should prioritize security audits before deploying new integrations.
Clear documentation helps users understand risks involved.
Regulatory clarity provides confidence for institutional participation without compromising decentralization principles.
Understanding what makes up effective governance models will further enhance system resilience against exploits while fostering responsible growth within this innovative space.
Final Thoughts
On-chain composability represents one of the most exciting frontiers in blockchain technology today—it unlocks unprecedented possibilities for creating sophisticated decentralized finance products through seamless integration across platforms worldwide . However , alongside its immense potential come notable challenges related primarilyto security vulnerabilities , scalability constraints ,and evolving regulatory landscapes . By staying informed about technological developments , adopting best practicesin security,and engaging proactivelywith policymakers,the community can harnesson-chaincomposabilit y's power responsibly — pavingthe wayfor sustainable growthand broader adoptionof truly decentralizedfinancial services .
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Covenants in Bitcoin Scripting?
Covenants in Bitcoin scripting are a set of rules or constraints that can be embedded within transactions to control how funds are spent in the future. Unlike traditional Bitcoin scripts, which primarily verify whether specific conditions are met for a transaction to be valid, covenants extend this capability by imposing more sophisticated restrictions. These restrictions can include enforcing time locks, multi-signature requirements, or even interactions with external data sources. The primary goal of covenants is to enhance the security and flexibility of smart contracts on the Bitcoin network.
In essence, covenants act as programmable rules that "bind" future transactions to certain conditions set at the time of their creation. This allows developers and users to implement complex financial logic directly into their Bitcoin transactions without relying on third-party intermediaries or external platforms.
Why Are Covenants Important for Bitcoin?
Bitcoin's scripting language has historically been intentionally limited in its capabilities—primarily designed for security and simplicity rather than complex programmability. This limitation means that while basic smart contracts like multi-signature wallets exist, more advanced features such as conditional spending based on multiple criteria have been challenging to implement securely.
Covenants address this gap by introducing new opcodes (operations) into the scripting language that enable more detailed control over how coins can be spent after they have been locked up. This advancement opens up possibilities for creating safer escrow arrangements, implementing better coin management strategies (like coin aging), and enabling complex financial instruments directly on-chain.
Furthermore, covenants contribute significantly toward improving overall network security by reducing vulnerabilities associated with simpler scripts. They allow for better enforcement of rules without requiring trust between parties—an essential feature aligned with Bitcoin’s core principles of decentralization and trustlessness.
How Do Covenants Work Within Bitcoin Scripts?
Traditional Bitcoin scripts operate under a simple model: they specify conditions under which coins can be spent—such as signatures from authorized parties or specific lock times. Covenants expand this model by adding constraints that persist beyond initial spending conditions.
For example:
- A covenant might restrict future spends so that only addresses derived from a specific script or pattern can spend those coins.
- It could enforce time-based restrictions where funds cannot be moved until certain block heights or timestamps.
- It might also prevent spending unless certain external data (via oracle services) confirms particular conditions.
These functionalities are enabled through new opcodes introduced into the scripting language—such as OP_CHECKCOVENANT—which check whether subsequent transactions adhere to predefined rules established during the initial transaction creation phase.
By embedding these constraints directly into transaction outputs (often called "covenant outputs"), developers gain granular control over how assets move across different addresses and states within the blockchain ecosystem.
Recent Developments in Covenant Technology
The concept of covenants has gained momentum over recent years due to ongoing research and community interest in expanding Bitcoin’s capabilities beyond simple transfers. Notably:
Proposal & Implementation: Several proposals have emerged advocating for new opcodes supporting covenant functionality; some have been integrated into experimental versions of the protocol.
Testing & Validation: These features undergo rigorous testing on testnets before deployment onto mainnet environments — ensuring stability without risking user funds.
Community Engagement: Developers actively explore use cases such as enhanced multisig schemes, coin control mechanisms, privacy improvements via constrained spends, and decentralized finance applications built atop these advanced scripts.
While adoption remains cautious due to potential risks like bugs or unforeseen vulnerabilities associated with new opcodes, early results suggest promising avenues for innovation within secure boundaries aligned with core principles.
Potential Benefits & Use Cases
Introducing covenants could revolutionize several aspects of cryptocurrency usage:
Enhanced Security: By constraining how coins can be spent after initial locking—e.g., limiting spenders’ options—they reduce attack surfaces against thefts or exploits.
Complex Smart Contracts: Covent-based scripts enable features like conditional payments tied to external events (via oracle integration), automated escrow releases upon fulfillment criteria, or multi-stage investment agreements.
Better Coin Management: Implementing policies such as coin aging ensures long-term holders benefit from reduced risk exposure while facilitating compliance with regulatory standards where necessary.
Decentralized Applications (dApps): Covent-enabled smart contracts facilitate building decentralized apps directly on-chain—for instance, decentralized exchanges requiring intricate trade logic without centralized oversight.
Financial Instruments: More sophisticated derivatives and structured products become feasible when assets follow programmable constraints embedded at protocol level rather than relying solely on off-chain solutions.
These use cases highlight how covenants could significantly expand what is possible within an entirely trustless environment rooted firmly in blockchain technology's security guarantees.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Covenants
Despite their promising potential benefits, implementing covenants involves notable challenges:
Security Concerns: New opcodes introduce complexity; if not carefully audited—and if bugs exist—they could open pathways for exploits leading to loss of funds.
Protocol Complexity: Adding advanced features increases script complexity which may lead users unfamiliar with these mechanisms making errors during transaction creation—a concern especially relevant given bitcoin's emphasis on simplicity and robustness.
Backward Compatibility & Adoption: Integrating covenant support requires consensus among miners and node operators; widespread adoption depends heavily on community agreement amid competing priorities about protocol upgrades.
Regulatory Implications: As smart contract capabilities grow more powerful within bitcoin’s ecosystem via covenants—and potentially facilitate untraceable financial arrangements—it raises questions about compliance obligations across jurisdictions.
Timeline & Future Outlook
The journey toward fully functional covenant support has seen steady progress:
- In 2020–2021 — Initial proposals surfaced discussing potential opcode additions aimed at enabling covenant-like functionalities; community debates ensued regarding design choices balancing power versus safety.
- 2022 — Protocol updates incorporated some experimental opcode implementations tested extensively across testnets before considering mainnet deployment options;3.. 2023 — Increasing developer interest led many projects exploring practical applications leveraging these new capabilities while ongoing research aims at refining standards further.
Looking ahead:
The evolution of covenant technology promises richer programmability within bitcoin’s ecosystem but will require careful governance frameworks ensuring safety alongside innovation.
How Covent Supports Blockchain Security And Innovation
By allowing precise rule enforcement through programmable constraints embedded directly into transactions—a hallmark feature—the development aligns strongly with core blockchain tenets like decentralization and transparency while fostering innovative use cases previously difficult under traditional scripting limitations.
Final Thoughts
Covenants represent an exciting frontier in enhancing what is possible within Bitcoin's scripting environment—from smarter asset management strategies to enabling complex DeFi applications—all while maintaining robust security foundations intrinsic to blockchain technology today.
This emerging feature underscores ongoing efforts by developers worldwide aiming not just at incremental improvements but transformative changes capable of broadening cryptocurrency utility well beyond simple peer-to-peer transfers.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 17:00
What is covenants in Bitcoin scripting?
What Are Covenants in Bitcoin Scripting?
Covenants in Bitcoin scripting are a set of rules or constraints that can be embedded within transactions to control how funds are spent in the future. Unlike traditional Bitcoin scripts, which primarily verify whether specific conditions are met for a transaction to be valid, covenants extend this capability by imposing more sophisticated restrictions. These restrictions can include enforcing time locks, multi-signature requirements, or even interactions with external data sources. The primary goal of covenants is to enhance the security and flexibility of smart contracts on the Bitcoin network.
In essence, covenants act as programmable rules that "bind" future transactions to certain conditions set at the time of their creation. This allows developers and users to implement complex financial logic directly into their Bitcoin transactions without relying on third-party intermediaries or external platforms.
Why Are Covenants Important for Bitcoin?
Bitcoin's scripting language has historically been intentionally limited in its capabilities—primarily designed for security and simplicity rather than complex programmability. This limitation means that while basic smart contracts like multi-signature wallets exist, more advanced features such as conditional spending based on multiple criteria have been challenging to implement securely.
Covenants address this gap by introducing new opcodes (operations) into the scripting language that enable more detailed control over how coins can be spent after they have been locked up. This advancement opens up possibilities for creating safer escrow arrangements, implementing better coin management strategies (like coin aging), and enabling complex financial instruments directly on-chain.
Furthermore, covenants contribute significantly toward improving overall network security by reducing vulnerabilities associated with simpler scripts. They allow for better enforcement of rules without requiring trust between parties—an essential feature aligned with Bitcoin’s core principles of decentralization and trustlessness.
How Do Covenants Work Within Bitcoin Scripts?
Traditional Bitcoin scripts operate under a simple model: they specify conditions under which coins can be spent—such as signatures from authorized parties or specific lock times. Covenants expand this model by adding constraints that persist beyond initial spending conditions.
For example:
- A covenant might restrict future spends so that only addresses derived from a specific script or pattern can spend those coins.
- It could enforce time-based restrictions where funds cannot be moved until certain block heights or timestamps.
- It might also prevent spending unless certain external data (via oracle services) confirms particular conditions.
These functionalities are enabled through new opcodes introduced into the scripting language—such as OP_CHECKCOVENANT—which check whether subsequent transactions adhere to predefined rules established during the initial transaction creation phase.
By embedding these constraints directly into transaction outputs (often called "covenant outputs"), developers gain granular control over how assets move across different addresses and states within the blockchain ecosystem.
Recent Developments in Covenant Technology
The concept of covenants has gained momentum over recent years due to ongoing research and community interest in expanding Bitcoin’s capabilities beyond simple transfers. Notably:
Proposal & Implementation: Several proposals have emerged advocating for new opcodes supporting covenant functionality; some have been integrated into experimental versions of the protocol.
Testing & Validation: These features undergo rigorous testing on testnets before deployment onto mainnet environments — ensuring stability without risking user funds.
Community Engagement: Developers actively explore use cases such as enhanced multisig schemes, coin control mechanisms, privacy improvements via constrained spends, and decentralized finance applications built atop these advanced scripts.
While adoption remains cautious due to potential risks like bugs or unforeseen vulnerabilities associated with new opcodes, early results suggest promising avenues for innovation within secure boundaries aligned with core principles.
Potential Benefits & Use Cases
Introducing covenants could revolutionize several aspects of cryptocurrency usage:
Enhanced Security: By constraining how coins can be spent after initial locking—e.g., limiting spenders’ options—they reduce attack surfaces against thefts or exploits.
Complex Smart Contracts: Covent-based scripts enable features like conditional payments tied to external events (via oracle integration), automated escrow releases upon fulfillment criteria, or multi-stage investment agreements.
Better Coin Management: Implementing policies such as coin aging ensures long-term holders benefit from reduced risk exposure while facilitating compliance with regulatory standards where necessary.
Decentralized Applications (dApps): Covent-enabled smart contracts facilitate building decentralized apps directly on-chain—for instance, decentralized exchanges requiring intricate trade logic without centralized oversight.
Financial Instruments: More sophisticated derivatives and structured products become feasible when assets follow programmable constraints embedded at protocol level rather than relying solely on off-chain solutions.
These use cases highlight how covenants could significantly expand what is possible within an entirely trustless environment rooted firmly in blockchain technology's security guarantees.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Covenants
Despite their promising potential benefits, implementing covenants involves notable challenges:
Security Concerns: New opcodes introduce complexity; if not carefully audited—and if bugs exist—they could open pathways for exploits leading to loss of funds.
Protocol Complexity: Adding advanced features increases script complexity which may lead users unfamiliar with these mechanisms making errors during transaction creation—a concern especially relevant given bitcoin's emphasis on simplicity and robustness.
Backward Compatibility & Adoption: Integrating covenant support requires consensus among miners and node operators; widespread adoption depends heavily on community agreement amid competing priorities about protocol upgrades.
Regulatory Implications: As smart contract capabilities grow more powerful within bitcoin’s ecosystem via covenants—and potentially facilitate untraceable financial arrangements—it raises questions about compliance obligations across jurisdictions.
Timeline & Future Outlook
The journey toward fully functional covenant support has seen steady progress:
- In 2020–2021 — Initial proposals surfaced discussing potential opcode additions aimed at enabling covenant-like functionalities; community debates ensued regarding design choices balancing power versus safety.
- 2022 — Protocol updates incorporated some experimental opcode implementations tested extensively across testnets before considering mainnet deployment options;3.. 2023 — Increasing developer interest led many projects exploring practical applications leveraging these new capabilities while ongoing research aims at refining standards further.
Looking ahead:
The evolution of covenant technology promises richer programmability within bitcoin’s ecosystem but will require careful governance frameworks ensuring safety alongside innovation.
How Covent Supports Blockchain Security And Innovation
By allowing precise rule enforcement through programmable constraints embedded directly into transactions—a hallmark feature—the development aligns strongly with core blockchain tenets like decentralization and transparency while fostering innovative use cases previously difficult under traditional scripting limitations.
Final Thoughts
Covenants represent an exciting frontier in enhancing what is possible within Bitcoin's scripting environment—from smarter asset management strategies to enabling complex DeFi applications—all while maintaining robust security foundations intrinsic to blockchain technology today.
This emerging feature underscores ongoing efforts by developers worldwide aiming not just at incremental improvements but transformative changes capable of broadening cryptocurrency utility well beyond simple peer-to-peer transfers.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Public vs. Private Blockchain: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the distinctions between public and private blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you're an investor, developer, or business leader. Both types of blockchains leverage distributed ledger technology (DLT), but they serve different purposes and operate under different principles. This article provides a clear overview of what sets them apart, their key features, use cases, and recent trends shaping their development.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open-source network where anyone can participate without restrictions. These networks are fully decentralized—meaning no single entity controls the entire system—and rely on consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to validate transactions. Because they are accessible to everyone globally, public blockchains promote transparency and security through widespread participation.
For example, Bitcoin was the first successful public blockchain that introduced peer-to-peer digital currency without intermediaries such as banks. Ethereum expanded on this concept by enabling smart contracts—self-executing agreements written into code—that facilitate complex decentralized applications (dApps). These platforms have fueled innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi), which allows users to lend, borrow, or trade assets directly on blockchain networks.
Public blockchains are particularly suited for applications requiring transparency and censorship resistance. Their open nature makes them ideal for financial transactions involving cryptocurrencies but also extends to supply chain tracking and voting systems where trustlessness is vital.
Characteristics of Public Blockchains
- Decentralization: Anyone can join as a node; no central authority controls the network.
- Open Access: No permission needed; anyone can read data or participate in validation.
- Transparency: All transaction data is publicly visible.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered retroactively.
- Security Through Consensus: Network security relies on collective agreement mechanisms like PoW or PoS.
These features foster trust among participants because they eliminate single points of failure while ensuring data integrity across all nodes.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants only. They are often used within organizations or consortia that require controlled environments for sharing sensitive information securely. Managed by a central authority—or sometimes by multiple trusted entities—private networks prioritize privacy and efficiency over complete decentralization.
Private blockchains enable organizations such as banks or supply chain companies to automate internal processes while maintaining strict control over who can view or modify data. For instance, Hyperledger Fabric—a popular private blockchain framework—is widely adopted in enterprise settings due to its modular architecture allowing customization according to specific compliance needs.
Because access is limited and permissions are managed centrally—or through consortium governance—private chains tend not to be fully transparent externally but offer higher throughput speeds suitable for enterprise-scale operations requiring confidentiality.
Key Features of Private Blockchains
- Controlled Access: Only selected users with permissions can join the network.
- Closed Source/Permissioned: The codebase may not be publicly available; modifications are controlled.
- Data Privacy: Transaction details are visible only among authorized parties.
- Higher Performance & Scalability: Reduced consensus overhead leads to faster transaction processing.
- Governance & Compliance Focused: Designed with regulatory requirements in mind—for example GDPR compliance in Europe.
This structure makes private blockchains attractive for industries needing secure yet confidential recordkeeping without exposing sensitive information externally.
Comparing Public vs Private Blockchains
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open worldwide | Restricted membership |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Partially centralized |
| Transparency | Complete visibility | Limited visibility |
| Speed & Scalability | Lower due to consensus complexity | Higher performance |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies; DeFi; voting systems | Internal processes; supply chains; compliance |
While both types aim at enhancing security through cryptography and distributed ledgers, their design choices reflect differing priorities: openness versus control depending on application needs.
Recent Trends & Developments
The landscape of blockchain continues evolving rapidly:
Enterprise Adoption: Many corporations prefer private chains like Hyperledger Fabric because they align with regulatory standards while offering scalability benefits necessary for large-scale operations such as banking transactions or healthcare records management.
Hybrid Models: Some projects combine elements from both worlds—public permissioned chains—to balance transparency with privacy concerns effectively—a trend gaining traction especially within regulated sectors like finance and government services.
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely—with notable figures such as SEC Chair Paul Atkins emphasizing oversight—the distinction between public tokens versus permissioned networks becomes increasingly significant from legal perspectives.
Security Considerations: While both models provide high levels of cryptographic security when properly implemented, private networks face risks related mainly to insider threats if governance isn’t robust enough.
Technological Innovations: Advances include interoperability solutions allowing seamless communication between different types of ledgers—a step toward integrated multi-chain ecosystems supporting diverse organizational needs.
Understanding these developments helps stakeholders make informed decisions about deploying appropriate blockchain solutions aligned with strategic goals and compliance requirements.
Which Type Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between a public versus private blockchain depends heavily on your specific objectives:
If your priority is transparency —such as tracking product provenance across global supply chains—or creating open financial ecosystems—public chains might be best suited—you should consider factors like scalability limitations due to consensus protocols though these remain areas under active research improving performance metrics over time.
Conversely if your organization handles sensitive customer data requiring strict confidentiality—and you need faster transaction speeds—a private chain offers better control over access rights while still leveraging core DLT benefits.
Ultimately understanding these differences enables better alignment with industry standards—including E-A-T principles—to ensure trustworthy implementation that meets user expectations regarding security expertise and authoritative practices.
Final Thoughts
The debate between public versus private blockchains centers around balancing openness against control based on application demands—from democratized cryptocurrency markets favoring decentralization towards highly regulated industries prioritizing privacy/security measures respectively.. As technological innovations continue pushing boundaries—including interoperability protocols—the lines may blur further creating hybrid models tailored precisely per organizational needs.
Staying informed about recent trends ensures stakeholders harness blockchain's full potential responsibly while adhering best practices rooted in transparency—and building trust among users across various sectors seeking reliable digital transformation tools today


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 12:19
What is the difference between a public and a private blockchain?
Public vs. Private Blockchain: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the distinctions between public and private blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you're an investor, developer, or business leader. Both types of blockchains leverage distributed ledger technology (DLT), but they serve different purposes and operate under different principles. This article provides a clear overview of what sets them apart, their key features, use cases, and recent trends shaping their development.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open-source network where anyone can participate without restrictions. These networks are fully decentralized—meaning no single entity controls the entire system—and rely on consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to validate transactions. Because they are accessible to everyone globally, public blockchains promote transparency and security through widespread participation.
For example, Bitcoin was the first successful public blockchain that introduced peer-to-peer digital currency without intermediaries such as banks. Ethereum expanded on this concept by enabling smart contracts—self-executing agreements written into code—that facilitate complex decentralized applications (dApps). These platforms have fueled innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi), which allows users to lend, borrow, or trade assets directly on blockchain networks.
Public blockchains are particularly suited for applications requiring transparency and censorship resistance. Their open nature makes them ideal for financial transactions involving cryptocurrencies but also extends to supply chain tracking and voting systems where trustlessness is vital.
Characteristics of Public Blockchains
- Decentralization: Anyone can join as a node; no central authority controls the network.
- Open Access: No permission needed; anyone can read data or participate in validation.
- Transparency: All transaction data is publicly visible.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered retroactively.
- Security Through Consensus: Network security relies on collective agreement mechanisms like PoW or PoS.
These features foster trust among participants because they eliminate single points of failure while ensuring data integrity across all nodes.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants only. They are often used within organizations or consortia that require controlled environments for sharing sensitive information securely. Managed by a central authority—or sometimes by multiple trusted entities—private networks prioritize privacy and efficiency over complete decentralization.
Private blockchains enable organizations such as banks or supply chain companies to automate internal processes while maintaining strict control over who can view or modify data. For instance, Hyperledger Fabric—a popular private blockchain framework—is widely adopted in enterprise settings due to its modular architecture allowing customization according to specific compliance needs.
Because access is limited and permissions are managed centrally—or through consortium governance—private chains tend not to be fully transparent externally but offer higher throughput speeds suitable for enterprise-scale operations requiring confidentiality.
Key Features of Private Blockchains
- Controlled Access: Only selected users with permissions can join the network.
- Closed Source/Permissioned: The codebase may not be publicly available; modifications are controlled.
- Data Privacy: Transaction details are visible only among authorized parties.
- Higher Performance & Scalability: Reduced consensus overhead leads to faster transaction processing.
- Governance & Compliance Focused: Designed with regulatory requirements in mind—for example GDPR compliance in Europe.
This structure makes private blockchains attractive for industries needing secure yet confidential recordkeeping without exposing sensitive information externally.
Comparing Public vs Private Blockchains
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open worldwide | Restricted membership |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Partially centralized |
| Transparency | Complete visibility | Limited visibility |
| Speed & Scalability | Lower due to consensus complexity | Higher performance |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies; DeFi; voting systems | Internal processes; supply chains; compliance |
While both types aim at enhancing security through cryptography and distributed ledgers, their design choices reflect differing priorities: openness versus control depending on application needs.
Recent Trends & Developments
The landscape of blockchain continues evolving rapidly:
Enterprise Adoption: Many corporations prefer private chains like Hyperledger Fabric because they align with regulatory standards while offering scalability benefits necessary for large-scale operations such as banking transactions or healthcare records management.
Hybrid Models: Some projects combine elements from both worlds—public permissioned chains—to balance transparency with privacy concerns effectively—a trend gaining traction especially within regulated sectors like finance and government services.
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely—with notable figures such as SEC Chair Paul Atkins emphasizing oversight—the distinction between public tokens versus permissioned networks becomes increasingly significant from legal perspectives.
Security Considerations: While both models provide high levels of cryptographic security when properly implemented, private networks face risks related mainly to insider threats if governance isn’t robust enough.
Technological Innovations: Advances include interoperability solutions allowing seamless communication between different types of ledgers—a step toward integrated multi-chain ecosystems supporting diverse organizational needs.
Understanding these developments helps stakeholders make informed decisions about deploying appropriate blockchain solutions aligned with strategic goals and compliance requirements.
Which Type Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between a public versus private blockchain depends heavily on your specific objectives:
If your priority is transparency —such as tracking product provenance across global supply chains—or creating open financial ecosystems—public chains might be best suited—you should consider factors like scalability limitations due to consensus protocols though these remain areas under active research improving performance metrics over time.
Conversely if your organization handles sensitive customer data requiring strict confidentiality—and you need faster transaction speeds—a private chain offers better control over access rights while still leveraging core DLT benefits.
Ultimately understanding these differences enables better alignment with industry standards—including E-A-T principles—to ensure trustworthy implementation that meets user expectations regarding security expertise and authoritative practices.
Final Thoughts
The debate between public versus private blockchains centers around balancing openness against control based on application demands—from democratized cryptocurrency markets favoring decentralization towards highly regulated industries prioritizing privacy/security measures respectively.. As technological innovations continue pushing boundaries—including interoperability protocols—the lines may blur further creating hybrid models tailored precisely per organizational needs.
Staying informed about recent trends ensures stakeholders harness blockchain's full potential responsibly while adhering best practices rooted in transparency—and building trust among users across various sectors seeking reliable digital transformation tools today
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Distinguish Between a True Breakout and a False Breakout at Resistance
Understanding the difference between a genuine breakout and a false one is essential for traders, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. Making informed decisions can prevent costly mistakes and improve your overall trading strategy. This guide explores key indicators, chart patterns, market sentiment factors, and recent developments that help traders identify whether a breakout at resistance is real or just a fleeting move.
What Is a Resistance Level in Technical Analysis?
In technical analysis, resistance refers to a price point where an asset's upward movement tends to pause or reverse due to increased selling pressure. Traders often view resistance levels as barriers that the price struggles to break through. When the price approaches this level, it signals potential trading opportunities—either for continuation if it breaks through or for reversal if it bounces back.
A breakout occurs when the price moves above this resistance level with significant momentum. Such movements are often seen as signals of strong buying interest and potential trend shifts upward. Conversely, false breakouts happen when prices temporarily breach resistance but then quickly fall back below it, trapping traders who entered positions expecting continued upward movement.
Key Technical Indicators for Identifying Breakouts
Technical indicators are vital tools that help traders assess whether a breakout is likely genuine or false. Here are some of the most effective:
Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price data over specific periods (e.g., 20-day or 50-day) and help identify trend direction. During true breakouts, prices tend to stay above key moving averages after crossing them convincingly. If the price briefly crosses above resistance but then reverts below these averages shortly after, it's often indicative of a false breakout.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The RSI measures momentum on a scale from 0 to 100; readings above 70 suggest overbought conditions while below 30 indicate oversold states. When assessing breakouts:
- A true breakout typically sees RSI rising above 50 with sustained momentum.
- A false breakout might show RSI crossing above 50 momentarily but failing to maintain strength before reverting.
Bollinger Bands
These bands adjust based on market volatility—widening during high volatility and narrowing during consolidation phases.
- In genuine breakouts, prices usually move outside the upper band with increased volume.
- False breakouts may see prices touching or slightly exceeding the upper band temporarily but quickly returning within bands without significant volume support.
Recognizing Chart Patterns That Signal Breakout Validity
Chart patterns provide visual cues about potential trend continuations or reversals:
Head and Shoulders Pattern
This pattern indicates possible reversals from bullish to bearish trends (or vice versa). After completing this pattern:
- A confirmed true breakout occurs when prices surpass the neckline with strong volume.
- An incomplete pattern or one accompanied by low volume may lead to false signals.
Triangular Patterns (Symmetrical Triangles)
These represent consolidation phases where buyers and sellers reach equilibrium before breaking out:
- A valid triangle breakout involves clear movement outside of triangle boundaries accompanied by higher-than-average volume.
- If prices only briefly pierce these boundaries without follow-through activity—or do so on low volume—it suggests an unreliable signal prone to reversal.
Market Sentiment Factors Influencing Breakout Reliability
Market sentiment plays an influential role in whether breakouts turn out authentic:
Impact of News & Events
Major news releases—such as regulatory announcements, technological upgrades in blockchain projects, or macroeconomic developments—can trigger rapid moves that appear as breakouts:
- Genuine reactions tend to be supported by sustained momentum.
- Fake reactions often occur due to rumors or speculative hype that dissipate once clarified.
Market Volatility & Manipulation Risks
High volatility environments increase chances of false signals because rapid swings can trigger temporary breaches of resistance levels:
- Traders should watch for sudden spikes driven by large trades designed intentionally (market manipulation), which can create artificial breakouts meant solely for deceiving other participants—a common tactic in crypto markets like pump-and-dump schemes.
Practical Strategies To Confirm True Breakouts
To avoid falling victim to false signals:
- Use Confirmation Signals: Wait for additional confirmation such as increased trading volume alongside price movement beyond resistance levels.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Protect yourself from sudden reversals by placing stop-loss orders just below recent support levels.
- Observe Price Action: Look for steady upward movement rather than sharp spikes followed by quick retracements.
- Monitor Multiple Indicators: Rely on several technical tools simultaneously rather than single indicators alone; convergence increases confidence in validity.
- Be Patient: Avoid rushing into trades immediately after initial breach attempts; patience allows clearer differentiation between true trends and fake-outs.
Recent Trends Enhancing Detection Capabilities
Advancements in technology have improved how traders analyze potential breakouts:
AI-Powered Trading Platforms: These systems analyze vast datasets—including historical patterns—and provide probabilistic assessments about whether upcoming movements are likely genuine based on complex algorithms trained on market behavior data.
Enhanced Charting Tools: Modern platforms offer more detailed visualizations such as heatmaps indicating trader activity levels around key levels—helping identify manipulation attempts versus organic moves.
Increased Awareness About Market Manipulation: Regulatory scrutiny has risen globally against practices like pump-and-dump schemes prevalent among smaller altcoins; awareness helps traders approach suspected fake-outs more cautiously.
Risks Associated With False Breakouts
Misinterpreting false breakthroughs can have serious consequences:
- Financial Losses: Entering trades prematurely based on unreliable signals leads directly into losses once prices revert back within previous ranges.2.. Eroded Confidence: Repeated failures diminish trader confidence—not only affecting individual strategies but also impacting overall market stability if many participants react similarly.3.. Regulatory Scrutiny: Persistent manipulative practices attracting regulatory attention could result in penalties against involved parties—and potentially impact legitimate investors' trustworthiness perceptions.
By understanding technical indicators like moving averages and RSI alongside chart patterns such as triangles—and considering external factors like news sentiment—you can significantly improve your ability to distinguish between true and false breakouts at resistance levels within cryptocurrency markets—or any financial asset class you trade actively.
Final Tips
Always combine multiple analytical methods before acting upon any perceived breakthrough signal; patience combined with disciplined risk management remains your best defense against deceptive market moves rooted in fake-out scenarios.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 04:01
How can you distinguish between a true breakout and a false breakout at resistance?
How to Distinguish Between a True Breakout and a False Breakout at Resistance
Understanding the difference between a genuine breakout and a false one is essential for traders, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. Making informed decisions can prevent costly mistakes and improve your overall trading strategy. This guide explores key indicators, chart patterns, market sentiment factors, and recent developments that help traders identify whether a breakout at resistance is real or just a fleeting move.
What Is a Resistance Level in Technical Analysis?
In technical analysis, resistance refers to a price point where an asset's upward movement tends to pause or reverse due to increased selling pressure. Traders often view resistance levels as barriers that the price struggles to break through. When the price approaches this level, it signals potential trading opportunities—either for continuation if it breaks through or for reversal if it bounces back.
A breakout occurs when the price moves above this resistance level with significant momentum. Such movements are often seen as signals of strong buying interest and potential trend shifts upward. Conversely, false breakouts happen when prices temporarily breach resistance but then quickly fall back below it, trapping traders who entered positions expecting continued upward movement.
Key Technical Indicators for Identifying Breakouts
Technical indicators are vital tools that help traders assess whether a breakout is likely genuine or false. Here are some of the most effective:
Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price data over specific periods (e.g., 20-day or 50-day) and help identify trend direction. During true breakouts, prices tend to stay above key moving averages after crossing them convincingly. If the price briefly crosses above resistance but then reverts below these averages shortly after, it's often indicative of a false breakout.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The RSI measures momentum on a scale from 0 to 100; readings above 70 suggest overbought conditions while below 30 indicate oversold states. When assessing breakouts:
- A true breakout typically sees RSI rising above 50 with sustained momentum.
- A false breakout might show RSI crossing above 50 momentarily but failing to maintain strength before reverting.
Bollinger Bands
These bands adjust based on market volatility—widening during high volatility and narrowing during consolidation phases.
- In genuine breakouts, prices usually move outside the upper band with increased volume.
- False breakouts may see prices touching or slightly exceeding the upper band temporarily but quickly returning within bands without significant volume support.
Recognizing Chart Patterns That Signal Breakout Validity
Chart patterns provide visual cues about potential trend continuations or reversals:
Head and Shoulders Pattern
This pattern indicates possible reversals from bullish to bearish trends (or vice versa). After completing this pattern:
- A confirmed true breakout occurs when prices surpass the neckline with strong volume.
- An incomplete pattern or one accompanied by low volume may lead to false signals.
Triangular Patterns (Symmetrical Triangles)
These represent consolidation phases where buyers and sellers reach equilibrium before breaking out:
- A valid triangle breakout involves clear movement outside of triangle boundaries accompanied by higher-than-average volume.
- If prices only briefly pierce these boundaries without follow-through activity—or do so on low volume—it suggests an unreliable signal prone to reversal.
Market Sentiment Factors Influencing Breakout Reliability
Market sentiment plays an influential role in whether breakouts turn out authentic:
Impact of News & Events
Major news releases—such as regulatory announcements, technological upgrades in blockchain projects, or macroeconomic developments—can trigger rapid moves that appear as breakouts:
- Genuine reactions tend to be supported by sustained momentum.
- Fake reactions often occur due to rumors or speculative hype that dissipate once clarified.
Market Volatility & Manipulation Risks
High volatility environments increase chances of false signals because rapid swings can trigger temporary breaches of resistance levels:
- Traders should watch for sudden spikes driven by large trades designed intentionally (market manipulation), which can create artificial breakouts meant solely for deceiving other participants—a common tactic in crypto markets like pump-and-dump schemes.
Practical Strategies To Confirm True Breakouts
To avoid falling victim to false signals:
- Use Confirmation Signals: Wait for additional confirmation such as increased trading volume alongside price movement beyond resistance levels.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Protect yourself from sudden reversals by placing stop-loss orders just below recent support levels.
- Observe Price Action: Look for steady upward movement rather than sharp spikes followed by quick retracements.
- Monitor Multiple Indicators: Rely on several technical tools simultaneously rather than single indicators alone; convergence increases confidence in validity.
- Be Patient: Avoid rushing into trades immediately after initial breach attempts; patience allows clearer differentiation between true trends and fake-outs.
Recent Trends Enhancing Detection Capabilities
Advancements in technology have improved how traders analyze potential breakouts:
AI-Powered Trading Platforms: These systems analyze vast datasets—including historical patterns—and provide probabilistic assessments about whether upcoming movements are likely genuine based on complex algorithms trained on market behavior data.
Enhanced Charting Tools: Modern platforms offer more detailed visualizations such as heatmaps indicating trader activity levels around key levels—helping identify manipulation attempts versus organic moves.
Increased Awareness About Market Manipulation: Regulatory scrutiny has risen globally against practices like pump-and-dump schemes prevalent among smaller altcoins; awareness helps traders approach suspected fake-outs more cautiously.
Risks Associated With False Breakouts
Misinterpreting false breakthroughs can have serious consequences:
- Financial Losses: Entering trades prematurely based on unreliable signals leads directly into losses once prices revert back within previous ranges.2.. Eroded Confidence: Repeated failures diminish trader confidence—not only affecting individual strategies but also impacting overall market stability if many participants react similarly.3.. Regulatory Scrutiny: Persistent manipulative practices attracting regulatory attention could result in penalties against involved parties—and potentially impact legitimate investors' trustworthiness perceptions.
By understanding technical indicators like moving averages and RSI alongside chart patterns such as triangles—and considering external factors like news sentiment—you can significantly improve your ability to distinguish between true and false breakouts at resistance levels within cryptocurrency markets—or any financial asset class you trade actively.
Final Tips
Always combine multiple analytical methods before acting upon any perceived breakthrough signal; patience combined with disciplined risk management remains your best defense against deceptive market moves rooted in fake-out scenarios.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🔹Deposit/Withdrawal Time: August 10, 2025, 01:50 (UTC)
🔹Trading Time: August 11, 2025, 01:50 (UTC)
🪧More:https://bit.ly/3UeEBF0



JuCoin Community
2025-08-05 02:44
JuCoin to List D3XAI/USDT Trading Pair on August 11, 2025
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🔹Deposit/Withdrawal Time: August 10, 2025, 01:50 (UTC)
🔹Trading Time: August 11, 2025, 01:50 (UTC)
🪧More:https://bit.ly/4m6LTqG



JuCoin Community
2025-08-05 02:41
JuCoin to List D3X/USDT Trading Pair on August 11, 2025
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
💚12 new spot listings added
💚8 campaigns launched this week
💚Platform token $JU surged over 6.33%
Stay connected with JuCoin and never miss an update!
👉 Register Now:https://www.jucoin.online/en/accounts/register?ref=MR6KTR
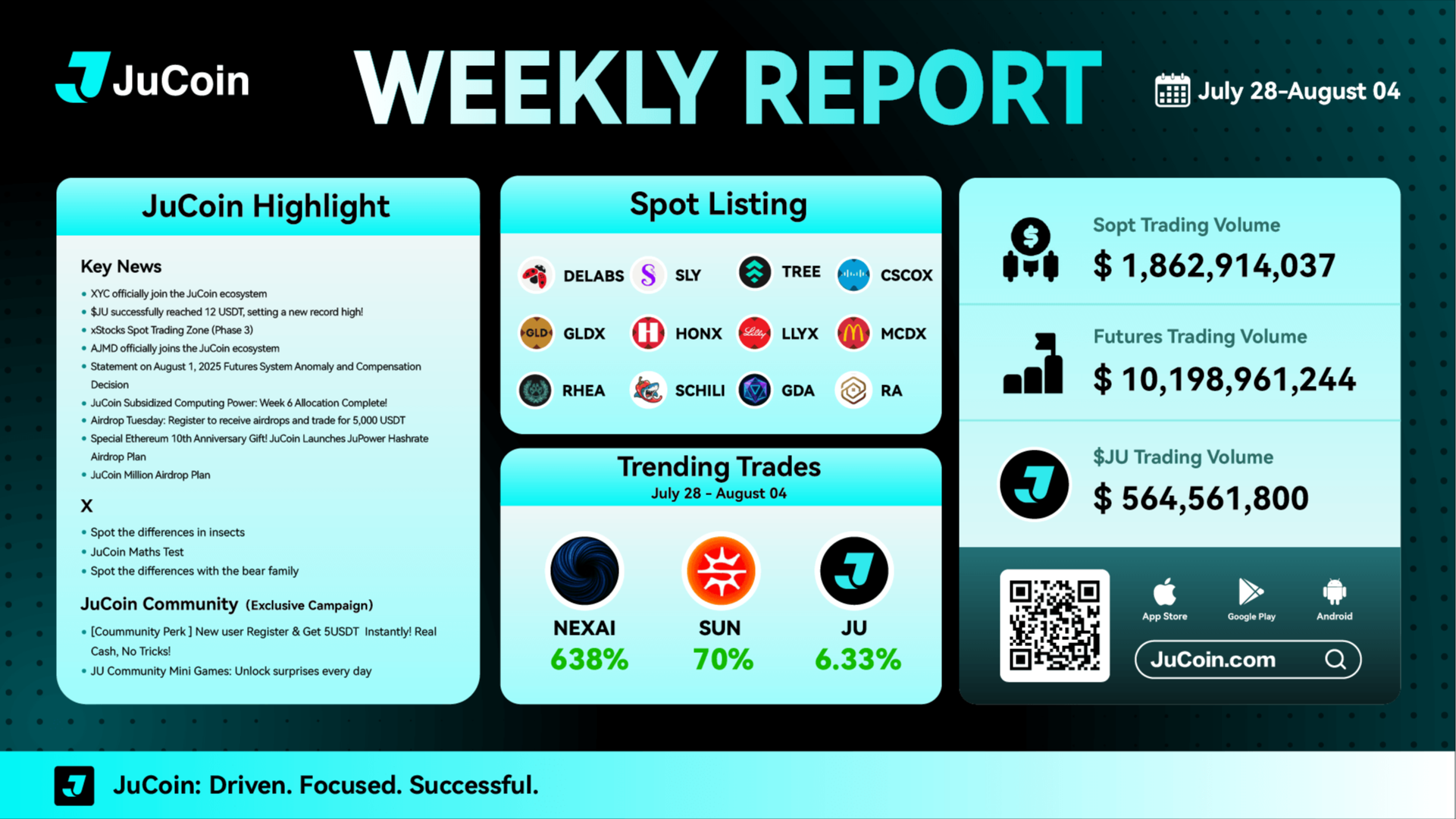


JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 09:41
👌JuCoin Weekly Report | July 28 – August 3 🔥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Exclusive community benefits are here! Invite 5+ friends to join JuCoin, climb the leaderboard, and earn USDT rewards!
⏰ Event Period:August 4, 08:00 – August 11, 08:00 (UTC)
🏆 Rewards for Top 5:
🥇 1st Place: $50 USDT
🥈 2nd Place: $40 USDT
🥉 3rd Place: $30 USDT
🏅 4th Place: $20 USDT
🏅 5th Place: $10 USDT
✅ How to Participate:
1️⃣ Log in to JuCoin and get your unique referral link.
2️⃣ Share your link – friends must register + complete KYC.
3️⃣ Reach 5+ valid invites to qualify for the leaderboard.
4️⃣ Submit your JuCoin UID to confirm entry:👉 https://forms.gle/vGi6c9LAksggH68D6
❗ Important Notice:
• Fraudulent activity (e.g., fake/bulk accounts) will result in immediate disqualification.
• Rewards will be distributed to winners’ JuCoin accounts after verification.
🚀 Start inviting now – dominate the leaderboard and claim your USDT!



JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 08:40
🔥 JuCoin Community Contest: Invite Friends & Win USDT! 🔥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
👌JuCoin will list the CMEW/USDT trading pair on August 7, 2025
🔹 Deposit: August 6, 2025 at 04:00 (UTC)
🔹 Trading: August 7, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
🔹 Withdrawal: August 8, 2025 at 09:00 (UTC)
🪧More:https://bit.ly/458FkfG



JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 07:45
📢 New Listing|CMEW (CelestialMew) 🔥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
TA used to be charts, indicators, and KD lines 🎯 Now it’s just tweets, vibes, and memes 🫥 Accurate enough, right?
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#TechnicalAnalysis #MemeTrading #CryptoTA


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:33
Technical Analysis Cryptocurrency 📊 | The Only Chart That Matters
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Me in 2050 telling my grandkids: “Bitcoin was only 100k back then!” 😌 They’ll never believe how good we had it 🪙 The golden age of crypto
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BitcoinMemories #FutureInvestorTales #CryptoLegend


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:29
My Bitcoin Investment Story They Won’t Believe in 2050 🕰️
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Losing trade — the classic crypto Squid Game 🤯 Do you sell at a loss or hold until zero? Both buttons hurt, but one might save your sanity 💀
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#LosingTrades #StopLossStruggle #CryptoMindGames


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:27
Losing Trade 🦑 | When You Hesitate, You Liquidate
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Bitcoin hits 108k and she’s crying 😭 Because I’m still broke. Why? I’m an altcoin holder 🧻 It be like that sometimes
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#AltcoinHolder #BitcoinVsAlts #CryptoPain


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:26
Investing in Cryptocurrency Means Bitcoin Pumps, Alts Dump 🎢
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Bitcoin Profit — every bull run cycle hits the same 😅 "This is my last year broke..." Meanwhile the house is collapsing behind you 🫠 Hopium never dies, even when profits do 🙃
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BullRunCycle #BitcoinProfit #HopiumLives


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:13
Hoping for That Bitcoin Profit Every Bull Run Cycle 📈
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The DeFi sector is experiencing a remarkable resurgence in 2025, transforming from speculative arena to robust financial infrastructure. Here's what's driving this explosive growth:
💰 Key Growth Drivers:
-
Layer 2 solutions (Optimism, Arbitrum, zk-Rollups) slashing costs & boosting speeds by 20%
$153 billion TVL reached in July 2025 - a three-year high!
Major institutional investment with $1.69B+ Ethereum holdings from leading firms
Enhanced regulatory clarity through EU's MiCA framework
🎯 What's Powering the Momentum:
1️⃣ Cross-Chain Revolution: Seamless asset transfers across Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche ecosystems 2️⃣ Yield Farming Evolution: Advanced protocols offering up to 25% returns on stablecoin strategies 3️⃣ Solana DEX Dominance: 81% of all DEX transactions, $890B trading volume in 5 months 4️⃣ Real-World Asset Tokenization: Converting real estate, commodities into tradeable blockchain tokens
🏆 Innovation Highlights:
-
Jupiter Perps averaging $1B daily perpetual trading volume
AI-powered security with real-time risk alerts and scam detection
Decentralized stablecoins driving cross-chain liquidity
Enhanced composability creating "money legos" for complex financial products
💡 Market Impact:
-
Ethereum maintains 60% DeFi TVL dominance with Lido & Aave leading
Solana surpassing Ethereum in transaction volumes and daily active users
Liquid restaking protocols attracting massive institutional inflows
Multi-signature wallets & advanced auditing boosting security confidence
🔮 Future Outlook: The shift from speculation to utility-focused infrastructure signals DeFi's maturation. With improved security, regulatory clarity, and institutional adoption, the sector is positioned for mainstream financial integration.
Read the complete analysis with detailed insights and market projections: 👇
https://blog.jucoin.com/explore-the-catalysts-behind-defis-recent-surge/?utm_source=blog
#DeFi #Layer2 #Ethereum #Solana #YieldFarming #Crypto #Blockchain #TVL #Institutions #RWA #CrossChain #JuCoin #Web3 #TradFi #Stablecoins #DEX #AI #Security



JU Blog
2025-08-01 08:54
🚀 DeFi Hits $153B TVL - Exploring the Key Catalysts Behind 2025's Massive Surge!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Succinct Network combines the world's fastest zkVM (SP1) with a decentralized marketplace for proof generation, making zero-knowledge proofs accessible to mainstream developers without deep cryptographic expertise.
💰 Key Highlights:
-
World's Fastest zkVM: SP1 is 28x faster than competing zkVMs on real-world workloads
PROVE Token Economics: Payment medium + staking security + governance rights
Real-Time Ethereum Proving: Under 40 seconds per block, 93% success rate with 200 RTX 4090s
$55M Series A: Led by Paradigm, demonstrating strong institutional confidence
🎯 Technical Breakthroughs:
-
SP1 Turbo (v4.0.0): Blazing fast performance with precompile-centric architecture
SP1 Hypercube: Sub-12-second Ethereum block proving milestone
Developer-Friendly: Write normal Rust code, automatically generate ZK proofs
100% Open Source: MIT licensed, all constraint logic public
🏆 Market Position:
-
Major Integrations: Polygon, Celestia, Avail, Taiko already using SP1
$1B+ TVL: Securing over $1 billion in total value locked
AggLayer Partnership: Will use SP1 for pessimistic proofs
💡 Use Cases:
-
ZK Rollups: Reduce finality from 7 days to minutes
Cross-Chain Bridges: Trustless blockchain interoperability
Verifiable AI: Cryptographic proof of AI model outputs
Privacy Identity: Verification without revealing sensitive data
Enterprise Auditing: Prove compliance without exposing proprietary data
⏰ Development Timeline:
-
Current: Testnet Stage 2
Coming Soon: Stage 2.5 with competitive auctions
February 10, 2025: "Crisis of Trust" testnet program launch
Future: Mainnet with full PROVE token functionality
⚠️ Investment Risks:
-
Technical competition (RISC Zero, Jolt, Nexus)
Computational resource requirements for real-time proving
Regulatory uncertainty around ZK privacy capabilities
Enterprise adoption timeline dependencies
🔥 Why It Matters: This democratization of ZK technology mirrors how cloud computing made enterprise infrastructure accessible to all developers. SP1's breakthrough performance enables real-time verification for next-gen blockchain applications.
PROVE token launch marks a significant milestone in decentralizing ZK infrastructure, potentially creating the economic foundation for verifiable applications across blockchain and traditional computing.
Read our complete technical analysis and investment guide: 👇
https://blog.jucoin.com/succinct-network-zkvm-prove-token/?utm_source=blog
#SuccinctNetwork #SP1 #PROVE #zkVM #ZeroKnowledge #Blockchain #Scalability #Polygon #Ethereum #Layer2 #ZKRollups #CrossChain #JuCoin #Web3 #Crypto #Decentralized #Paradigm #VerifiableAI #Privacy



JU Blog
2025-08-01 08:49
🚀 Succinct Network: Revolutionary SP1 zkVM & PROVE Token Launch!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
